Note:
- This tutorial requires access to Oracle Cloud. To sign up for a free account, see Get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
- It uses example values for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure credentials, tenancy, and compartments. When completing your lab, substitute these values with ones specific to your cloud environment.
Secure Shell to Oracle Exadata Database Service from a Microsoft Azure Linux VM in Oracle Database@Azure
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will explore the recent release of Oracle Database@Azure which provides customers access to Oracle Exadata Database Service within Microsoft Azure. We will examine how to Secure Shell (SSH) into the Oracle Exadata Database Service that make up the Exadata Virtual Machines (VM) cluster within the Exadata Cloud Infrastructure in Microsoft Azure. This allows quick access from the command line to connect to an Exadata database to verify database connectivity and run initial test queries to ensure data is being retrieved properly. It is a fast way to ensure that everything is functioning as expected in your Oracle Database@Azure environment so that you can build the needed application or tool communication to your Exadata data source.
Objectives
-
Generate an Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) key pair.
-
Allow access to an Exadata VM cluster with an SSH public key.
-
SSH to Oracle Exadata Database Service.
-
Initiate a SQL*Plus session on Oracle Exadata Database Service.
-
Execute a SQL query and retrieve data from the Exadata database.
Prerequisites
-
Access to Microsoft Azure cloud, OCI tenancy, and Oracle Database@Azure. Oracle Database@Azure available through the Multicloud link of the Microsoft Azure subscription and OCI tenancy.
-
Use of PuTTY SSH client or similar SSH tool.
-
Access to the SSH key pair of the desired Exadata VM cluster provisioned from Microsoft Azure.
Task 1: Connect to your Microsoft Azure VM which acts as a Jumpbox
Configure PuTTY tool to connect the Microsoft Azure VM which will be used as a jumpbox to connect your Oracle Exadata Database Service.
-
Open PuTTY Configuration and define the Microsoft Azure VM connection parameters.

Add your Microsoft Azure VM SSH private key.
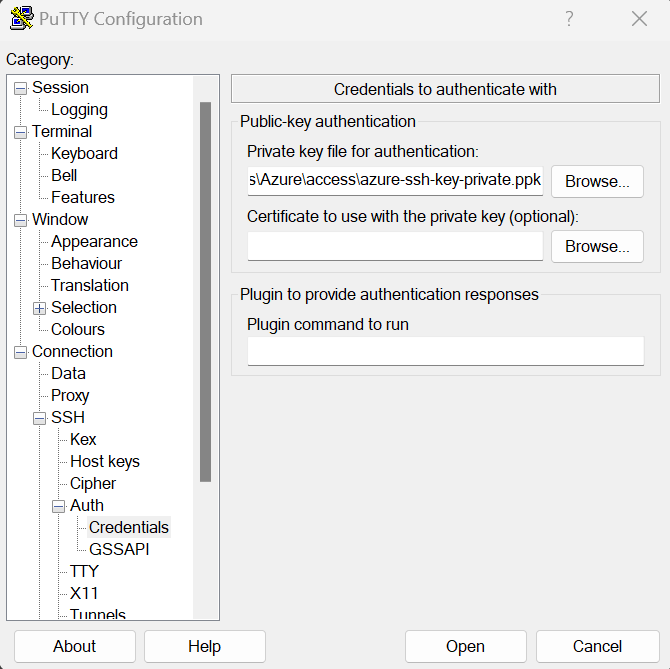
-
Run the
ssh-keygencommand to create a new SSH authentication key pair on the existing Microsoft Azure VM.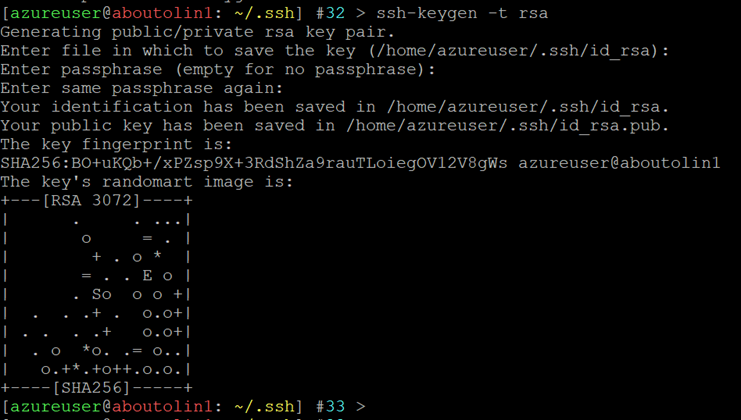
-
Copy the content of the public key from
id_rsa.pubfile to your clipboard.
Task 2: Authorize your Microsoft Azure VM to access the Oracle Exadata Database Service VM Cluster
-
In the Exadata VM Cluster Details page, click Add SSH Keys to add the SSH RSA public key.
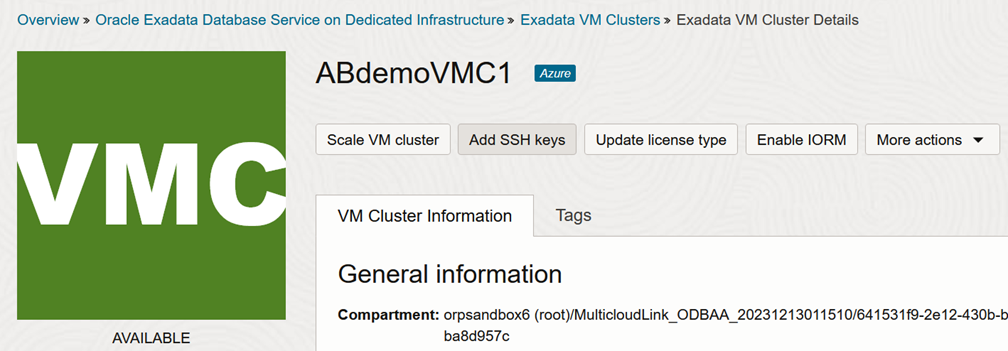
-
Select Paste SSH keys and enter your SSH key content.
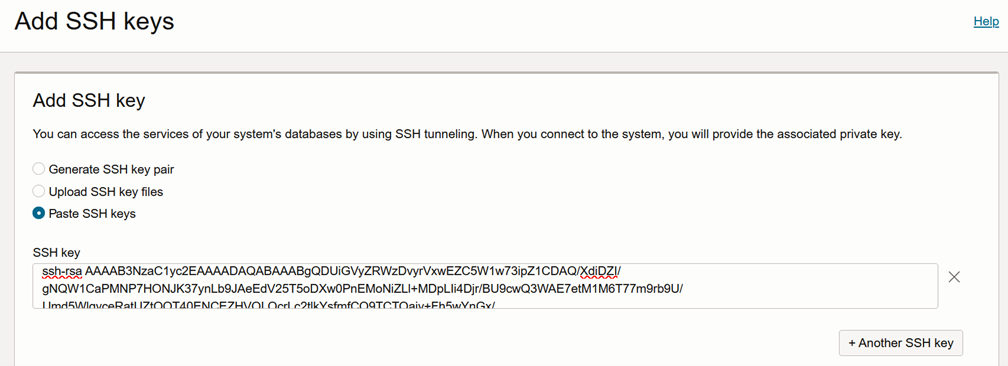
-
Click Save changes.

Task 3: Connect to the Oracle Exadata Database Service VM Cluster
-
Note the Private IP addresses for each of the two database servers.
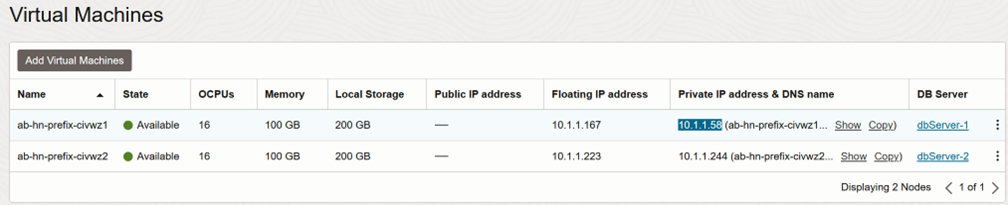
-
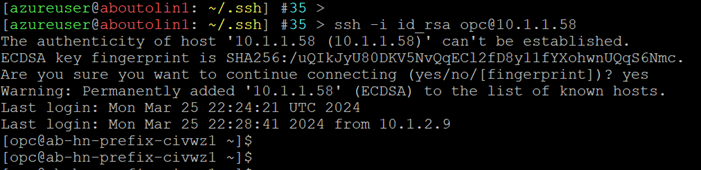
Initiate a connection to the Oracle Exadata Database Service from your Microsoft Azure VM.
Task 4: Set up the required Oracle Environment to start SQL*Plus
-
Log in as the Oracle user on the database server.
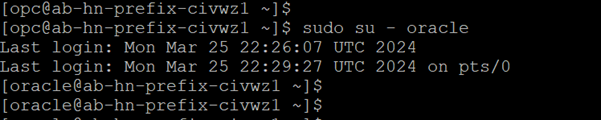
-
Update the Oracle user environment settings based on the desired target Exadata database.
[oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ ls -l total 8 -rwxrwx--- 1 oracle oinstall 667 Jan 24 17:36 ABDBOUT1.env -rwxrwx--- 1 oracle oinstall 667 Mar 12 14:49 ABDBOUT2.env [oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ [oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ source ABDBOUT1.env [oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ -
Run
SQL*Pluscommand line tool to interact with the database.[oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ sqlplus SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Mon Mar 25 22:31:19 2024 Version 19.21.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2022, Oracle. All rights reserved. Enter user-name: sys as sysdba Enter password: Connected to: Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.21.0.0.0 SQL> -
Connect to the pluggable database (PDB) by changing to the corresponding PDB.
SQL> alter session set container=ABDBOUT1PDB; Session altered. SQL>
Task 5: Run SQL query and Review the Result
-
Run the following command to format the SQL*Plus display.
SQL> COL table_name FORMAT a40; -
Run the SQL query to verify data being retrieved from the Exadata database.
SQL> SELECT table_name, num_rows, last_analyzed FROM dba_tables where owner='SH' AND table_name NOT LIKE 'DR%' ORDER BY num_rows DESC; -
Verify the SQL output.
TABLE_NAME NUM_ROWS LAST_ANAL ---------------------------------------- -------- --------- SALES 918843 21-FEB-24 COSTS 82112 12-MAR-24 CUSTOMERS 55500 21-FEB-24 TIMES 1826 19-FEB-24 PROMOTIONS 503 21-FEB-24 PRODUCTS 72 29-FEB-24 COUNTRIES 35 19-FEB-24 CHANNELS 5 21-FEB-24 FWEEK_PSCAT_SALES_MV 0 19-FEB-24 SUPPLEMENTARY_DEMOGRAPHICS 0 19-FEB-24 CAL_MONTH_SALES_MV 0 19-FEB-24 11 rows selected. SQL>
Task 6: Terminate the Session
-
Run the following command to exit the SQL*Plus session.
SQL> exit Disconnected from Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.21.0.0.0 [oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ -
Run the following command to exit the Oracle user session.
[oracle@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ exit logout [opc@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ -
Close your connection to the Oracle Exadata Database Service.
[opc@ab-hn-prefix-civwz1 ~]$ exit logout Connection to 10.1.1.58 closed. [azureuser@aboutolin1: ~] #3 > -
Close your PuTTy session to the Microsoft Azure Linux VM.
[azureuser@aboutolin1: ~] #3 exit
Related Links
Acknowledgments
- Author - Anwar Belayachi (Senior Principal Solution Architect - OCI Multicloud)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Secure Shell to Oracle Exadata Database Service from a Microsoft Azure Linux VM in Oracle Database@Azure
F99189-01
May 2024