25 Using Parameters in Task Flows
This chapter includes the following sections:
About Using Parameters in Task Flows
When used with an ADF task flow, parameters allow you to expand the horizon of the task flow from its default activity to multiple activities. For example, you can manipulate the data in task flows and share data between multiple task flows.
A task flow´s ability to accept input parameters and return parameter values allow you to manipulate data in task flows and share data between task flows. Using these abilities, you can optimize the reuse of task flows in your Fusion web application.
You can use view activity input page parameters as aliases. The alias allows you to map bounded task flow input parameters to page parameters. The view activity input page parameters map managed beans and any information available to the calling task flow to a managed bean on the page itself. To pass values out of view activities, store values in pageFlow scope or managed beans. For information about using view activities in a task flow, see Using View Activities.
For example, a page might specify #{pageFlowScope.empNo} as a page parameter and a bounded task flow might specify #{pageFlowScope.employeeID} as the value of an input parameter definition.
The from-value on the view activity input page parameter would be #{pageFlowScope.employeeID} and the to-value would be #{pageFlowScope.empNo}. This enables reuse of both the page definition and bounded task flow because you do not have to redefine parameters for every context in which each is used.
Other values contained within the task flow can be mapped to input page parameters, not just bounded task flow input parameter definition values.
Task Flow Parameters Use Cases and Examples
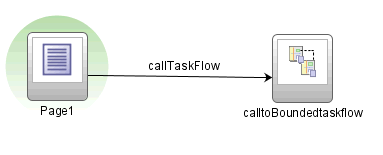
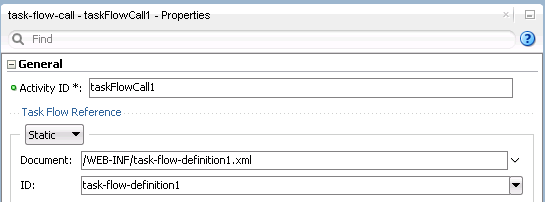
Figure 25-1 shows a task flow that defines an input parameter definition to hold information about a user in a pageFlow scope.
Figure 25-1 Task Flow Defining an Input Parameter
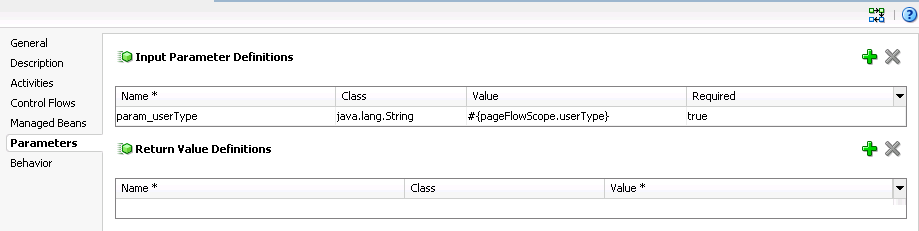
Description of "Figure 25-1 Task Flow Defining an Input Parameter "
Additional Functionality for Task Flows Using Parameters
You may find it helpful to understand other Oracle ADF features before you configure or use a task flow with parameters. Additionally, you may want to read about what you can do with your configured task flows. Following are links to other functionality that may be of interest.
-
Data controls can be shared between task flows. For more information about sharing data controls, see Sharing Data Controls Between Task Flows .
-
A task flow can access a managed bean that is registered with it. For more information about managed beans and task flows, see Using a Managed Bean in a Fusion Web Application.
-
Bounded task flows can be secured by defining the privileges that are required for someone to use them. For more information, see Enabling ADF Security in a Fusion Web Application.
Passing Parameters to a View Activity
In the cases where you want to pass the value from one activity to another without modifying the value, the ADF task flow view activity is useful. You can either pass a parameter to a value or a value to a managed bean using an EL expression or a literal expression.
Figure 25-2 illustrates how to configure an input page parameter mapping. You can pass a parameter to the Employee activity as a pageFlowScope value or a value on a managed bean. You can pass a parameter to the Employee activity using an EL expression or a literal expression. The Employee activity, in turn, can pass a value to the Target activity by specifying the value it wants to pass to the Target activity in the to-value element.
Figure 25-2 Task Flow with Two Activities
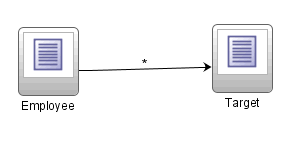
How to Pass Parameters to a View Activity
You add one or more input page parameters to the view activity that you want to pass parameters to.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the configuration options available to you before you define an input page parameter for a view activity. For more information, see Passing Parameters to a View Activity.
You may also find it helpful to understand functionality that can be added using other task flow features. For more information, see Additional Functionality for Task Flows Using Parameters.
To define an input page parameter for a view activity:
What Happens When You Pass Parameters to a View Activity
JDeveloper writes entries to the source file of the task flow at design time, as illustrated in the following example.
<view id="reducedAccess">
<page>/secured/Information.jsf</page>
<input-page-parameter>
<from-value>#{res['infoUsage.reducedAccess.messageHeader']}</from-value>
<to-value>#{pageFlowScope.infoPageHeaderText}</to-value>
</input-page-parameter>
<input-page-parameter>
<from-value>#{res['infoUsage.reducedAccess.messageHeader']}</from-value>
<to-value>#{pageFlowScope.infoPageMsg}</to-value>
</input-page-parameter>
<input-page-parameter>
<from-value>info</from-value>
<to-value>#{pageFlowScope.infoPageType}</to-value>
</input-page-parameter>
</view>
At runtime, the view activity retrieves the value of the input parameter from the location you specified in the <from-value> element. The view activity makes the value of the parameter available to its associated page in the location you specified in the <to-value> element.
What You May Need to Know About Specifying Parameter Values
You can specify parameter values using standard EL expressions if you call a bounded task flow using a task flow call activity or you render the bounded task flow in an ADF region or an ADF dynamic region. For example, you can specify parameters using the following syntax for EL expressions:
-
#{bindings.bindingId.inputValue} -
#{CustomerBean.zipCode}
The following example shows the metadata for a task flow binding that renders in an ADF region.
<taskFlow id="Department1" taskFlowId="/WEB-INF/Department.xml#Department"
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/Controller/binding">
<parameters>
<parameter id="DepartmentId" value="#{bindings.DepartmentId.inputValue}"
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/uimodel"/>
</parameters>
</taskFlow>
Appending inputValue to the EL expression makes sure that you assign the parameter the value of the binding rather than the actual binding object.
Passing Parameters to a Bounded Task Flow
From an ADF task flow, you can call a bounded task flow and pass values to it. The bounded task flow can accept the values through input parameters or from a task flow binding. You must specify one or more input parameters and parameter definitions in the task flow invoking the bounded task flow.
A called bounded task flow can accept input parameters from the task flow that calls it or from a task flow binding. To pass an input parameter to a bounded task flow, you specify one or more:
-
Input parameters on the task flow call activity in the calling task flow
Input parameters specify where the calling task flow stores parameter values.
-
Input parameter definitions on the called bounded task flow
Input parameter definitions specify where the called bounded task flow can retrieve parameter values at runtime.
Specify the same name for the input parameter that you define on the task flow call activity in the calling task flow and the input parameter definition on the called bounded task flow. Do this so you can map input parameter values to the called bounded task flow.
If you do not specify an EL expression to reference the value of the input parameter, the EL expression for value defaults to the following at runtime:
#{pageFlowScope.parmName}
where parmName is the value you entered for the input parameter name.
In an input parameter definition for a called bounded task flow, you can specify an input parameter as required. If the input parameter does not receive a value at runtime or design time, the task flow raises a warning in a log file of the Fusion web application that contains the task flow. An input parameter that you do not specify as required can be ignored during task flow call activity creation.
Task flow call activity input parameters can be passed by reference or passed by value when calling a task flow using a task flow call activity unless you are calling a task flow in an ADF region. If the task flow renders in an ADF region, the task flow call activity passes the input parameters by reference. By default, primitive types (for example, int, long, or boolean) are passed by value (pass-by-value).
The Pass By Value checkbox applies only to objects, not primitives and is used to override the default setting of passing by reference. Mixing the two, however, can lead to unexpected behavior in cases where parameters reference each other. If input parameter A on the task flow call activity is passed by value and if input parameter B on the task flow call activity is passed by reference, and B has a reference to A, the result can be two different instances of A and B.
How to Pass an Input Parameter to a Bounded Task Flow, describes how to pass an input parameter from a calling task flow to a called bounded task flow using a task flow call activity. Although you can pass parameter values from any activity on the calling task flow, the passed parameter in How to Pass an Input Parameter to a Bounded Task Flow contains the value of an input text field on a page in the calling task flow.
If you call a bounded task flow using a URL rather than a task flow call activity, you pass parameters and values on the URL itself. See How to Call a Bounded Task Flow Using a URL.
Instead of explicitly passing data controls as parameters between task flows, you can simply share them by specifying the data-control-scope option on the called bounded task flow. For more information, see Sharing Data Controls Between Task Flows .
A called task flow can also return values to the task flow that called it when it exits. For more information about returning values from a bounded task flow, see Configuring a Return Value from a Bounded Task Flow.
How to Pass an Input Parameter to a Bounded Task Flow
You define values on the calling task flow and the called task flow.
Before you begin:
-
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the configuration options available to you before you configure a bounded task flow to receive an input parameter. For more information, see Passing Parameters to a Bounded Task Flow.
-
You may also find it helpful to understand functionality that can be added using other task flow features. For more information, see Additional Functionality for Task Flows Using Parameters.
You will need to complete these tasks:
-
Create a calling and called task flow
The calling task flow can be bounded or unbounded. The called task flow must be bounded. For more information about creating task flows, see Creating a Task Flow.
-
Add a task flow call activity to the calling task flow
Figure 25-3 shows an example where the view activity passes control to the task flow call activity.
To pass an input parameter to a bounded task flow:
What Happens When You Pass an Input Parameter to a Bounded Task Flow
JDeveloper writes entries to the source files for the calling task flow and called task flow based on the values that you select. Example 25-1 shows an input parameter definition specified on a a bounded task flow.
Example 25-2 shows the input parameter metadata for the task flow call activity that calls the bounded task flow shown in Example 25-1. At runtime, the task flow call activity calls the bounded task flow and passes it the value specified by its value element.
Example 25-1 Input Parameter Definition
<task-flow-definition id="sourceTaskflow">
...
<input-parameter-definition>
<name>inputParameter1</name>
<value>#{pageFlowScope.parmValue1}</value>
<class>java.lang.String</class>
</input-parameter-definition>
...
</task-flow-definition>
Example 25-2 Input Parameter on Task Flow Call Activity
<task-flow-call id="taskFlowCall1">
...
<input-parameter>
<name>inputParameter1</name>
<value>#{pageFlowScope.newCustomer}</value>
<pass-by-value/>
</input-parameter>
...
</task-flow-call>
Configuring a Return Value from a Bounded Task Flow
A bounded task flow can be invoked from an ADF task flow and values can be passed to it. The bounded task flow, upon processing the values submitted, returns a parameter value to the task flow that has called it. The return value is in addition to the outcome activity that the bounded task flow returns to the calling task flow. You must add return value definitions in the bounded task flow and return values on the calling task flow.
You can configure a bounded task flow to return a parameter value to the task flow that calls it. The value that the bounded task flow returns is in addition to the outcome that it returns to the caller when the bounded task flow invokes a task flow return activity, as described in Using Task Flow Return Activities . To return a value, you must configure:
-
Return value definitions on the called bounded task flow
The return value definition specifies where you store the value that you want to return from the called bounded task flow.
-
Return values on the task flow call activity in the calling task flow to identify where the calling task flow can find the returned value
You can configure the calling task flow to ignore return value definition from the called task flow by not identifying any return values on the task flow call activity in the calling task flow.
The task flow call activity returns values by reference. For this reason, you do not need to make a copy of the values that you want to return to the calling task flow.
How to Configure a Return Value from a Bounded Task Flow
You configure a return value definition on the called task flow and add a parameter to the task flow call activity in the calling task flow that retrieves the return value at runtime.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the interaction between the calling task flow and the called task flow. For more information, see Configuring a Return Value from a Bounded Task Flow.
You may also find it helpful to understand functionality that can be added using other task flow features and parameters. For more information, see Additional Functionality for Task Flows Using Parameters.
You will need to complete this task:
- Create a bounded or unbounded task flow (calling task flow) and a bounded task flow (called task flow). For more information, see Creating a Task Flow.
To configure a return value from a called bounded task flow:
What Happens When You Configure a Return Value from a Bounded Task Flow
At design time, JDeveloper writes entries to the source files for the task flows that you configured. The following example shows an entry that JDeveloper writes to the source file for the calling task flow.
<task-flow-call id="taskFlowCall1">
<return-value id="__3">
<name id="__4">returnValue1</name>
<value id="__2">#{pageFlowScope.ReturnValueDefinition}</value>
</return-value>
</task-flow-call>
The following example shows entries that JDeveloper writes to the source file for the called task flow.
<return-value-definition id="__2">
<name id="__3">returnValue1</name>
<value>#{pageFlowScope.ReturnValueDefinition}/</value>
<class>java.lang.String</class>
</return-value-definition>
At runtime, the called task flow returns a value. If configured to do so, the task flow call activity in the calling task flow retrieves this value.