4 Upgrading Oracle Access Manager Highly Available Environments
Describes the process of upgrading an Oracle Access Manager highly available environments from 11g Release 2 (11.1.2.3.0) to 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
Topics
- About the Oracle Access Manager Multinode Upgrade Process
Review the topology and the roadmap for an overview of the upgrade process for Oracle Access Manager highly available environments. - Completing the Pre-Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Access Manager
Complete the pre-upgrade tasks described in this section before you upgrade Oracle Access Manager. - Creating 12c Oracle Home Folder on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
Create a folder for 12c Oracle Home on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2. - Installing Product Distributions on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
You must install the 12c binaries onto OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2 or onto shared storage accessible by both. If you are using redundant binaries ensure you install into each of the redundant locations - Installing the Latest Stack Patch Bundle
After you install the product distributions, Oracle strongly recommends you to apply the latest IDM Stack Patch Bundle (SPB) 12.2.1.3.0 before proceeding with the upgrade process. You can apply the patch by using the Opatch tool. Applying the SPB helps eliminate most of the upgrade issues or workarounds. - Upgrading Schemas on OAMHOST1
Upgrade all of the necessary schemas for Oracle Access Manager, on OAMHOST1 by using the Upgrade Assistant. - Reconfiguring the Domain on OAMHOST1
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard on OAMHOST1 to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.3.0). - Replicating the Domain Configurations on each OAMHOST
Replicate the domain configurations on OAMHOST2. This involves packing the upgraded domain on OAMHOST1 and unpacking it on OAMHOST2. - Upgrading Domain Component Configurations on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration. - Starting the Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
After you upgrade Oracle Access Manager on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2, start the servers. - Performing Post-Upgrade Tasks
After performing the upgrade of Oracle Access Manager to 12c (12.2.1.3), you should complete the tasks summarized in this section, if required. - Performing the Post-Patch Install Steps
After completing the upgrade, you have to perform the post-patch installation steps.
Parent topic: In-Place Upgrade of Oracle Access Manager
About the Oracle Access Manager Multinode Upgrade Process
Review the topology and the roadmap for an overview of the upgrade process for Oracle Access Manager highly available environments.
The steps you take to upgrade your existing domain will vary depending on how your domain is configured and which components are being upgraded. Follow only those steps that are applicable to your deployment.
Upgrade Topology
The following topology shows the Oracle Access Manager cluster set up that can be upgraded to 12c (12.2.1.3.0) by following the procedure described in this chapter.
Figure 4-1 Oracle Access Manager High Availability Upgrade Topology
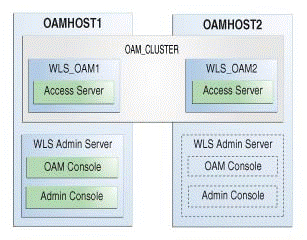
Description of "Figure 4-1 Oracle Access Manager High Availability Upgrade Topology"
-
An Oracle Access Management Access Manager instance has been installed in the WLS_OAM1 Managed Server.
-
A WebLogic Server Administration Server has been installed. Under normal operations, this is the active Administration Server.
On OAMHOST2, the following installations have been performed:
-
An Oracle Access Management Access Manager instance has been installed in the WLS_OAM2 Managed Server.
-
A WebLogic Server Administration Server has been installed. Under normal operations, this is the passive Administration Server. You make this Administration Server active if the Administration Server on OAMHOST1 becomes unavailable.
The instances in the WLS_OAM1 and WLS_OAM2 Managed Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2 are configured in a cluster named OAM_CLUSTER.
Table 4-1 Tasks for Upgrading Oracle Access Manager Highly Available Environments
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
|
Required If you have not done so already, review the introductory topics in this guide and complete the required pre-upgrade tasks. |
See: |
|
Required Complete the necessary pre-upgrade tasks specific to Oracle Access Manager. |
See Completing the Pre-Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Access Manager. |
|
Required Create the 12c Oracle Home Folder on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2, so that you can use the location for installing the product distributions. |
See Creating 12c Oracle Home Folder on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2. |
|
Required Install Oracle Access Manager 12c (12.2.1.3.0) in the new Oracle home. |
See Installing Product Distributions on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2. |
|
Required Apply the latest bundle patches |
|
|
Required Upgrade the necessary schemas on OAMHOST1. |
|
|
Required Reconfigure the Oracle Access Manager domain on OAMHOST1. |
|
|
Required Replicate the Oracle Access Manager domain configurations on OAMHOST2. |
This includes packing the domain on OAMHOST1 and unpacking it on OAMHOST2. |
|
Required Upgrade the domain component configurations on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2. |
The Upgrade Assistant is used to update the reconfigured domain’s component configurations. See Upgrading Domain Component Configurations on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2. |
|
Required Start the servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHSOT2. |
See Starting the Servers. |
|
Required Complete any necessary post-upgrade tasks. |
These tasks are optional. See Performing Post-Upgrade Tasks. |
|
Required Complete the post-patch install steps. |
Completing the Pre-Upgrade Tasks for Oracle Access Manager
Complete the pre-upgrade tasks described in this section before you upgrade Oracle Access Manager.
- Checking the Supported Starting Point for Oracle Access Manager Upgrade
The Oracle Access Manager version that is supported for upgrade is11g Release 2 (11.1.2.3.0). - Checking if OAM is in a Different Domain to OAAM and OIM
In the case of Oracle Access Manager (OAM), Oracle Adaptive Access Management (OAAM), and Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) integrated setup, where OAM and OAAM are in same domain, and OIM is in a separate domain, the OAM domain needs to be cloned that works with OAAM and OIM in the source domain. - Removing the IAMSuiteAgent Deployment
TheIAMSuiteAgentdeployment is not supported in 12c. Therefore, undeploy theIAMSuiteAgentbefore you proceed with the upgrade. - Upgrading Java JSE Policy
Upgrade Java JSE Policy, if required. - Disabling Deprecated Services in OAM
Applies only to Mobile and Social, Security Token Service, Mobile Security Service, and MSAS proxy users.
Checking the Supported Starting Point for Oracle Access Manager Upgrade
The Oracle Access Manager version that is supported for upgrade is 11g Release 2 (11.1.2.3.0).
11g Release 2 (11.1.2.3.0) first, and then to 12c.
Checking if OAM is in a Different Domain to OAAM and OIM
In the case of Oracle Access Manager (OAM), Oracle Adaptive Access Management (OAAM), and Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) integrated setup, where OAM and OAAM are in same domain, and OIM is in a separate domain, the OAM domain needs to be cloned that works with OAAM and OIM in the source domain.
Note:
Ensure that Oracle Access Manager and Oracle Identity Manager are in different domains. If they are in the same domain, then you need to separate them into multiple domains. For more information, see Separating Oracle Identity Management Applications Into Multiple Domains.To separate the OAM and OAAM domain, do the following:
If OIM is installed in a separate domain, and is integrated with OAM and OAAM, do the following:
-
Update the following Oracle Identity Manager properties to contain the details of the new OAAM host:
OIM.ChangePasswordURLOIM.ChallengeQuestionModificationURL
For information about setting the Oracle Identity Manager properties for OAAM, see Setting Oracle Identity Manager Properties for Oracle Adaptive Access Manager in the Integration Guide for Oracle Identity Management Suite for 11g Release 2 (11.1.2.3.0).
-
Restart the Oracle Identity Manager server.
Note:
You must upgrade the OAM domain whose Managed Server is in the running state after the domain separation.
For example, if you have followed the steps in this section, you will have to upgrade OAM that resides on machine-1, to 12c.
Removing the IAMSuiteAgent Deployment
The IAMSuiteAgent deployment is not supported in
12c. Therefore, undeploy the IAMSuiteAgent before you proceed
with the upgrade.
Removing IAMSuiteAgent from the OAM Console
Note:
Before you delete IAMSuiteAgent from the OAM console,
complete the following tasks:
- Replace
IAMSuiteAgentwith an 11g WebGate. See Replacing the IAMSuiteAgent with an 11g WebGate. RemovingIAMSuiteAgentwithout replacing it with an 11g WebGate may result in a loss of the OAM functionalities in the 11g server. - Back up the OAM configuration.
- Log in to the OAM console.
- Go to the Application Security tab, click Agents, and then Managed single sign-on agents.
- From the list of SSO agents, select
IAMSuiteAgent, and then click Delete. - Confirm the deletion.
Upgrading Java JSE Policy
Upgrade Java JSE Policy, if required.
Note:
This is required if any of the Identity Management components like Oracle Access Management (OAM), Oracle Identity Manager (OIM), Oracle Adaptive Access Manager (OAAM), or Oracle Access Manager Webgates of a data center are yet to be upgraded to 12c (12.2.1.3.0). This is for the phased transition to 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
For a Multi Data Center setup, this is required if any of the data centers has 12c (12.2.1.2.0) components (OAM, OIM, OAAM, OAM Webgates).
The jar files local_policy.jar and US_export_policy.jar are present in the directory $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security. You can upgrade Java JSE policy by overwriting these jar files with the specified versions. To do this, complete the following steps:
Disabling Deprecated Services in OAM
Applies only to Mobile and Social, Security Token Service, Mobile Security Service, and MSAS proxy users.
Mobile and Social, Security Token Service, Mobile Security, and MSAS proxy Service cannot be used in OAM 12c (12.2.1.3.0). If your current installation makes use of any of these services, you must disable them before attempting to perform this upgrade. If any of these services are active during the upgrade, the upgrade will fail with an upgrade not feasible error message. You can find additional information about these features in the Oracle Mobile Security Suite Statement Of Direction support document.
Creating 12c Oracle Home Folder on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
Create a folder for 12c Oracle Home on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2.
For example:
/home/Oracle/product/ORACLE_HOME
Installing Product Distributions on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
You must install the 12c binaries onto OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2 or onto shared storage accessible by both. If you are using redundant binaries ensure you install into each of the redundant locations
-
Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure 12c (12.2.1.3.0)
-
Oracle Access Manager 12c (12.2.1.3.0)
-
Any additional distributions for your pre-upgrade environment
For instructions to install the 12c binaries, see Installing Product Distributions.
Note:
If you have redundantOracle_Home installations, binaries must be installed into each of the redundant locations.
- Installing Product Distributions
Before beginning your upgrade, download Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure and Oracle Access Manager 12c (12.2.1.3.0) distributions on the target system and install them using Oracle Universal Installer.
Installing Product Distributions
Before beginning your upgrade, download Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure and Oracle Access Manager 12c (12.2.1.3.0) distributions on the target system and install them using Oracle Universal Installer.
Note:
- The 12c binaries are installed in a different location from the previous 11g binaries. You can install 12c binaries before any planned downtime for upgrade.
- If you are using Redundant binary locations, ensure that you install the software into each of those redundant locations.
Note:
- If your 11.1.2.3.0 setup was deployed using Life Cycle Management (LCM) tool, you must install Oracle HTTP Server 12c (12.2.1.3.0) in the 12c Middleware home. See Preparing to Install and Configure Oracle HTTP Server in Installing and Configuring Oracle HTTP Server.
- By using the opatch tool, apply the latest recommended patchsets from Oracle Support. Complete only the binary installation of patchsets and follow any post-patch steps after the upgrade process is complete. This provides the latest known fixes for upgrade process, if any.
Installing the Latest Stack Patch Bundle
After you install the product distributions, Oracle strongly recommends you to apply the latest IDM Stack Patch Bundle (SPB) 12.2.1.3.0 before proceeding with the upgrade process. You can apply the patch by using the Opatch tool. Applying the SPB helps eliminate most of the upgrade issues or workarounds.
- Initial Preparation: In this phase, you stage the software, read the
README.txtfile, and verify and/or update the Opatch tool to the appropriate versions. - Analysis Phase: In this phase, you run the
prestopcommand with the variables from theREADME.txtfile to determine if the system is ready for patching. - Patching Phase: In this phase, you backup MW_HOME and
DOMAIN_HOME, run the downtime command for OIG with the
variables from the
README.txtfile, and then clear any temporary files.
Note:
At this point, you will not restart the servers. There is currently no link between the schemas, the local configuration, and the new bits. The remainder of the patching process will happen after the bootstrap.config.xml for the
com.oracle.cie.comdev_7.8.2.0 and
com.oracle.cie.xmldh_3.4.2.0
libraries:<name>com.oracle.cie.comdev#3.0.0.0@7.8.2.0</name>
com.oracle.cie.comdev_7.8.2.0.jar<name>com.oracle.cie.xmldh#2.0.0.0@3.4.2.0</name>
com.oracle.cie.xmldh_3.4.2.0.jar<library>
<name>com.oracle.cie.comdev#3.0.0.0@7.8.2.0</name>
<target>oim_cluster</target>
<source-path><MW_HOME>/oracle_common/modules/com.oracle.cie.comdev_7.8.2.0.jar
</source-path>
<deployment-order>511</deployment-order>
<security-dd-model>DDOnly</security-dd-model>
<staging-mode>nostage</staging-mode>
</library>
<library>
<name>com.oracle.cie.xmldh#2.0.0.0@3.4.2.0</name>
<target>oim_cluster</target>
<source-path><MW_HOME>/oracle_common/modules/com.oracle.cie.xmldh_3.4.2.0.jar<
/source-path>
<deployment-order>511</deployment-order>
<security-dd-model>DDOnly</security-dd-model>
<staging-mode>nostage</staging-mode>
</library><library>
<name>com.oracle.cie.comdev#3.0.0.0@7.8.4.0</name>
<target>oim_cluster</target>
<source-path><MW_HOME>/oracle_common/modules/com.oracle.cie.comdev_7.8.4.0.jar
</source-path>
<deployment-order>511</deployment-order>
<security-dd-model>DDOnly</security-dd-model>
<staging-mode>nostage</staging-mode>
</library>
<library>
<name>com.oracle.cie.xmldh#2.0.0.0@3.4.4.0</name>
<target>oim_cluster</target>
<source-path><MW_HOME>/oracle_common/modules/com.oracle.cie.xmldh_3.4.4.0.jar<
/source-path>
<deployment-order>511</deployment-order>
<security-dd-model>DDOnly</security-dd-model>
<staging-mode>nostage</staging-mode>
</library>This update to the config.xml file changes the name of the libraries and
version of the jar file in each library to the one that will be used post the patching
process. Ensure that both nodes have the same settings.
For more information on the patching process, see Doc ID 2657920.1.
Note:
If you are using Windows or Solaris OS, download the individual Bundle Patches (BPs) from Doc ID 2457034.1.After completing the upgrade, you have to perform the post-patch install steps. See Performing the Post-Patch Install Steps.
Upgrading Schemas on OAMHOST1
Upgrade all of the necessary schemas for Oracle Access Manager, on OAMHOST1 by using the Upgrade Assistant.
- Upgrading Product Schemas
After stopping servers and processes, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade supported product schemas to the current release of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Upgrading Product Schemas
After stopping servers and processes, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade supported product schemas to the current release of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
The Upgrade Assistant allows you to upgrade individually selected schemas or all schemas associated with a domain. The option you select determines which Upgrade Assistant screens you will use.
- Identifying Existing Schemas Available for Upgrade
This optional task enables you to review the list of available schemas before you begin the upgrade by querying the schema version registry. The registry contains schema information such as version number, component name and ID, date of creation and modification, and custom prefix. - Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.3.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time. - Upgrading Oracle Access Manager Schemas Using the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the product schemas. - Verifying the Schema Upgrade
After completing all the upgrade steps, verify that the upgrade was successful by checking that the schema version inschema_version_registryhas been properly updated.
Parent topic: Upgrading Schemas on OAMHOST1
Identifying Existing Schemas Available for Upgrade
This optional task enables you to review the list of available schemas before you begin the upgrade by querying the schema version registry. The registry contains schema information such as version number, component name and ID, date of creation and modification, and custom prefix.
You can let the Upgrade Assistant upgrade all of the schemas in the domain, or you can select individual schemas to upgrade. To help decide, follow these steps to view a list of all the schemas that are available for an upgrade:
-
If you are using an Oracle database, connect to the database by using an acount that has Oracle DBA privileges, and run the following from SQL*Plus:
SET LINE 120 COLUMN MRC_NAME FORMAT A14 COLUMN COMP_ID FORMAT A20 COLUMN VERSION FORMAT A12 COLUMN STATUS FORMAT A9 COLUMN UPGRADED FORMAT A8 SELECT MRC_NAME, COMP_ID, OWNER, VERSION, STATUS, UPGRADED FROM SCHEMA_VERSION_REGISTRY ORDER BY MRC_NAME, COMP_ID; -
Examine the report that is generated.
If an upgrade is not needed for a schema, the
schema_version_registrytable retains the schema at its pre-upgrade version. -
Note the schema prefix name that was used for your existing schemas. You will use the same prefix when you create new 12c schemas.
Notes:
-
If you used an OID-based policy store in 11g, make sure to create a new OPSS schema before you perform the upgrade. After the upgrade, the OPSS schema remains an LDAP-based store.
-
You can only upgrade schemas for products that are available for upgrade in Oracle Fusion Middleware release 12c (12.2.1.3.0). Do not attempt to upgrade a domain that includes components that are not yet available for upgrade to 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.3.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
Note:
Before you start the Upgrade Assistant, make sure that the JVM character encoding is set to UTF-8 for the platform on which the Upgrade Assistant is running. If the character encoding is not set to UTF-8, then you will not be able to download files containing Unicode characters in their names. This can cause the upgrade to fail.
To ensure that UTF-8 is used by the JVM, use the JVM option -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8.
- Go to the
oracle_common/upgrade/bindirectory:- (UNIX)
ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/bin - (Windows)
ORACLE_HOME\oracle_common\upgrade\bin
- (UNIX)
- Start the Upgrade Assistant:
- (UNIX) ./ua
- (Windows) ua.bat
Note:
In the above command,ORACLE_HOME refers to the 12c (12.2.1.3.0) Oracle Home.
For information about other parameters that you can specify on the command line, such as logging parameters, see:
Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-2 Upgrade Assistant Command-Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
Note: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant creates log files and temporary files. The default locations are: (UNIX)
(Windows)
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command-line options. |
Parent topic: Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Upgrading Oracle Access Manager Schemas Using the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the product schemas.
Caution:
You can skip this step if you have already upgraded your schemas using RCU.Note:
-
If the pre-upgrade environment has Audit schema (IAU), you must first upgrade Audit schema only, using the Individually Selected Schema option on the Selected Schemas screen, and selecting Oracle Audit Services schema. Ensure that you select the appropriate IAU schema from the list of available IAU schemas. The upgrade assistant will not detect the corresponding IAU schema from the provided domain directory automatically. Hence, you must select it manually. Once the IAU schema is upgraded, run the Upgrade Assistant again to upgrade the remaining schemas using the All Schema Used by a domain option on the Selected Schemas screen.
-
If there is no Audit schema (IAU) in your pre-upgrade environment, use the All Schema Used by a Domain option on the Selected Schemas screen and proceed.
-
To check whether the pre-upgrade environment has the IAU schema, run the following SQL command using the user with sysdba privileges:
select username from dba_users where username like '%IAU%';This command lists the IAU schemas available in your configured database.
Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
Verifying the Schema Upgrade
After completing all the upgrade steps, verify that the upgrade was successful by checking that the schema version in schema_version_registry has been properly updated.
If you are using an Oracle database, connect to the database as a user having Oracle DBA privileges, and run the following from SQL*Plus to get the current version numbers:
SET LINE 120 COLUMN MRC_NAME FORMAT A14 COLUMN COMP_ID FORMAT A20 COLUMN VERSION FORMAT A12 COLUMN STATUS FORMAT A9 COLUMN UPGRADED FORMAT A8 SELECT MRC_NAME, COMP_ID, OWNER, VERSION, STATUS, UPGRADED FROM SCHEMA_VERSION_REGISTRY ORDER BY MRC_NAME, COMP_ID ;
In the query result:
-
Check that the number in the
VERSIONcolumn matches the latest version number for that schema. For example, verify that the schema version number is 12.2.1.3.0.Note:
However, that not all schema versions will be updated. Some schemas do not require an upgrade to this release and will retain their pre-upgrade version number.
-
The
STATUSfield will be eitherUPGRADINGorUPGRADEDduring the schema patching operation, and will becomeVALIDwhen the operation is completed. -
If the status appears as
INVALID, the schema update failed. You should examine the logs files to determine the reason for the failure. -
Synonym objects owned by
IAU_APPENDandIAU_VIEWERwill appear asINVALID, but that does not indicate a failure.They become invalid because the target object changes after the creation of the synonym. The synonyms objects will become valid when they are accessed. You can safely ignore these
INVALIDobjects.
Note:
Undo any non-SSL port changes and any non-SYSDBA user that you made when preparing for the upgrade.Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
Reconfiguring the Domain on OAMHOST1
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard on OAMHOST1 to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
- About Reconfiguring the Domain
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
About Reconfiguring the Domain
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
When you reconfigure a WebLogic Server domain, the following items are automatically updated, depending on the applications in the domain:
-
WebLogic Server core infrastructure
-
Domain version
Note:
Before you begin the domain reconfiguration, note the following limitations:
-
The Reconfiguration Wizard does not update any of your own applications that are included in the domain.
-
Transforming a non-dynamic cluster domain to a dynamic cluster domain during the upgrade process is not supported.
The dynamic cluster feature is available when running the Reconfiguration Wizard, but Oracle only supports upgrading a non-dynamic cluster upgrade and then adding dynamic clusters. You cannot add dynamic cluster during the upgrade process.
-
The domain version number in the
config.xmlfile for the domain is updated to the Administration Server's installed WebLogic Server version. -
Reconfiguration templates for all installed Oracle products are automatically selected and applied to the domain. These templates define any reconfiguration tasks that are required to make the WebLogic domain compatible with the current WebLogic Server version.
-
Start scripts are updated.
If you want to preserve your modified start scripts, be sure to back them up before starting the Reconfiguration Wizard.
Note:
When the domain reconfiguration process starts, you can’t undo the changes that it makes. Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, ensure that you have backed up the domain as covered in the pre-upgrade checklist. If an error or other interruption occurs while running the Reconfiguration Wizard, you must restore the domain by copying the files and directories from the backup location to the original domain directory. This is the only way to ensure that the domain has been returned to its original state before reconfiguration.- Backing Up the Domain
- Starting the Reconfiguration Wizard
- Reconfiguring the Oracle Access Manager Domain
Navigate through the screens in the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your existing 11g domain.
Parent topic: Reconfiguring the Domain on OAMHOST1
Backing Up the Domain
Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, create a backup copy of the domain directory.
To create a backup of the Administration server domain directory:
Parent topic: About Reconfiguring the Domain
Starting the Reconfiguration Wizard
Note:
Shut down the administration server and all collocated managed servers before starting the reconfiguration process. See Stopping Servers and Processes.To start the Reconfiguration Wizard in graphical mode:
Parent topic: About Reconfiguring the Domain
Reconfiguring the Oracle Access Manager Domain
Navigate through the screens in the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your existing 11g domain.
Note:
If the source is a clustered environment, run the Reconfiguration Wizard on the primary node only. Where, primary node is the Administration Server. Use the pack/unpack utility to apply the changes to other cluster members in the domain.Parent topic: About Reconfiguring the Domain
Replicating the Domain Configurations on each OAMHOST
Replicate the domain configurations on OAMHOST2. This involves packing the upgraded domain on OAMHOST1 and unpacking it on OAMHOST2.
- On OAMHOST1, run the following command from the location
$ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/common/binto pack the upgraded domain:- On UNIX:
sh pack.sh -domain=<Location_of_OAM_domain> -template=<Location_where_domain_configuration_jar_to_be_created> -template_name="OAM Domain" -managed=true - On Windows:
pack.cmd -domain=<Location_of_OAM_domain> -template=<Location_where_domain_configuration_jar_to_be_created> -template_name="OAM Domain" -managed=true
- On UNIX:
- Copy the domain configuration jar file created by the pack command on OAMHOST1 to any accessible location on OAMHOST2.
- On OAMHOST2, run the following command from the location
$ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/common/binto unpack the domain:- On UNIX:
sh unpack.sh -domain=<Location_of_OAM_domain> -template=<absolute_path_to the_location_of_domain_configuration_jar_file> -overwrite_domain=true - On Windows:
unpack.cmd -domain=<Location_of_OAM_domain> -template=<absolute_path_to the_location_of_domain_configuration_jar_file> -overwrite_domain=true
- On UNIX:
- If you have other OAMHOSTs, repeat step 2 through step 3 on those hosts.
Note:
If you are following the EDG methodology you also need to pack and unpack the domain in the OAM managed server location on OAMHOST1.Upgrading Domain Component Configurations on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration.
- Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration.
Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration.
- Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.3.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time. - Upgrading Oracle Access Manager Domain Component Configurations
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade component configurations in the WebLogic domain. - Removing Oracle Mobile Security Manager Servers From the Domain
Remove the Oracle Mobile Security Manager (MSM) servers from the upgraded domain, as they are not supported in 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.3.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
Note:
Before you start the Upgrade Assistant, make sure that the JVM character encoding is set to UTF-8 for the platform on which the Upgrade Assistant is running. If the character encoding is not set to UTF-8, then you will not be able to download files containing Unicode characters in their names. This can cause the upgrade to fail.
To ensure that UTF-8 is used by the JVM, use the JVM option -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8.
- Go to the
oracle_common/upgrade/bindirectory:- (UNIX)
ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/bin - (Windows)
ORACLE_HOME\oracle_common\upgrade\bin
- (UNIX)
- Start the Upgrade Assistant:
- (UNIX) ./ua
- (Windows) ua.bat
Note:
In the above command,ORACLE_HOME refers to the 12c (12.2.1.3.0) Oracle Home.
For information about other parameters that you can specify on the command line, such as logging parameters, see:
Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-3 Upgrade Assistant Command-Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
Note: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant creates log files and temporary files. The default locations are: (UNIX)
(Windows)
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command-line options. |
Parent topic: Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Upgrading Oracle Access Manager Domain Component Configurations
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade component configurations in the WebLogic domain.
After running the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure the WebLogic domain to 12c (12.2.1.3.0), you must run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations to match the updated domain configuration.
Parent topic: Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
Removing Oracle Mobile Security Manager Servers From the Domain
Remove the Oracle Mobile Security Manager (MSM) servers from the upgraded domain, as they are not supported in 12c (12.2.1.3.0).
Parent topic: Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
Starting the Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
After you upgrade Oracle Access Manager on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2, start the servers.
-
Start the Node Manager on both OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2.
-
Start the Administration Server on OAMHOST1.
-
Start the Oracle Access Manager Managed Servers on OAMHOST1.
-
Start the Oracle Access Manager Managed Servers on OAMHOST2.
- Starting Servers and Processes
After a successful upgrade, start all processes and servers, including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers. - Configuring Oracle HTTP Servers to Front End OIM, and SOA Managed Servers
- Verifying the Domain-Specific-Component Configurations Upgrade
To verify that the domain-specific-component configurations upgrade was successful, sign in to the Administration console and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and verify that the version numbers for each component is 12.2.1.3.0.
Starting Servers and Processes
After a successful upgrade, start all processes and servers, including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers.
The components may be dependent on each other so they must be started in the correct order.
Note:
The procedures in this section describe how to start servers and process using the WLST command line or a script. You can also use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Control and the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. See Starting and Stopping Administration and Managed Servers and Node Manager in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.To start your Fusion Middleware environment, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Start Node Manager
Start the Node Manager in the Administration Server domain home.
Go to the WLS_HOME/server/bin directory and run the following command:
Where, WLS_HOME is the top-level directory for the WebLogic Server installation.
-
(UNIX)
nohup ./startNodeManager.sh > DOMAIN_HOME/nodemanager/nodemanager.out 2>&1 & -
(Windows)
nohup .\startNodeManager.sh > DOMAIN_HOME\nodemanager\nodemanager.out 2>&1 &
Where, DOMAIN_HOME is the Administration server domain home.
Step 2: Start the Administration Server
When you start the Administration Server, you also start the processes running in the Administration Server, including the WebLogic Server Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control.
nohup DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startWeblogic.sh &cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin
./wlst.sh
wlst offline> nmConnect('nodemanager_username','nodemanager_password',
'ADMINVHN','5556','domain_name',
'DOMAIN_HOME')
nmStart('AdminServer')Step 3: Start the Managed Servers
Note:
In an HA environment, it is preferred to use the console or node manager to start servers.- Log into Weblogic console as a
weblogicAdmin. - Go to Servers > Control tab.
- Select the required managed server.
- Click Start.
Parent topic: Starting the Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
Configuring Oracle HTTP Servers to Front End OIM, and SOA Managed Servers
Complete the following steps:
Parent topic: Starting the Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
Verifying the Domain-Specific-Component Configurations Upgrade
To verify that the domain-specific-component configurations upgrade was successful, sign in to the Administration console and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and verify that the version numbers for each component is 12.2.1.3.0.
To sign in to the Administration Console, go to: http://administration_server_host:administration_server_port/console
To sign in to the Administration Console in an EDG deployment, see Validating the Virtual Server Configuration and Access to the Consoles.
To sign in to Oracle Enterprise Manager
Fusion Middleware Control Console, go to: http://administration_server_host:administration_server_port/em
Note:
- After upgrade, ensure you run the administration tools from the new 12c Oracle home directory and not from the previous Oracle home directory.
- During the upgrade process, some OWSM documents, including policy sets and predefined documents such as policies and assertion templates, may need to be upgraded. If a policy set or a predefined document is upgraded, its version number is incremented by 1.
- In the site-specific configuration, the WebLogic and EM consoles must be accessible with the URLs either directly or through proxy URLs.
Parent topic: Starting the Servers on OAMHOST1 and OAMHOST2
Performing Post-Upgrade Tasks
After performing the upgrade of Oracle Access Manager to 12c (12.2.1.3), you should complete the tasks summarized in this section, if required.
This section includes the following tasks:
- WebGates Configuration Fails during Authentication
WebGates configured with thehmacEnabled=truein environments whereglobalHMACEnabledis not set totruefails during authentication. - Updating the java.security File
If you have multiple components of Oracle Identity and Access Management (Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Identity Manager, WebGates and so on) deployed, until you upgrade all of the components to 12c (12.2.1.3.0), you must update thejava.securityfile with the changes described in this section.
WebGates Configuration Fails during Authentication
WebGates configured with the hmacEnabled=true in environments where globalHMACEnabled is not set to true fails during authentication.
For more information, see Upgrading to OHS/OTD 12c WebGate.
Parent topic: Performing Post-Upgrade Tasks
Updating the java.security File
If you have multiple components of Oracle Identity and Access Management (Oracle Access Manager, Oracle Identity Manager, WebGates and so on) deployed, until you upgrade all of the components to 12c (12.2.1.3.0), you must update the java.security file with the changes described in this section.
Parent topic: Performing Post-Upgrade Tasks
Performing the Post-Patch Install Steps
After completing the upgrade, you have to perform the post-patch installation steps.
The post-patch installation steps comprises the following:
Running the Poststart Command to Confirm Successful Binary Patching
poststart command for your product, as shown below:
$ ./spbat.sh -type oig -phase poststart -mw_home /<INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>/IAM12c -spb_download_dir /<DOWNLOAD_LOCATION>/IDM_SPB_12.2.1.4.200714 -log_dir /<DOWNLOAD_LOCATION>/OIGlogsFor details, see Doc ID 2657920.1.
Parent topic: Performing the Post-Patch Install Steps
Performing a Clean Restart of the Servers
Restart all the servers including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers. See Starting Servers and Processes.
Parent topic: Performing the Post-Patch Install Steps