4 Upgrading Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure from a Previous 12c Release
You can upgrade to Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure 12c (12.2.1.4.0) from a previous 12c release.
Complete the steps in the following topics to perform the upgrade:
- About the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Upgrade Process (from a Previous 12c Release)
Review the flowchart and roadmap for an overview of the upgrade process for Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure from a previous 12c release. - Installing Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure
Installing Fusion Middleware Infrastructure creates an Oracle home directory and lays down supporting software to install other Fusion Middleware products. - Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
To identify potential issues with the upgrade, Oracle recommends that you run a readiness check before you start the upgrade process. Be aware that the readiness check may not be able to discover all potential issues with your upgrade. An upgrade may still fail, even if the readiness check reports success. - Stopping Servers and Processes
Before running the Upgrade Assistant, shut down all Oracle Fusion Middleware Managed Servers, Administration Servers, and system components (such as OHS) that may be using the schemas or configurations you want to update. Failure to do so may result in an incomplete or failed upgrade. - Upgrading Product Schemas
After stopping servers and processes, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade supported product schemas to the current release of Oracle Fusion Middleware. - About Reconfiguring the Domain
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.4.0). - Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration. - Starting Servers and Processes
After a successful upgrade, restart all processes and servers, including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers. - Using the Upgrade Validation Checklist
After the upgrade, make sure that you can successfully complete the basic administration tasks, such as verifying whether you are able to start the Node Manager, Administration Server, Webtier, Administration Console, and Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control. - Reapplying Custom Configuration Settings to setDomainEnv
To complete the upgrade of your application environment to 12c it might be necessary to reapply any custom configuration settings to startup scripts, such assetDomainEnv. During the upgrade, the scripts are overwritten with new 12c versions. You must manually reapply the custom configuration settings you had made in previous releases. - Maintaining the Security Status of Older Java EE Web Service Applications
The introduction of global policy attachment support for Java EE web services and clients in 12c may impact the backwards compatibility of existing Java EE web services and clients (12.1.2 and earlier). If a Java EE web service or client endpoint that depends on the absence of a policy falls within the scope of a global policy attachment, the presence of the globally-attached policy can alter the security behavior of that endpoint. - Documentation Resources for Managing your Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c Software
This topic provides a list of common administration tasks you likely want to perform after upgrading to Infrastructure 12c and associated documentation resources. - If Your Existing Environment is a Clustered Configuration...
If your existing environment is a clustered configuration, then you must apply the changes to other cluster members in the domain by using the pack and unpack utilities. - Starting Servers and Processes
After a successful upgrade, restart all processes and servers, including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers.
About the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Upgrade Process (from a Previous 12c Release)
Review the flowchart and roadmap for an overview of the upgrade process for Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure from a previous 12c release.
Figure 4-1 Upgrade Process Flowchart for Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure from a Previous 12c Release
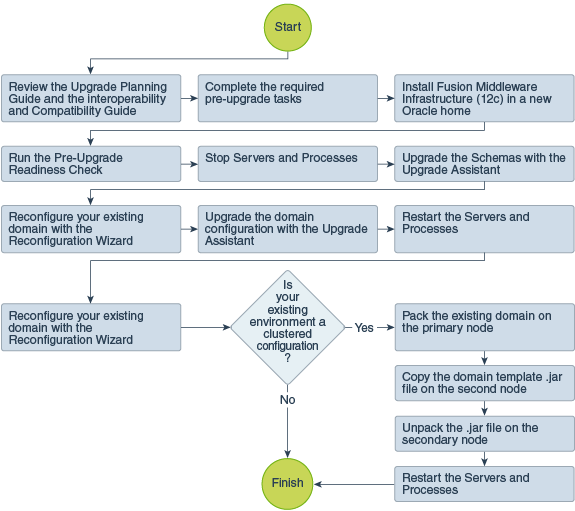
Description of "Figure 4-1 Upgrade Process Flowchart for Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure from a Previous 12c Release"
Table 4-1 lists the high-level steps that you need to perform to upgrade to Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure Release 12.2.1.4.0:
Table 4-1 Tasks for Upgrading Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure from a Previous 12c Release
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
|
Optional Learn about the interoperability and compatibility factors that could affect how you upgrade to Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure 12.2.1.4.0. |
It is important to understand how two or more Oracle Fusion Middleware products of the same version or different versions work together (interoperate) in a supported Oracle Fusion Middleware configuration. You can learn more about interoperability and compatibility in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Understanding Interoperability and Compatibility. |
|
Required If you have not done so already, review the introductory topics in this guide and complete the required pre-upgrade tasks. |
The pre-upgrade tasks include cloning your production environment, verifying system requirements and certifications, purging unused data, and creating non-SYSDBA user. For a complete list of pre-upgrade tasks, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Pre-Upgrade Checklist. |
|
Required Download and install the 12.2.1.4.0 Fusion Middleware Infrastructure distribution. |
The Infrastructure distribution packs the WebLogic Server and the Java Required Files (JRF) that are required to set up the foundation to install other Fusion Middleware products. As per the upgrade topology defined in this guide, you must install the Infrastructure in a new Oracle home. Therefore, follow the procedure described in Installing Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure. |
|
Optional Run the Readiness Check. |
Running the Readiness Check by using the Upgrade Assistant helps you to determine
whether your pre-upgrade environment is ready for upgrade.
For the complete procedure, see Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check. |
|
Required Stop the servers and processes. |
Before starting the upgrade process, stop all the servers, components, and processes. |
|
Required Upgrade the schemas with the Upgrade Assistant. |
The Upgrade Assistant allows you to select All schemas used by a domain option. When you select this option, the Upgrade Assistant automatically selects all the schemas that are available for upgrade within that domain. |
|
Required Reconfigure the existing domain with the Reconfiguration Wizard. |
When you run the Reconfiguration Wizard on your existing domain, it prepares your domain for upgrade by selecting and applying the recongifuration templates. It also tests the JDBC data sources and component schemas that are present within your domain. To reconfigure you domain, follow the procedure described in About Reconfiguring the Domain. |
|
Required Upgrade the existing domain configurations with the Upgrade Assistant. |
After you have reconfigured your existing domain, you must run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade all configurations used by your existing domain. You can see all the components within your domain that will be upgraded on the Component List screen when you run the Upgrade Assistant. See Upgrading Domain Component Configurations. |
|
Required Restart the servers and processes. |
The upgrade process is complete. You can now restart the servers, components, and processes. |
|
Required Perform the post-upgrade tasks. |
For a list of post-upgrade tasks, see Using the Upgrade Validation Checklist. |
|
Required only if your existing environment is a clustered configuration Pack the existing domain on the primary node. |
Run the |
|
Required only if your existing environment is a clustered configuration Copy the domain template.jar file on the secondary node. |
Copy the |
|
Required only if your existing environment is a clustered configuration Unpack the jar file on the secondary node |
Run the |
|
Required only if your existing environment is a clustered configuration Restart the servers and processes. |
The upgrade process is complete. You can now restart the servers, components, and processes. |
Installing Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure
Installing Fusion Middleware Infrastructure creates an Oracle home directory and lays down supporting software to install other Fusion Middleware products.
Note:
If you are upgrading from a previous 12c release, then you must install the12c (12.2.1.4.0) distributions into a new Oracle home. Do not attempt to reuse the existing Oracle home for this upgrade. Upgrading to 12c (12.2.1.4.0) is not a patch release.Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
To identify potential issues with the upgrade, Oracle recommends that you run a readiness check before you start the upgrade process. Be aware that the readiness check may not be able to discover all potential issues with your upgrade. An upgrade may still fail, even if the readiness check reports success.
- About Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
You can run the Upgrade Assistant in-readinessmode to detect issues before you perform the actual upgrade. You can run the readiness check in GUI mode using the Upgrade Assistant or in silent mode using a response file. - Starting the Upgrade Assistant in Readiness Mode
Use the-readinessparameter to start the Upgrade Assistant in readiness mode. - Performing a Readiness Check with the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to complete the pre-upgrade readiness check. - Understanding the Readiness Report
After performing a readiness check for your domain, review the report to determine whether you need to take any action for a successful upgrade.
About Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
You can run the Upgrade Assistant in -readiness mode to detect issues before you perform the actual upgrade. You can run the readiness check in GUI mode using the Upgrade Assistant or in silent mode using a response file.
The Upgrade Assistant readiness check performs a read-only, pre-upgrade review of your Fusion Middleware schemas and WebLogic domain configurations that are at a supported starting point. The review is a read-only operation.
The readiness check generates a formatted, time-stamped readiness report so you can address potential issues before you attempt the actual upgrade. If no issues are detected, you can begin the upgrade process. Oracle recommends that you read this report thoroughly before performing an upgrade.
You can run the readiness check while your existing Oracle Fusion Middleware domain is online (while other users are actively using it) or offline.
You can run the readiness check any number of times before performing any actual upgrade. However, do not run the readiness check after an upgrade has been performed, as the report results may differ from the result of pre-upgrade readiness checks.
Note:
To prevent performance from being affected, Oracle recommends that you run the readiness check during off-peak hours.
Parent topic: Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
Starting the Upgrade Assistant in Readiness Mode
Use the -readiness parameter to start the Upgrade Assistant in readiness mode.
Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-2 Upgrade Assistant Command-Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
Note: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant creates log files and temporary files. The default locations are: (UNIX)
(Windows)
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command-line options. |
Parent topic: Starting the Upgrade Assistant in Readiness Mode
Performing a Readiness Check with the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to complete the pre-upgrade readiness check.
Parent topic: Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
Understanding the Readiness Report
After performing a readiness check for your domain, review the report to determine whether you need to take any action for a successful upgrade.
The format of the readiness report file is:
readiness_timestamp.txt
where timestamp indicates the date and time of when the readiness check was run.
A readiness report contains the following information:
Table 4-3 Readiness Report Elements
| Report Information | Description | Required Action |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Readiness Status: SUCCESS or FAILURE | The top of the report indicates whether the readiness check passed or completed with one or more errors. | If the report completed with one or more errors, search for FAIL and correct the failing issues before attempting to upgrade. You can re-run the readiness check as many times as necessary before an upgrade. |
|
Timestamp |
The date and time that the report was generated. |
No action required. |
|
Log file location
|
The directory location of the generated log file. |
No action required. |
|
Readiness report location
|
The directory location of the generated readiness report. |
No action required. |
|
Names of components that were checked |
The names and versions of the components included in the check and status. |
If your domain includes components that cannot be upgraded to this release, such as SOA Core Extension, do not attempt an upgrade. |
|
Names of schemas that were checked |
The names and current versions of the schemas included in the check and status. |
Review the version numbers of your schemas. If your domain includes schemas that cannot be upgraded to this release, do not attempt an upgrade. |
|
Individual Object Test Status: FAIL |
The readiness check test detected an issue with a specific object. |
Do not upgrade until all failed issues have been resolved. |
|
Individual Object Test Status: PASS |
The readiness check test detected no issues for the specific object. |
If your readiness check report shows only the PASS status, you can upgrade your environment. Note, however, that the Readiness Check cannot detect issues with externals such as hardware or connectivity during an upgrade. You should always monitor the progress of your upgrade. |
| Completed Readiness Check of <Object> Status: FAILURE | The readiness check detected one or more errors that must be resolved for a particular object such as a schema, an index, or datatype. | Do not upgrade until all failed issues have been resolved. |
| Completed Readiness Check of <Object> Status: SUCCESS | The readiness check test detected no issues. | No action required. |
Upgrade readiness check completed with one or more errors.
This readiness check report was created on Tue May 30 11:15:52 EDT 2016
Log file is located at: NEW_ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/logs/ua2016-05-30-11-14-06AM.log
Readiness Check Report File: NEW_ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/logs/readiness2016-05-30-11-15-52AM.txt
Starting readiness check of components.
Oracle Metadata Services
Starting readiness check of Oracle Metadata Services.
Schema User Name: DEV11_MDS
Database Type: Oracle Database
Database Connect String: machinename@yourcompany.com
VERSION Schema DEV11_MDS is currently at version 12.1.1.1.0. Readiness checks will now be performed.
Starting schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_TABLES Test that the schema contains all the required tables
Completed schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_TABLES --> Test that the schema contains all the required tables +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_PROCEDURES Test that the schema contains all the required stored procedures
EXCEPTION Schema is missing a required procedure: GETREPOSITORYFEATURES
Completed schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_PROCEDURES --> Test that the schema contains all the required stored procedures +++ FAIL
Starting schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_VIEWS Test that the schema contains all the required database views
Completed schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_VIEWS --> Test that the schema contains all the required database views +++ PASS
Starting index test for table MDS_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_REQUIRED_INDEXES --> Test that the table contains all the required indexes
Completed index test for table MDS_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_REQUIRED_INDEXES --> Test that the table contains all the required indexes +++ PASS
Starting index test for table MDS_COMPONENTS: TEST_REQUIRED_INDEXES --> Test that the table contains all the required indexes
Completed index test for table MDS_TXN_LOCKS: TEST_REQUIRED_INDEXES --> Test that the table contains all the required indexes +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_TRIGGERS Test that the schema has all the required triggers
Completed schema test: TEST_REQUIRED_TRIGGERS --> Test that the schema has all the required triggers +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_MISSING_COLUMNS Test that tables and views are not missing any required columns
Completed schema test: TEST_MISSING_COLUMNS --> Test that tables and views are not missing any required columns +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_TABLES Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected tables
Completed schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_TABLES --> Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected tables +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_PROCEDURES Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected stored procedures
Completed schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_PROCEDURES --> Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected stored procedures +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_VIEWS Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected views
Completed schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_VIEWS --> Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected views +++ PASS
Starting index test for table MDS_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_UNEXPECTED_INDEXES --> Test that the table does not contain any unexpected indexes
Completed index test for table MDS_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_UNEXPECTED_INDEXES --> Test that the table does not contain any unexpected indexes +++ PASS
Completed index test for table MDS_LABELS: TEST_UNEXPECTED_INDEXES --> Test that the table does not contain any unexpected indexes +++ PASS
Starting index test for table MDS_LARGE_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_UNEXPECTED_INDEXES --> Test that the table does not contain any unexpected indexes
Starting schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_TRIGGERS Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected triggers
Completed schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_TRIGGERS --> Test that the schema does not contain any unexpected triggers +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_COLUMNS Test that tables and views do not contain any unexpected columns
Completed schema test: TEST_UNEXPECTED_COLUMNS --> Test that tables and views do not contain any unexpected columns +++ PASS
Starting datatype test for table MDS_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_COLUMN_DATATYPES_V2 --> Test that all table columns have the proper datatypes
Completed datatype test for table MDS_ATTRIBUTES: TEST_COLUMN_DATATYPES_V2 --> Test that all table columns have the proper datatypes +++ PASS
Starting datatype test for table MDS_COMPONENTS: TEST_COLUMN_DATATYPES_V2 --> Test that all table columns have the proper datatypes
Starting permissions test: TEST_DBA_TABLE_GRANTS Test that DBA user has privilege to view all user tables
Completed permissions test: TEST_DBA_TABLE_GRANTS --> Test that DBA user has privilege to view all user tables +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_ENOUGH_TABLESPACE Test that the schema tablespaces automatically extend if full
Completed schema test: TEST_ENOUGH_TABLESPACE --> Test that the schema tablespaces automatically extend if full +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_USER_TABLESPACE_QUOTA Test that tablespace quota for this user is sufficient to perform the upgrade
Completed schema test: TEST_USER_TABLESPACE_QUOTA --> Test that tablespace quota for this user is sufficient to perform the upgrade +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_ONLINE_TABLESPACE Test that schema tablespaces are online
Completed schema test: TEST_ONLINE_TABLESPACE --> Test that schema tablespaces are online +++ PASS
Starting schema test: TEST_DATABASE_VERSION Test that the database server version number is supported for upgrade
INFO Database product version: Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.3.0 - 64bit Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP, Data Mining and Real Application Testing options
Completed schema test: TEST_DATABASE_VERSION --> Test that the database server version number is supported for upgrade +++ PASS
Finished readiness check of Oracle Metadata Services with status: FAILURE.
If you are running the 12.1.3.0 version of Oracle Fusion Middleware IAU Schemas, and those schemas were upgraded from 11g (11.1.1.7 and later) or 12c (12.1.2.0), your readiness check may fail with the following error:
Starting index test for table IAU_COMMON: TEST_REQUIRED_INDEXES --> Test
that the table contains all the required indexes
INFO Audit schema index DYN_EVENT_CATEGORY_INDEX in table IAU_COMMON is
missing the required columns or index itself is missing. This maybe caused by
a known issue, anyway, this missing index will be added in 12.2.2 upgrade.
INFO Audit schema index DYN_EVENT_TYPE_INDEX in table IAU_COMMON is
missing the required columns or index itself is missing. This maybe caused by
a known issue, anyway, this missing index will be added in 12.2.2 upgrade.
INFO Audit schema index DYN_TENANT_INDEX in table IAU_COMMON is missing
the required columns or index itself is missing. This maybe caused by a known
issue, anyway, this missing index will be added in 12.2.2 upgrade.
INFO Audit schema index DYN_USER_INDEX in table IAU_COMMON is missing
the required columns or index itself is missing. This maybe caused by a known
issue, anyway, this missing index will be added in 12.2.2 upgrade.
INFO Audit schema index DYN_COMPONENT_TYPE_INDEX in table IAU_COMMON is
missing the required columns or index itself is missing. This maybe caused by
a known issue, anyway, this missing index will be added in 12.2.2 upgrade.
INFO Audit schema index DYN_USER_TENANT_INDEX in table IAU_COMMON is
missing the required columns or index itself is missing. This maybe caused by
a known issue, anyway, this missing index will be added in 12.2.2 upgrade.
Completed index test for table IAU_COMMON: TEST_REQUIRED_INDEXES --> Test
that the table contains all the required indexes +++ FAILNote:
You can ignore the missing index error in the readiness report. This is a known issue. The corresponding missing index is added during the schema upgrade operation. This error does not occur if the schema to be upgraded was created in 12c using the RCU.Parent topic: Running a Pre-Upgrade Readiness Check
Stopping Servers and Processes
Before running the Upgrade Assistant, shut down all Oracle Fusion Middleware Managed Servers, Administration Servers, and system components (such as OHS) that may be using the schemas or configurations you want to update. Failure to do so may result in an incomplete or failed upgrade.
If you are running the Node Manager, you should also stop the Node Manager. You can do this by closing the console window in which the Node Manager is running, or by using the stopNodeManager WLST command.
For instructions to stop an Oracle Fusion Middleware environment, see Stopping an Oracle Fusion Middleware Environment in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Upgrading Product Schemas
After stopping servers and processes, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade supported product schemas to the current release of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
The Upgrade Assistant allows you to upgrade individually selected schemas or all schemas associated with a domain. The option you select determines which Upgrade Assistant screens you will use.
- Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.4.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time. - Upgrading Schemas Using the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the product schemas. - Verifying the Schema Upgrade
After completing all the upgrade steps, verify that the upgrade was successful by checking that the schema version inschema_version_registryhas been properly updated.
Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.4.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
Note:
Before you start the Upgrade Assistant, make sure that the JVM character encoding is set to UTF-8 for the platform on which the Upgrade Assistant is running. If the character encoding is not set to UTF-8, then you will not be able to download files containing Unicode characters in their names. This can cause the upgrade to fail.
- Go to the
oracle_common/upgrade/bindirectory:- (UNIX)
NEW_ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/bin - (Windows)
NEW_ORACLE_HOME\oracle_common\upgrade\bin
- (UNIX)
- Start the Upgrade Assistant:
- (UNIX) ./ua
- (Windows) ua.bat
For information about other parameters that you can specify on the command line, such as logging parameters, see:
Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-4 Upgrade Assistant Command-Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
Note: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant creates log files and temporary files. The default locations are: (UNIX)
(Windows)
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command-line options. |
Parent topic: Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Upgrading Schemas Using the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the product schemas.
Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
Verifying the Schema Upgrade
After completing all the upgrade steps, verify that the upgrade was successful by checking that the schema version in schema_version_registry has been properly updated.
If you are using an Oracle database, connect to the database as a user having Oracle DBA privileges, and run the following from SQL*Plus to get the current version numbers:
SET LINE 120 COLUMN MRC_NAME FORMAT A14 COLUMN COMP_ID FORMAT A20 COLUMN VERSION FORMAT A12 COLUMN STATUS FORMAT A9 COLUMN UPGRADED FORMAT A8 SELECT MRC_NAME, COMP_ID, OWNER, VERSION, STATUS, UPGRADED FROM SCHEMA_VERSION_REGISTRY ORDER BY MRC_NAME, COMP_ID ;
In the query result:
-
Check that the number in the
VERSIONcolumn matches the latest version number for that schema. For example, verify that the schema version number is 12.2.1.4.0.Note:
However, that not all schema versions will be updated. Some schemas do not require an upgrade to this release and will retain their pre-upgrade version number.
-
The
STATUSfield will be eitherUPGRADINGorUPGRADEDduring the schema patching operation, and will becomeVALIDwhen the operation is completed. -
If the status appears as
INVALID, the schema update failed. You should examine the logs files to determine the reason for the failure. -
Synonym objects owned by
IAU_APPENDandIAU_VIEWERwill appear asINVALID, but that does not indicate a failure.They become invalid because the target object changes after the creation of the synonym. The synonyms objects will become valid when they are accessed. You can safely ignore these
INVALIDobjects.
Parent topic: Upgrading Product Schemas
About Reconfiguring the Domain
Run the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your domain component configurations to 12c (12.2.1.4.0).
When you reconfigure a WebLogic Server domain, the following items are automatically updated, depending on the applications in the domain:
-
WebLogic Server core infrastructure
-
Domain version
Note:
Before you begin the domain reconfiguration, note the following limitations:
-
The Reconfiguration Wizard does not update any of your own applications that are included in the domain.
-
Transforming a non-dynamic cluster domain to a dynamic cluster domain during the upgrade process is not supported.
The dynamic cluster feature is available when running the Reconfiguration Wizard, but Oracle only supports upgrading a non-dynamic cluster upgrade and then adding dynamic clusters. You cannot add dynamic cluster during the upgrade process.
-
The domain version number in the
config.xmlfile for the domain is updated to the Administration Server's installed WebLogic Server version. -
Reconfiguration templates for all installed Oracle products are automatically selected and applied to the domain. These templates define any reconfiguration tasks that are required to make the WebLogic domain compatible with the current WebLogic Server version.
-
Start scripts are updated.
If you want to preserve your modified start scripts, be sure to back them up before starting the Reconfiguration Wizard.
Note:
When the domain reconfiguration process starts, you can’t undo the changes that it makes. Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, ensure that you have backed up the domain as covered in the pre-upgrade checklist. If an error or other interruption occurs while running the Reconfiguration Wizard, you must restore the domain by copying the files and directories from the backup location to the original domain directory. This is the only way to ensure that the domain has been returned to its original state before reconfiguration.- Backing Up the Domain
- Starting the Reconfiguration Wizard
- Reconfiguring the Domain with the Reconfiguration Wizard
The Reconfiguration Wizard reconfigures the domain while retaining the location of the domain. Navigate through the screens in the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your existing domain.
Backing Up the Domain
Before running the Reconfiguration Wizard, create a backup copy of the domain directory.
To create a backup of the domain directory:
Parent topic: About Reconfiguring the Domain
Starting the Reconfiguration Wizard
Note:
Shut down the administration server and all collocated managed servers before starting the reconfiguration process. See Stopping Servers and Processes.To start the Reconfiguration Wizard in graphical mode:
Parent topic: About Reconfiguring the Domain
Reconfiguring the Domain with the Reconfiguration Wizard
The Reconfiguration Wizard reconfigures the domain while retaining the location of the domain. Navigate through the screens in the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure your existing domain.
Important:
If the source is a clustered environment, run the Reconfiguration Wizard on the primary node only. Use the pack/unpack utility to apply the changes to other cluster members in the domain as described in If Your Existing Environment is a Clustered Configuration....For all the Advanced Configurations-related screens, such as Managed Servers, Clusters, Machines, HTTP Proxy Applications, Coherence Clusters, and System Components, see Upgrading Oracle WebLogic Server.
If an error occurs while reconfiguring your domain, refer to the Important Notes About the Domain Upgrade Process in Upgrading Oracle WebLogic Server.
Parent topic: About Reconfiguring the Domain
Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
After reconfiguring the domain, use the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations inside the domain to match the updated domain configuration.
- Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.4.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time. - Upgrading the Domain Configurations with the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade component configurations in the WebLogic domain. - Verifying the Domain-Specific-Component Configurations Upgrade
To verify that the domain-specific-component configurations upgrade was successful, sign in to the Administration console and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and verify that the version numbers for each component is 12.2.1.4.0.
Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade product schemas, domain component configurations, or standalone system components to 12c (12.2.1.4.0). Oracle recommends that you run the Upgrade Assistant as a non-SYSDBA user, completing the upgrade for one domain at a time.
Note:
Before you start the Upgrade Assistant, make sure that the JVM character encoding is set to UTF-8 for the platform on which the Upgrade Assistant is running. If the character encoding is not set to UTF-8, then you will not be able to download files containing Unicode characters in their names. This can cause the upgrade to fail.
- Go to the
oracle_common/upgrade/bindirectory:- (UNIX)
NEW_ORACLE_HOME/oracle_common/upgrade/bin - (Windows)
NEW_ORACLE_HOME\oracle_common\upgrade\bin
- (UNIX)
- Start the Upgrade Assistant:
- (UNIX) ./ua
- (Windows) ua.bat
For information about other parameters that you can specify on the command line, such as logging parameters, see:
Upgrade Assistant Parameters
When you start the Upgrade Assistant from the command line, you can specify additional parameters.
Table 4-6 Upgrade Assistant Command-Line Parameters
| Parameter | Required or Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Required for readiness checks
Note: Readiness checks cannot be performed on standalone installations (those not managed by the WebLogic Server). |
Performs the upgrade readiness check without performing an actual upgrade. Schemas and configurations are checked. Do not use this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Identifies the number of threads available for concurrent schema upgrades or readiness checks of the schemas. The value must be a positive integer in the range 1 to 8. The default is 4. |
|
|
Required for silent upgrades or silent readiness checks |
Runs the Upgrade Assistant using inputs saved to a response file generated from the data that is entered when the Upgrade Assistant is run in GUI mode. Using this parameter runs the Upgrade Assistant in silent mode (without displaying Upgrade Assistant screens). |
|
|
Optional |
Performs the examine phase but does not perform an actual upgrade. Do not specify this parameter if you have specified the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the logging level, specifying one of the following attributes:
The default logging level is Consider setting the |
|
|
Optional |
Sets the default location of upgrade log files and temporary files. You must specify an existing, writable directory where the Upgrade Assistant creates log files and temporary files. The default locations are: (UNIX)
(Windows)
|
|
|
Optional |
Displays all of the command-line options. |
Parent topic: Starting the Upgrade Assistant
Upgrading the Domain Configurations with the Upgrade Assistant
Navigate through the screens in the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade component configurations in the WebLogic domain.
After running the Reconfiguration Wizard to reconfigure the WebLogic domain to 12c (12.2.1.4.0), you must run the Upgrade Assistant to upgrade the domain component configurations to match the updated domain configuration.
Parent topic: Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
Verifying the Domain-Specific-Component Configurations Upgrade
To verify that the domain-specific-component configurations upgrade was successful, sign in to the Administration console and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and verify that the version numbers for each component is 12.2.1.4.0.
To sign in to the Administration Console, go to: http://administration_server_host:administration_server_port/console
To sign in to Oracle Enterprise Manager
Fusion Middleware Control Console, go to: http://administration_server_host:administration_server_port/em
Note:
After upgrade, make sure you run the administration tools from the new 12c Oracle home directory and not from the previous Oracle home directory.
During the upgrade process, some OWSM documents, including policy sets and predefined documents such as policies and assertion templates, may need to be upgraded. If a policy set or a predefined document is upgraded, its version number is incremented by 1.
Parent topic: Upgrading Domain Component Configurations
Starting Servers and Processes
After a successful upgrade, restart all processes and servers, including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers.
The components may be dependent on each other so they must be started in the correct order.
Note:
The procedures in this section describe how to start servers and process using the WLST command line or a script. You can also use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Control and the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. See Starting and Stopping Administration and Managed Servers and Node Manager in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.To start your Fusion Middleware environment, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Start the Administration Server
When you start the Administration Server, you also start the processes running in the Administration Server, including the WebLogic Server Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control.
To start the Administration Server, use the startWebLogic script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startWebLogic.sh -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startWebLogic.cmd
When prompted, enter your user name, password, and the URL of the Administration Server.
Step 2: Start Node Manager
To start Node Manager, use the startNodeManager script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startNodeManager.sh -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startNodeManager.cmd
Step 3: Start Oracle Identity Management Components
Start any Oracle Identity Management components, such as Oracle Internet Directory, that form part of your environment:-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startComponent.sh component_name -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startComponent.cmd component_name
Step 4: Start the Managed Servers
To start a WebLogic Server Managed Server, use the startManagedWebLogic script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startManagedWebLogic.sh managed_server_name admin_url -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startManagedWebLogic.cmd managed_server_name admin_url
When prompted, enter your user name and password.
Note:
The startup of a Managed Server will typically start the applications that are deployed to it. Therefore, it should not be necessary to manually start applications after the Managed Server startup.Step 5: Start System Components
To start system components, such as Oracle HTTP Server, use the startComponent script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startComponent.sh component_name -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startComponent.cmd component_name
You can start system components in any order.
Using the Upgrade Validation Checklist
After the upgrade, make sure that you can successfully complete the basic administration tasks, such as verifying whether you are able to start the Node Manager, Administration Server, Webtier, Administration Console, and Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control.
Note:
The order in which you start the following servers is important and failure to start (or stop) them in the correct order can cause issues with the deployment.
Reapplying Custom Configuration Settings to setDomainEnv
To complete the upgrade of your application environment to 12c it might be necessary to reapply any custom configuration settings to startup scripts, such as setDomainEnv. During the upgrade, the scripts are overwritten with new 12c versions. You must manually reapply the custom configuration settings you had made in previous releases.
See Re-apply Customizations to Startup Scripts.
Note:
To prevent losing your custom configuration settings in a future upgrade, see Maintaining Your Custom setDomainEnv Settings.
Maintaining the Security Status of Older Java EE Web Service Applications
The introduction of global policy attachment support for Java EE web services and clients in 12c may impact the backwards compatibility of existing Java EE web services and clients (12.1.2 and earlier). If a Java EE web service or client endpoint that depends on the absence of a policy falls within the scope of a global policy attachment, the presence of the globally-attached policy can alter the security behavior of that endpoint.
Note:
In Fusion Middleware 12.1.2 and earlier, global policy attachments defined for SOAP Web Service and SOAP Web Service Client subject types were applicable to Oracle Infrastructure web services and clients only, and were ignored by Java EE web services and clients. After upgrading to 12c (12.2.1), the global policy attachments defined for these subject types apply to Java EE web services and clients, as well, and may alter the security behavior of existing Java EE web services and clients.
To maintain backwards compatibility, you can disable the global policy attachments for specific endpoints by attaching an OWSM no behavior policy to the service or client, such as no_authentication_service_policy, no_authorization_service_policy, or no_messageprotection_service_policy. See Disabling a Globally Attached Policy in Securing Web Services and Managing Policies with Oracle Web Services Manager.
Note:
You can use the WebLogic Wssp1.5-No-Op.xml no behavior policy. However, since WebLogic security policies can only be attached to web service clients programmatically, it requires code change. See Disabling a Globally Attached Policy in Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Documentation Resources for Managing your Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c Software
This topic provides a list of common administration tasks you likely want to perform after upgrading to Infrastructure 12c and associated documentation resources.
Table 5-1 lists some common administration tasks you will likely want to perform after upgrading to Infrastructure 12c.
Table 4-7 Basic Administration Tasks
| Task | Description | More Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Getting familiar with Fusion Middleware administration tools |
Get familiar with the various tools available which you can use to manage your environment. |
Overview of Oracle Fusion Middleware Administration Tools in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
|
Starting and stopping products and servers |
Learn how to start and stop Oracle Fusion Middleware, including the Administration Server, Managed Servers, and components. |
Starting and Stopping Oracle Fusion Middleware in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
|
Configuring Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) |
Learn how to set up secure communications among between Oracle Fusion Middleware components using SSL. |
Configuring SSL in Oracle Fusion Middleware in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
|
Monitoring Oracle Fusion Middleware |
Learn how to keep track of the status of Oracle Fusion Middleware components. |
Monitoring Oracle Fusion Middleware in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
|
Understanding Backup and Recovery Procedures |
Learn the recommended backup and recovery procedures for Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
Introducing Backup and Recovery in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
If Your Existing Environment is a Clustered Configuration...
If your existing environment is a clustered configuration, then you must apply the changes to other cluster members in the domain by using the pack and unpack utilities.
Starting Servers and Processes
After a successful upgrade, restart all processes and servers, including the Administration Server and any Managed Servers.
The components may be dependent on each other so they must be started in the correct order.
Note:
The procedures in this section describe how to start servers and process using the WLST command line or a script. You can also use the Oracle Fusion Middleware Control and the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. See Starting and Stopping Administration and Managed Servers and Node Manager in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.To start your Fusion Middleware environment, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Start the Administration Server
When you start the Administration Server, you also start the processes running in the Administration Server, including the WebLogic Server Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control.
To start the Administration Server, use the startWebLogic script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startWebLogic.sh -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startWebLogic.cmd
When prompted, enter your user name, password, and the URL of the Administration Server.
Step 2: Start Node Manager
To start Node Manager, use the startNodeManager script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startNodeManager.sh -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startNodeManager.cmd
Step 3: Start Oracle Identity Management Components
Start any Oracle Identity Management components, such as Oracle Internet Directory, that form part of your environment:-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startComponent.sh component_name -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startComponent.cmd component_name
Step 4: Start the Managed Servers
To start a WebLogic Server Managed Server, use the startManagedWebLogic script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startManagedWebLogic.sh managed_server_name admin_url -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startManagedWebLogic.cmd managed_server_name admin_url
When prompted, enter your user name and password.
Note:
The startup of a Managed Server will typically start the applications that are deployed to it. Therefore, it should not be necessary to manually start applications after the Managed Server startup.Step 5: Start System Components
To start system components, such as Oracle HTTP Server, use the startComponent script:
-
(UNIX)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME/bin/startComponent.sh component_name -
(Windows)
NEW_DOMAIN_HOME\bin\startComponent.cmd component_name
You can start system components in any order.