2 Preparing to Install and Configure Oracle Identity and Access Management
To prepare for your Oracle Identity and Access Management installation, verify that your system meets the basic requirements, then obtain the correct installation software.
Note:
The product Oracle Identity Manager is referred to as Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) and Oracle Identity Governance (OIG) interchangeably in the guide.
- Roadmap for Installing and Configuring a Standard Installation Topology
This roadmap provides the steps required to install and configure Oracle Access Management and Oracle Identity Governance. - Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
Before you begin the installation and configuration process, you must verify your system environment. - Obtaining the Product Distribution
You can obtain the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure and Oracle Identity and Access Management distribution on Technical Resources from Oracle. - List of Supported Languages
Roadmap for Installing and Configuring a Standard Installation Topology
This roadmap provides the steps required to install and configure Oracle Access Management and Oracle Identity Governance.
Table 2-1 provides the high-level steps required for installing a standard installation topology.
Table 2-1 Standard Installation Roadmap
| Task | Description | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
|
Verify your system environment. |
Before you begin the installation, verify that the minimum system and network requirements are met. |
|
|
Check for any mandatory patches that are required before the installation. |
Review the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure release notes to see if there are any mandatory patches required for the software products that you are installing. |
See Install and Configure in Release Notes for Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure. Note: For Oracle Identity Governance, if you plan to configure a High Availability setup and have Oracle HTTP Servers (OHS) 12.2.1.4 in your environment with IPV6, then apply patch 31900098. |
|
Obtain the appropriate distributions. |
For Oracle Access Management (OAM): Obtain the following distributions:
--------------------------- For Oracle Identity Governance (OIG): If you choose to install all the software in one go, obtain the following distributions:
If you choose to individually install each product, obtain the following distributions:
|
See Obtaining the Product Distribution. Note: After downloading the required For information about supported installation methods for Oracle Identity and Access Management, see About Supported Installation Methods. |
|
Determine your installation directories. |
Verify that the installer can access or create the required installer directories. Also, verify that the directories exist on systems that meet the minimum requirements. |
See What Are the Key Oracle Fusion Middleware Directories? in Understanding Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
|
Install prerequisite software. |
If you are configuring OAM 12.2.1.4.0, you must install Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure 12.2.1.4.0. If you are configuring OIG:
|
See Installing the Infrastructure Software in Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure. See Installing the Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management Software in Installing and Configuring Oracle SOA Suite and Business Process Management. |
|
Install the software. |
Run the Oracle Identity and Access Management installer to install the OAM and OIG binaries. Note: If you are using both Oracle Identity Governance and OIG then you must install them in separate Installing the software transfers the software to your system and creates the Oracle home directory. |
For OAM, see Installing the Oracle Access Management Software. For OIG, see Installing the Oracle Identity Governance Software. For an OAM and OIG integrated environment, see Integrating Oracle Identity Governance and Oracle Access Manager Using LDAP Connectors in Integration Guide for Oracle Identity Management Suite. |
|
Select a database profile and review any required custom variables. |
Before you install the required schemas in the database, review the information about any custom variables you need to set for the Oracle Identity and Access Management schemas. |
See About Database Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation. |
|
Create the schemas. |
Run the Repository Creation Utility to create the schemas required for configuration. |
For OAM, see Creating the Database Schemas. For OIG, see Creating the Database Schemas. |
|
Create a WebLogic domain. |
Use the Configuration Wizard/Assistant to create and configure the WebLogic domain. Note: Configure OAM and OIG in two different |
For OAM, see Configuring the Oracle Access Management Domain. For OIG, see Configuring the Oracle Identity Governance Domain. |
|
Administer and prepare your domain for high availability. |
Discover additional tools and resources to administer your domain and configure your domain to be highly available. |
Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
Before you begin the installation and configuration process, you must verify your system environment.
Table 2-2 identifies important tasks and checks to perform to ensure that your environment is prepared to install and configure Oracle Identity and Access Management.
Table 2-2 Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
| Task | Description | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
|
Verify certification and system requirements. |
Verify that your operating system is certified and configured for installation and configuration. |
See Verifying Certification, System, and Interoperability Requirements. |
|
Identify a proper installation user. |
Verify that the installation user has the required permissions to install and configure the software. |
|
|
Select the installation and configuration directories on your system. |
Verify that you can create the necessary directories to install and configure the software, according to the recommended directory structure. |
See About the Directories for Installation and Configuration. |
|
Install a certified JDK. |
The installation program for the distribution requires a certified JDK present on your system. |
See About JDK Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation. |
|
Install and configure a database for mid-tier schemas. |
To configure your WebLogic domain, you must have access to a certified database that is configured for the schemas required by Oracle Identity and Access Management. |
See About Database Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation. |
- Verifying Certification, System, and Interoperability Requirements
Oracle recommends that you use the certification matrix and system requirements documents with each other to verify that your environment meets the requirements for installation. - Selecting an Installation User
The user who installs and configures your system must have the required permissions and privileges. - About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
During the installation and domain configuration process, you must plan on providing the locations for these directories: Oracle home, Domain home, and the Application home. - About JDK Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation
Most Fusion Middleware products are in.jarfile format. These distributions do not include a JDK. To run a.jardistribution installer, you must have a certified JDK installed on your system. - About Database Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation
Many Oracle Fusion Middleware products require database schemas prior to configuration. If you do not already have a database where you can install these schemas, you must install and configure a certified database.
Verifying Certification, System, and Interoperability Requirements
Oracle recommends that you use the certification matrix and system requirements documents with each other to verify that your environment meets the requirements for installation.
-
Verifying that your environment meets certification requirements:
Make sure that you install your product on a supported hardware and software configuration. See the certification document for your release on the Oracle Fusion Middleware Supported System Configurations page.
Oracle has tested and verified the performance of your product on all certified systems and environments. Whenever new certifications are released, they are added to the certification document right away. New certifications can be released at any time. Therefore, the certification documents are kept outside the documentation libraries and are available on Oracle Technology Network.
-
Using the system requirements document to verify certification:
Oracle recommends that you use the Oracle Fusion Middleware System Requirements and Specifications document to verify that the certification requirements are met. For example, if the certification document indicates that your product is certified for installation on 64-Bit Oracle Linux 6.5, use this document to verify that your system meets the required minimum specifications. These include disk space, available memory, specific platform packages and patches, and other operating system-specific requirements. System requirements can change in the future. Therefore, the system requirement documents are kept outside of the documentation libraries and are available on Oracle Technology Network.
-
Verifying interoperability among multiple products:
To learn how to install and run multiple Fusion Middleware products from the same release or mixed releases with each other, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Interoperability and Compatibility in Understanding Interoperability and Compatibility.
Parent topic: Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
Selecting an Installation User
The user who installs and configures your system must have the required permissions and privileges.
- About User Permissions
The user who installs a Fusion Middleware product owns the files and has certain permissions on the files. - About Non-Default User Permissions on UNIX Operating Systems
Changing the default permission setting reduces the security of the installation and your system. Oracle does not recommend that change the default permission settings. - Verifying that the Installation User has Administrator Privileges on Windows Operating Systems
To update the Windows Registry, you must have administrator privileges.
Parent topic: Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
About User Permissions
The user who installs a Fusion Middleware product owns the files and has certain permissions on the files.
-
Read and write permissions on all non-executable files (for example,
.jar,.properties, or.xml). All other users in the same group as the file owner have read permissions only. -
Read, write, and execute permissions on all executable files (for example,
.exe,.sh, or.cmd). All other users in the same group as the file owner have read and execute permissions only.
This means that someone other than the person who installs the software can use the installed binaries in the Oracle home directory to configure a domain or set of Fusion Middleware products.
During configuration, the files generated by the configuration process are owned by the user who ran the Configuration Wizard. This user has the same permissions as described above for the installation user. However, security-sensitive files are not created with group permissions. Only the user that created the domain has read and write permissions and can administer the domain.
Consider the following examples:
-
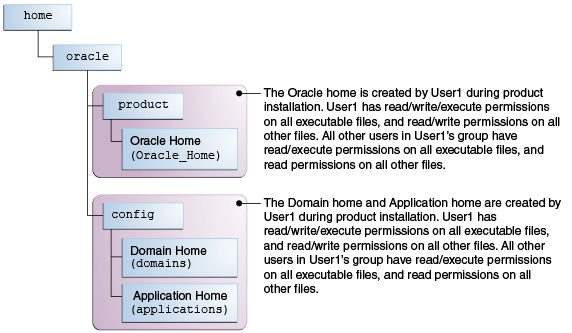
Example 1: A Single User Installs the Software and Configures the Domain
This example explains the file permissions where the same user installs the software and configures the domain.
To ensure proper permissions and privileges for all files, Oracle recommends that the same owner perform both tasks: install the Oracle Fusion Middleware product and configure the WebLogic Server domain by using the Configuration Wizard.
Figure 2-1 Directory Structure when a Single User Installs the Software and Configures the Domain
If the user who creates the domain is different than the user who installed the software, then both users must have the same privileges, as shown in the next example.
-
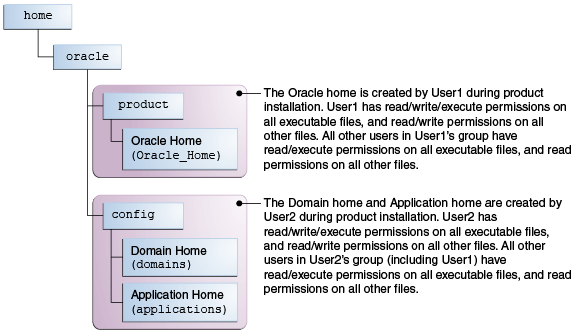
Example 2: The Oracle Home Directory and Domain are Created by Different Users
This example explains the file permissions where one user creates the Oracle home and another user configures the domain.
Figure 2-2 Directory Structure when Different Users Install the Software and Configure the Domain
Note:
Certain domain files do not have group permissions. For example,cwallet.sso.
Consider the following points before you run the installer:
-
On UNIX operating systems, Oracle recommends that you set
umaskto027on your system before you install the software. This ensures that the file permissions are set properly during installation. Use the following command:umask 027You must enter this command in the same terminal window from which you plan to run the product installer.
-
On UNIX operating systems, do not run the installation program as a
rootuser. If you run the installer as a root user, the startup validation may fail and you cannot continue the installation. -
When you manage a product installation (for example, applying patches or starting managed Servers), use the same user ID that you used to install the product.
-
On Windows operating systems, you must have administrative privileges to install the product. See Verifying the Installation User has Administrator Privileges on Windows Operating Systems.
Parent topic: Selecting an Installation User
About Non-Default User Permissions on UNIX Operating Systems
Changing the default permission setting reduces the security of the installation and your system. Oracle does not recommend that change the default permission settings.
If other users require access to a particular file or executable, use the UNIX sudo command or other similar commands to change the file permissions.
Refer to your UNIX operating system Administrator's Guide or contact your operating system vendor, if you need further assistance.
Parent topic: Selecting an Installation User
Verifying that the Installation User has Administrator Privileges on Windows Operating Systems
To update the Windows Registry, you must have administrator privileges.
By default, users with the administrator privilege sign in to the system with regular privileges, but can request elevated permissions to perform administrative tasks.
To perform a task with elevated privileges:
Parent topic: Selecting an Installation User
About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
During the installation and domain configuration process, you must plan on providing the locations for these directories: Oracle home, Domain home, and the Application home.
- About the Recommended Directory Structure
Oracle recommends specific locations for the Oracle Home, Domain Home, and Application Home. - About the Oracle Home Directory
When you install any Oracle Fusion Middleware product, you must use an Oracle home directory. - About the Domain Home Directory
The Domain home is the directory where domains that you configure are created. - About the Application Home Directory
The Application home is the directory where applications for domains you configure are created. - Preparing for Shared Storage
Oracle Fusion Middleware allows you to configure multiple WebLogic Server domains from a single Oracle home. This allows you to install the Oracle home in a single location on a shared volume and reuse the Oracle home for multiple host installations.
Parent topic: Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
About the Recommended Directory Structure
Oracle recommends specific locations for the Oracle Home, Domain Home, and Application Home.
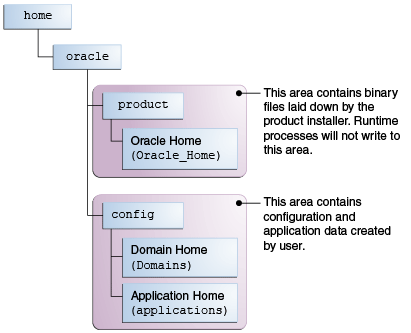
Oracle recommends a directory structure similar to the one shown in Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3 Recommended Oracle Fusion Middleware Directory Structure
A base location (Oracle base) should be established on your system (for example, /home/oracle). From this base location, create two separate branches, namely, the product directory and the config directory. The product directory should contain the product binary files and all the Oracle home directories. The config directory should contain your domain and application data.
Oracle recommends that you do not keep your configuration data in the Oracle home directory; if you upgrade your product to another major release, are required to create a new Oracle home for binaries. You must also make sure that your configuration data exists in a location where the binaries in the Oracle home have access.
The /home/oracle/product (for the Oracle home) and /home/oracle/config (for the application and configuration data) directories are used in the examples throughout the documentation; be sure to replace these directories with the actual directories on your system.
Parent topic: About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
About the Oracle Home Directory
When you install any Oracle Fusion Middleware product, you must use an Oracle home directory.
This directory is a repository for common files that are used by multiple Fusion Middleware products installed on the same machine. These files ensure that Fusion Middleware operates correctly on your system. They facilitate checking of cross-product dependencies during installation. For this reason, you can consider the Oracle home directory a central support directory for all Oracle Fusion Middleware products installed on your system.
Fusion Middleware documentation refers to the Oracle home directory as ORACLE_HOME.
Oracle Home Considerations
Keep the following in mind when you create the Oracle home directory and install Fusion Middleware products:
-
Do not include spaces in the name of your Oracle home directory; the installer displays an error message if your Oracle home directory path contains spaces.
-
You can install only one instance of each Oracle Fusion Middleware product in a single Oracle home directory. If you need to maintain separate versions of a product on the same machine, each version must be in its own Oracle home directory.
Although you can have several different products in a single Oracle home, only one version of each product can be in the Oracle home.
Multiple Home Directories
Although in most situations, a single Oracle home directory is sufficient, it is possible to create more than one Oracle home directory. For example, you need to maintain multiple Oracle home directories in the following situations:
-
You prefer to maintain separate development and production environments, with a separate product stack for each. With two directories, you can update your development environment without modifying the production environment until you are ready to do so.
-
You want to maintain two different versions of a Fusion Middleware product at the same time. For example, you want to install a new version of a product while keeping your existing version intact. In this case, you must install each product version in its own Oracle home directory.
-
You need to install multiple products that are not compatible with each other. See Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c (12.2.1.4.0) Interoperability and Compatibility in Understanding Interoperability and Compatibility .
Note:
If you create more than one Oracle home directory, you must provide non-overlapping port ranges during the configuration phase for each product.Parent topic: About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
About the Domain Home Directory
The Domain home is the directory where domains that you configure are created.
The default Domain home location is ORACLE_HOME/user_projects/domains/domain_name. However, Oracle strongly recommends that you do not use this default location. Put your Domain home outside of the Oracle home directory, for example, in /home/oracle/config/domains. The config directory should contain domain and application data. Oracle recommends a separate domain directory so that new installs, patches, and other operations update the ORACLE_HOME only, not the domain configuration.
Note:
Use different domain_names for Oracle Access Management and Oracle Identity Governance.See About the Recommended Directory Structure for more on the recommended directory structure and locating your Domain home.
Fusion Middleware documentation refers to the Domain home directory as DOMAIN_HOME and includes all folders up to and including the domain name. For example, if you name your domain exampledomain and locate your domain data in the /home/oracle/config/domains directory, the documentation would use DOMAIN_HOME to refer to /home/oracle/config/domains/exampledomain.
Parent topic: About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
About the Application Home Directory
The Application home is the directory where applications for domains you configure are created.
The default Application home location is ORACLE_HOME/user_projects/applications/domain_name. However, Oracle strongly recommends that you locate your Application home outside of the Oracle home directory; if you upgrade your product to another major release, you must create a new Oracle home for binaries.
See About the Recommended Directory Structure for more on the recommended directory structure and locating your Application home.
Fusion Middleware documentation refers to the Application home directory as APPLICATION_HOME and includes all folders up to and including the domain name. For example, if you name your domain exampledomain and you locate your application data in the /home/oracle/config/applications directory, the documentation uses APPLICATION_HOME to refer to /home/oracle/config/applications/exampledomain.
Parent topic: About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
Preparing for Shared Storage
Oracle Fusion Middleware allows you to configure multiple WebLogic Server domains from a single Oracle home. This allows you to install the Oracle home in a single location on a shared volume and reuse the Oracle home for multiple host installations.
If you plan to use shared storage in your environment, see Using Shared Storage in High Availability Guide for more information.
Parent topic: About the Directories for Installation and Configuration
About JDK Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation
Most Fusion Middleware products are in .jar file format. These distributions do not include a JDK. To run a .jar distribution installer, you must have a certified JDK installed on your system.
Make sure that the JDK is installed outside of the Oracle home. If you install the JDK under the Oracle home, you may encounter problems when you try to perform tasks in the future. Oracle Universal Installer validates that the Oracle home directory is empty; the install does not progress until you specify an empty directory. Oracle recommends that you locate your JDK installation in the /home/oracle/products/jdk directory.
Platform-specific distributions have a .bin (for UNIX operating systems) or .exe (for Windows operating systems) installer; in these cases, a platform-specific JDK is in the distribution and you do not need to install a JDK separately. However, you may need to upgrade this JDK to a more recent version, depending on the JDK versions that are certified.
Always verify the required JDK version by reviewing the certification information on the Oracle Fusion Middleware Supported System Configurations page. For 12c (12.2.1.4.0), the certified JDK is 1.8.0_211 and later.
To download the required JDK, navigate to the following URL and download the Java SE JDK:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
Parent topic: Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
About Database Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation
Many Oracle Fusion Middleware products require database schemas prior to configuration. If you do not already have a database where you can install these schemas, you must install and configure a certified database.
Note:
Multi-tenancy feature is supported, that is, Pluggable Database (PDB) and Container Database (CDB) are supported.To find a certified database for your operating system, see the certification document for your release on the Oracle Fusion Middleware Supported System Configurations page on Technical Resources from Oracle.
To make sure that your database is properly configured for schema creation, see Repository Creation Utility Requirements in the Oracle Fusion Middleware System Requirements and Specifications document.
- For OIG you need to run a few prerequisite
sqlfiles prior to creating Oracle Identity Management schemas. See Oracle Database requirements when using Oracle Identity Governance in the System Requirements and Specifications document. - Based on your deployment topology and the work load, it is recommended that you refer to the following note on My Oracle Support, and take appropriate actions for your deployment. See Performance Tuning Guidelines and Diagnostics Collection for Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) (Doc ID 1539554.1)
After your database is properly configured, you use the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) to create product schemas in your database. This tool is available in the Oracle home for your Oracle Fusion Middleware product. See About the Repository Creation Utility in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
Parent topic: Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment
Obtaining the Product Distribution
You can obtain the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure and Oracle Identity and Access Management distribution on Technical Resources from Oracle.
To prepare to install Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure and Oracle Identity and Access Management:
-
Enter
java -versionon the command line to verify that a certified JDK is installed on your system. For 12c (12.2.1.4.0), the certified JDK is 1.8.0_211 and later.See About JDK Requirements for an Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation.
-
Locate and download the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure and Oracle Identity and Access Management software. To configure Oracle Identity Governance in traditional mode, you must download Oracle SOA Suite 12.2.1.4.0.
See Obtaining Product Distributions in Planning an Installation of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
- For Oracle Access Management, go to Chapter 3: Installing and Configuring the Oracle Access Management Software.
- For Oracle Identity Governance, go to Chapter 4: Installing and Configuring the Oracle Identity Management Software.
List of Supported Languages
Oracle Identity and Access Manager supports the following languages:
Brazilian Portuguese, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Simplified Chinese, Spanish, Traditional Chinese, Arabic, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, Greek, Hebrew, Hungarian, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Slovak, Swedish, Thai, and Turkish.
Note:
The following special characters are not allowed in the user login name:
[!@#$%^&*()_-+=[{]}\|;:'",<.>?/~