2 Understanding Object-Relational and MOXy Internals
These are the primary features of the Object-Relational and MOXy architecture.
About Metadata
The EclipseLink metadata is the bridge between the development of an application and its deployed run-time environment.
The EclipseLink metadata is the bridge between the development of an application and its deployed run-time environment. Capture the metadata using the following:
-
Annotations, and elements property extensions in the persistence.xml file. The persistence provider interprets all these sources of metadata to create an in-memory session and project at run time.
-
Java and the EclipseLink API (this approach is the most labor-intensive).
The metadata lets you pass configuration information into the run-time environment. The run-time environment uses the information in conjunction with the persistent classes (Java objects or entities) and the code written with the EclipseLink API, to complete the application.
Advantages of the Metadata Architecture
The EclipseLink metadata architecture provides many important benefits.
The EclipseLink metadata architecture provides many important benefits, including the following:
-
Stores mapping information in XML—not in the domain model objects
-
By using the metadata, EclipseLink does not intrude in the object model or the database schema
-
Allows you to design the object model as needed, without forcing any specific design
-
Allows DBAs to design the database as needed, without forcing any specific design
-
Does not rely on code-generation (which can cause serious design, implementation, and maintenance issues)
-
Is unobtrusive: adapts to the object model and database schema, rather than requiring you to design their object model or database schema to suit EclipseLink
Using EclipseLink JPA, you have the flexibility of expressing persistence metadata using standard JPA annotations, deployment XML, or both and you can optionally take advantage of EclipseLink JPA annotation and persistence.xml property extensions.
Creating Project Metadata
A project contains the mapping metadata that the EclipseLink runtime uses to map objects to a data source.
A project contains the mapping metadata that the EclipseLink runtime uses to map objects to a data source. The project is the primary object used by the EclipseLink runtime.
The principal contents of project metadata include the following:
-
Entity Mappings
-
Data Source Login Information
For Object-relational mapping, the EclipseLink runtime constructs an in-memory project based on any combination of JPA annotations, persistence.xml, and EclipseLink JPA annotations and persistence.xml property extensions.
For MOXy mapping, the EclipseLink runtime uses a combination of JAXB annotations and eclipselink-oxm bindings. See "Overriding and Merging" in Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink.
Entity Mappings
EclipseLink maps persistent entities to the database in the application. There are several approaches to project development, including the following:
-
Importing classes and tables for mapping
-
Importing classes and generating tables and mappings
-
Importing tables and generating classes and mappings
-
Creating both class and table definitions
The most common solution is to develop the persistent entities using a development tool, such as a modeling tool or an integrated development environment (IDE) like JDeveloper, and to develop the relational model through appropriate relational design tools. You then use JDeveloper to construct mappings that relate these two models.
Although JDeveloper offers the ability to generate persistent entities or the relational model components for an application, these utilities are intended only to assist in rapid initial development strategies—not complete round-trip application development.
For more information, see Understanding Descriptors and Understanding Mappings.
Data Source Login Information
For POJO projects, you configure a session login in the session metadata that specifies the information required to access the data source.
For more information, see Creating Session Metadata.
Creating Session Metadata
An EclipseLink session contains the information required to access the data source. The session is the primary object used by your application to access the features of the EclipseLink runtime.
Using EclipseLink JPA, the EclipseLink runtime constructs an in-memory session based on any combination of JPA and EclipseLink annotations, JPA persistence properties (in the persistence.xml file), and EclipseLink property extensions. See "Overriding and Merging" in Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink.
About the Object-Relational Solution
EclipseLink provides a complete, JPA-compliant JPA implementation.
For more information, see Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink.
Understanding Object-Relational Entity Architecture
The entity architecture is composed of entities, persistence units, persistence contexts, entity manager factories, and entity managers.
The following figure illustrates the relationships between these elements:
-
Persistence creates one or more EntityManagerFactory objects.
-
Each EntityManagerFactory is configured by one persistence unit.
-
EntityManagerFactory creates one or more EntityManager objects.
-
One or more EntityManagers manage one PersistenceContext.
Figure 2-2 Relationships Between Entity Architecture Elements
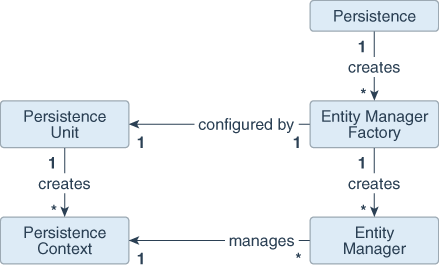
Description of "Figure 2-2 Relationships Between Entity Architecture Elements"
Entities
An entity is any application-defined object with the following characteristics:
-
It can be made persistent.
-
It has a persistent identity (a key that uniquely identifies an entity instance and distinguishes it from other instances of the same entity type. An entity has a persistent identity when there is a representation of it in a data store).
-
It is transactional in a sense that a persistence view of an entity is transactional (an entity is created, updated, and deleted within a transaction, and a transaction is required for the changes to be committed in the database). However, in-memory entities can be changed without the changes being persisted.
-
It is not a primitive, a primitive wrapper, or built-in object. An entity is a fine-grained object that has a set of aggregated states that is typically stored in a single place (such as a row in a table) and have relationships to other entities.
The entity also contains entity metadata that describes the entity. Entity metadata is not persisted to the database. It is used by the persistence layer to manage the entity from when it is loaded until it is invoked at runtime. Metadata can be expressed as annotations on the Java programming elements or in XML files (descriptors). For more information, see Understanding Entities.
Beginning with the current release, you can define and use extensible entities where mappings can be added spontaneously. In this case, the entity stores extended attributes within a map instead of static attributes. The entity then defines how values from this map are mapped to the database using an eclipselink-orm.xml mapping file. In addition to being able to dynamically define mappings, EclipseLink also enables these extended mappings to be stored and managed externally. This external storage enables your extended mappings to be defined while the application is running. For more information on making entities extensible, see "Providing Software as a Service" in Solutions Guide for EclipseLink.
Persistence and Persistence Units
Persistence is a characteristic of an entity. This means that the entity can be represented in a data store, and it can be accessed at a later time.
A persistence unit identifies a persistable unit and defines the properties associated with it. It also defines the objects that must be persisted. The objects can be entity classes, embeddable classes, or mapped superclasses. The persistence unit provides the configuration for the entity manager factory. Entity managers created by the entity manager factory inherit the properties defined in the persistence unit.
Entity Managers
An entity manager enables API calls to perform operations on an entity. Until an entity manager is used to create, read, or write an entity, the entity is a nonpersistent Java object. When an entity manager obtains a reference to an entity, that entity becomes managed by the entity manager. The set of managed entity instances within an entity manager at any given time is called its persistence context; only one Java instance with the same persistent identity can exist in a persistence context at any time.
You can configure an entity manager to read or write to a particular database, to persist or manage certain types of objects, and to be implemented by a specific persistence provider. The persistence provider supplies the implementation for JPA, including the EntityManager interface implementation, the Query implementation, and the SQL generation.Entity managers are provided by an EntityManagerFactory. The configuration for an entity manager is bound to the EntityManagerFactory, but it is defined separately as a persistence unit. You name persistence units to enable differentiation between EntityManagerFactory objects. This way, your application obtains control over which configuration to use for operations on a specific entity. The configuration that describes the persistence unit is defined in a persistence.xml file. You name persistence units to be able to request a specific configuration to be bound to an EntityManagerFactory.
Adding Metadata Using Annotations
An annotation is a simple, expressive means of decorating Java source code with metadata that is compiled into the corresponding Java class files for interpretation at run time by a JPA persistence provider to manage persistent behavior.
A metadata annotation represents a Java language feature that lets you attach structured and typed metadata to the source code. Annotations alone are sufficient for the metadata specification—you do not need to use XML. Standard JPA annotations are in the javax.persistence package.
For more information, see Chapter 10 "Metadata Annotations" in the JPA Specification http://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=338
EclipseLink provides a set of proprietary annotations as an easy way to add metadata to the Java source code. The metadata is compiled into the corresponding Java class files for interpretation at run time by a JPA persistence provider to manage persistent behavior. You can apply annotations at the class, method, and field levels.
EclipseLink annotations expose some features that are currently not available through the use of JPA metadata:
-
Basic properties—By default, the EclipseLink persistence provider automatically configures a basic mapping for simple types. Use these annotations to fine-tune the immediate state of an entity in its fields or properties.
-
Relationships—EclipseLink has defaults for some relationships, such as One-To-One and One-To-Many. Other relationships must be mapped explicitly. Use the annotations to specify the type and characteristics of entity relationships and to fine-tune how your database implements these relationships.
-
Embedded objects—An embedded object does not have its own persistent identity; it is dependent upon an entity for its identity. By default, the persistence provider assumes that every entity is mapped to its own table. Use annotations to override this behavior for entities that are owned by other entities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Annotations
Using annotations provides several advantages:
-
They are relatively simple to use and understand.
-
They provide in-line metadata within with the code that it describes; you do not need to replicate the source code context of where the metadata applies.
The primary disadvantage of annotations is that the metatdata becomes unnecessarily coupled to the code; changes to metadata require changing and recompiling the source code.
About Configuration Basics
TopLink includes several configuration files in an Object Relational Mapping project.
The following sections describe some of the key configuration files in an Object Relational Mapping project.
Default Annotation Values
Each annotation has a default value (consult the JPA specification for defaults). A persistence engine defines defaults that apply to the majority of applications. You only need to supply values when you want to override the default value. Therefore, having to supply a configuration value is not a requirement, but the exception to the rule. This is known as configuration by exception.
Note:
You should be familiar with the defaults to be able to change the behavior when necessary.
The default values are described in Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink. See also Chapter 10, "Metadata Annotations" in the JPA specification.
http://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=338
The configuration is done by exception: if a value is not specified in one of the configuration files, then a default value is used.
Configuring Persistence Units Using persistence.xml
A persistence unit defines the details that are required when you acquire an entity manager. You specify a persistence unit by name when you acquire an entity manager factory. Use the JPA persistence file, persistence.xml, to configure a persistence unit. You can specify any vendor-specific extensions in the file by using a <properties> element.
This file appears in the META-INF/ directory of your persistence unit JAR file or in the classpath.
For more information, see About the Persistence Unit. See also "Persistence Property Extensions Reference" in Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink.
Object-Relational Data Type Mappings
Object-relational data type mappings transform certain object data member types to structured data source representations optimized for storage in specialized object-relational databases such as Oracle Database. Object-relational data type mappings let you map an object model into an object-relational model. You can use only object-relational data type mappings with specialized object-relational databases optimized to support object-relational data type data source representations.
For more information, see Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink.
About Data Sources
An important part of the definition of the persistence unit is the location where the provider can find data to read and write: the data source.
The data source is typically a database. The database location is specified in the form of a JDBC data source in the JNDI namespace of the server.
Typically, applications that use EclipseLink are run in the context of a JTA transaction. Specify the name of the data source in the jta-data-source element in the persistence.xml file. If the application is not run in the context of a transaction, then it is considered to be resource-local. In this case, specify the name of the data source in the non-jta-data-source element.
You can also specify a non-relational database data source, such as an XML schema.
For more information, see Understanding Data Access.
Applications can be run in standalone, or Java SE, mode. In this mode, the application runs outside the server, with a non-JTA compliant data source, and in a non-Oracle stack. In this case, you must provide driver-specific information, such as the JDBC driver class, the URL that the client uses to connect to the database, and the user name and password to access the database. For more information and an example of running an application in standalone mode, see "Testing EclipseLink JPA Outside a Container" in Solutions Guide for EclipseLink.
About EclipseLink Caches
By default, EclipseLink uses a shared object cache that caches a subset of all objects read and persisted for the persistence unit.
The shared cache differs from the local EntityManager cache. The shared cache exists for the duration of the persistence unit (EntityManagerFactory or server) and is shared by all EntityManagers and users of the persistence unit. The local EntityManager cache is not shared and only exists for the duration of the EntityManager or transaction.
The benefit of the shared cache is that after an object is read, the database does not need to be accessed if the object is read again. Also, if the object is read by using a query, it does not need to be rebuilt, and its relationships do not need to be fetched again.
The limitation of the shared cache is that if the database is changed directly through JDBC, or by another application or server, the objects in the shared cache will be stale.
EclipseLink offers several mechanism to deal with stale data including:
-
Refreshing
-
Invalidation
-
Optimistic locking
-
Cache coordination
-
Database Change Notification (DCN)
The shared cache can also be disabled, or it can be selectively enabled and disabled by using the @Cache or @Cacheable annotations. EclipseLink also offers several different caching strategies, to configure how many objects are cached and how much memory is used.
If the application detects that the cache is out of date, it can clear, refresh, or invalidate it programmatically. Clearing the cache can cause object identity issues if any of the cached objects are in use, so invalidating is safer. If you know that none of the cached objects are in use, then you can clear the cache.
For more information, see Understanding Caching.
Defining Cache Behavior
EclipseLink provides an @Cache annotation which lets you define cache properties. The properties include cache type, size, and refresh rules, among others. See Java Persistence API (JPA) Extensions Reference for EclipseLink.Caching in Clustered Environments
Caching in a clustered environment can have problems because changes made on one server are not reflected on objects cached in other servers. This is not a problem for read-only objects, but it is for objects that are frequently updated.
EclipseLink offers several solutions to this problem.
-
The cache can be disabled for the classes that frequently change.
-
Cache coordination can be used to broadcast changes between the servers in the cluster to update or invalidate changed objects.
-
Cache invalidation based on time-to-live or time-of-day.
-
Optimistic locking prevents updates to stale objects and triggers the objects to be invalidated in the cache.
For more information, see Clustering and Cache Coordination.
About Database Queries
The object-relational component of EclipseLink supports a variety of queries.
-
JPQL queries
-
SQL queries
-
Criteria API queries
-
Native SQL queries
-
EclipseLink JPA query hints
-
Query casting
-
Oracle Extensions for queries
-
Advanced EclipseLink native queries
For information on these queries, see Chapter 9, "Understanding Queries."
About the MOXy Solution
The MOXy component, supplied by EclipseLink, enables you to efficiently bind Java classes to XML schemas. MOXy implements JAXB, enabling you to provide your mapping information through annotations and providing support for storing the mappings in XML format.
JAXB (Java Architecture for XML Binding—JSR 222) is the standard for XML Binding in Java. JAXB covers 100 percent of XML Schema concepts. EclipseLink provides a JAXB implementation with many extensions.
When using EclipseLink MOXy as the JAXB provider, no metadata is required to convert your existing object model to XML. You can supply metadata (using annotations or XML) if you want to fine-tune the XML representation.
MOXy includes many advanced mappings that let you handle complex XML structures without having to mirror the schema in your Java class model.
For more information, see Developing JAXB Applications EclipseLink MOXy.
Using EclipseLink MOXy as the JAXB Provider
To use MOXy as your JAXB provider, you must identify the entry point to the JAXB runtime. This entry point is the EclipseLink JAXBContextFactory class.
To identify the entry point, create a text file called jaxb.properties and enter the path to the JAXBContextFactory class as the value of the javax.xml.bind.context.factory context parameter, for example:
javax.xml.bind.context.factory=org.eclipse.persistence.jaxb.JAXBContextFactoryThe jaxb.properties file must appear in the same package as the domain classes.
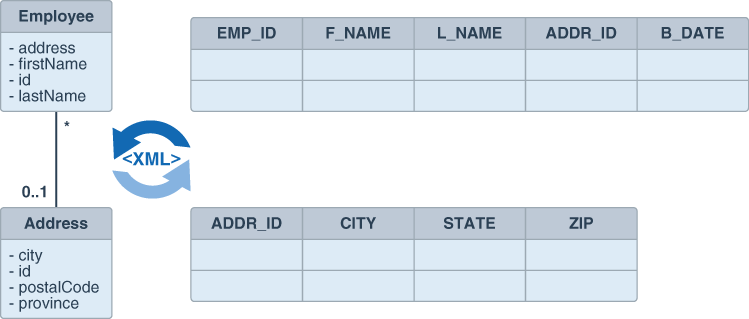
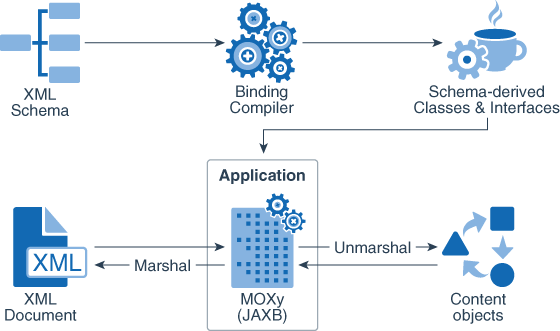
Understanding MOXy Architecture
In a sample MOXy architecture, the starting point is an XML schema.
As illustrated in this figure, a binding compiler binds the source schema to a set of schema-derived program classes and interfaces. JAXB-annotated classes within the application are generated either by a schema compiler or the result of a developer adding JAXB annotations to existing Java classes. The application can either marshal data to an XML document or unmarshal the data to a tree of content objects. Each content object is an instance of either a schema derived or an existing program element mapped by the schema generator and corresponds to an instance in the XML.
JAXB Contexts and JAXB Context Factories
The JAXBContextFactory class is the entry point into the EclipseLink JAXB runtime. It provides the required factory methods and can create new instances of JAXBContext objects.
The JAXBContextFactory class has the ability to:
-
Create a JAXBContext object from an array of classes and a properties object
-
Create a JAXBContext object from a context path and a classloader
The JAXBContext class provides the client's entry point to the JAXB API. The JAXBContext class is responsible for interpreting the metadata, generating schema files, and for creating instances of these JAXB objects: Marshaller, Unmarshaller, Binder, Introspector, and Validator.
MOXy offers several options when creating the JAXBContext object. You have the option of booting from:
-
A list of one or more JAXB-annotated classes
-
A list of one or more EclipseLink XML Bindings documents defining the mappings for your Java classes
-
A combination of classes and XML Bindings
-
A list of context paths
Serving Metadata for MOXy
MOXy provides the concept of a MetadataSource object.
This object lets you to store mapping information outside of your application and retrieve it when the application's JAXBContext object is being created or refreshed. For information on implementing MetadataSource, see Developing JAXB Applications EclipseLink MOXy.
About XML Bindings
XML binding is how you represent information in an XML document as an object in computer memory.
This allows applications to access the data in the XML from the object rather than using the Domain Object Model (DOM), the Simple API for XML (SAX) or the Streaming API for XML (StAX) to retrieve the data from a direct representation of the XML itself. When binding, JAXB applies a tree structure to the graph of JPA entities. Multiple tree representations of a graph are possible and will depend on the root object chosen and the direction the relationships are traversed.
EclipseLink enables you to use all of the standard JAXB annotations. In addition to the standard annotations, EclipseLink offers another way of expressing your metadata—the EclipseLink XML Bindings document. Not only can XML Bindings separate your mapping information from your actual Java class, it can also be used for more advanced metadata tasks such as:
-
Augmenting or overriding existing annotations with additional mapping information.
-
Specifying all mappings information externally, without using Java annotations.
-
Defining your mappings across multiple Bindings documents.
-
Specifying virtual mappings that do not correspond to concrete Java fields.
For more information, see Developing JAXB Applications EclipseLink MOXy.
Querying Objects by XPath
EclipseLink MOXy also lets you access values using an XPath statement.
In addition to using conventional Java access methods to get and set your object's values, . There are special APIs on EclipseLink's JAXBContext object that enable you to get and set values by XPath. For more information, see Developing JAXB Applications EclipseLink MOXy.