8.7 Realtime Parquet Ingestion into Azure Data Lake Storage with Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics 23.8 and later
Overview
This Quickstart covers a step-by-step process showing how to ingest parquet files into Azure Storage containers in real-time with Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics (GG for DAA).
Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) is a centralized repository provided by Azure where you can store all your data, both structured and unstructured.
GG for DAA ADLS handler works in conjunction with File Writer Handler and Parquet Handler (if parquet is required). File Writer Handler produces files locally. Optionally, Parquet Handler converts to parquet format and ADLS Handler loads into Azure Storage containers.
GG for DAA provides different alternatives for ADLS connection. This Quickstart uses BLOB endpoint for connection.
.
- Prerequisites
- Install Required Dependency Files
- Create a Replicat in Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics
Parent topic: Quickstarts
8.7.1 Prerequisites
To successfully complete this Quicktart, you must have the following:
- Azure Storage Account and a Container
- Azure Storage Account login credentials
In this Quickstart, a sample trail file, such as tr, which is shipped
with GG for DAA is used. If you want to continue with sample trail file, then it is
located at GG_HOME/opt/AdapterExamples/trail in your GG for DAA
instance.
8.7.2 Install Required Dependency Files
- GG for DAA uses a 3-step process to ingest parquet into Azure Storage containers:
- Generating local files from trail files
- Converting local files to Parquet format
- Loading files into Azure Storage containers
- In your GG for DAA VM, go to dependency downloader utility. It is located at
GG_HOME/opt/DependencyDownloader/. - Run
parquet.shandhadoop.shwithazure_blob_storage.shwith the required versions.Figure 8-43 Install Required Dependency Files
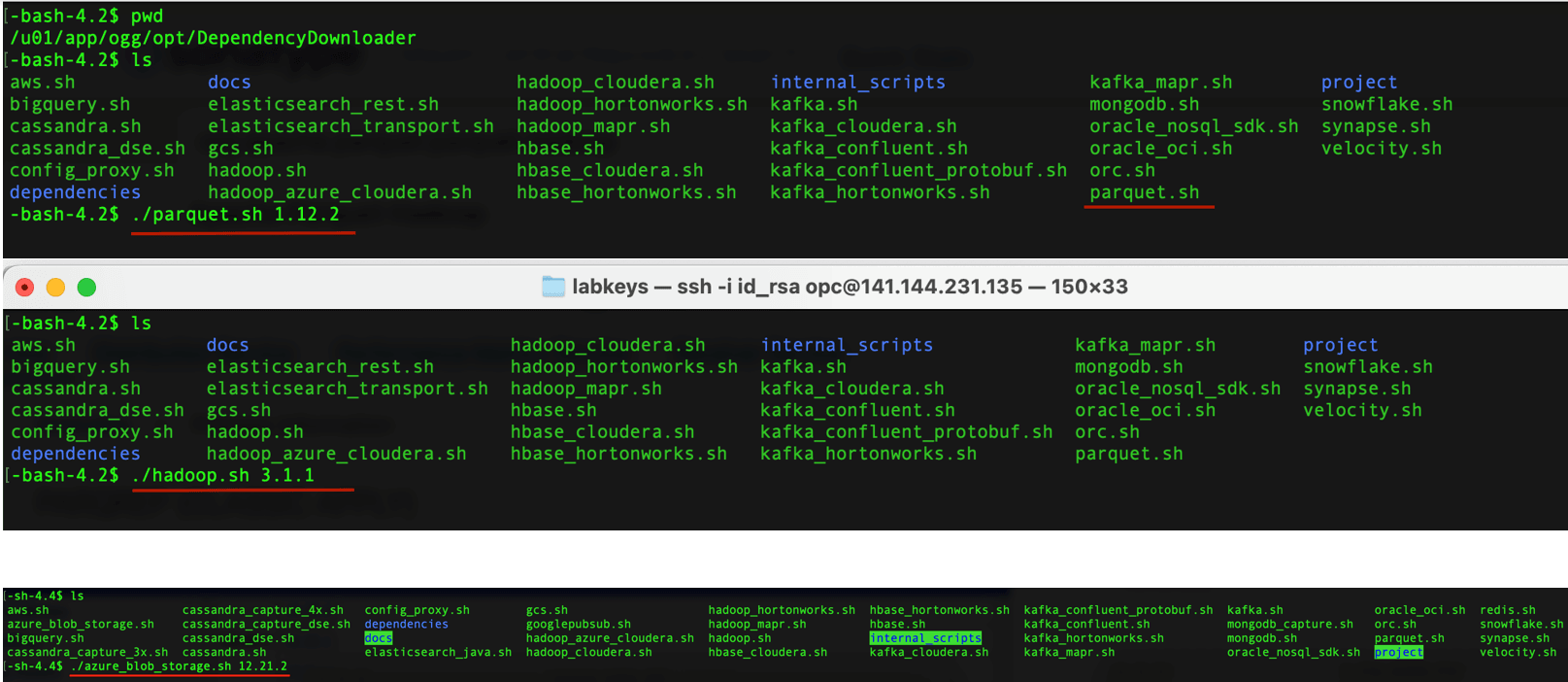
- 3 directories are created in
GG_HOME/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies. Make a note of these directories.For example:/u01/app/ogg/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies/azure_blob_storage_12.21.2 /u01/app/ogg/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies/hadoop_3.3.0 /u01/app/ogg/opt/DependencyDownloader/dependencies/parquet_1.12.3
8.7.3 Create a Replicat in Oracle GoldenGate for Distributed Applications and Analytics
- Go to Administration Service and click + sign to add a replicat.
Figure 8-44 Administration Service
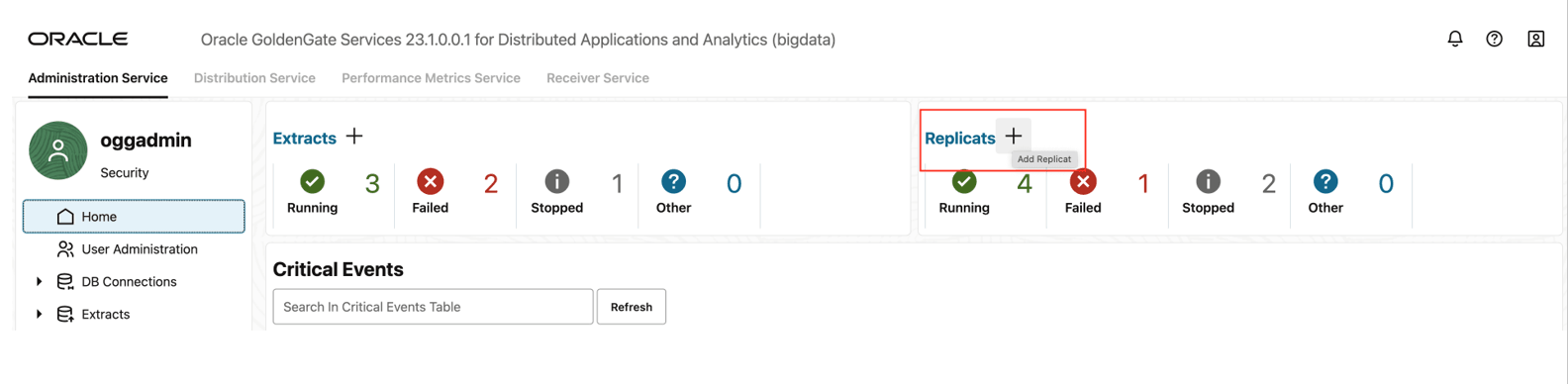
- Select the Replicat Type, provide Process Name and click Next.
There are two different Replicat types available: Classic and Coordinated. Classic Replicat is a single threaded process whereas Coordinated Replicat is a multithreaded one that applies transactions in parallel.
Figure 8-45 Add Replicat
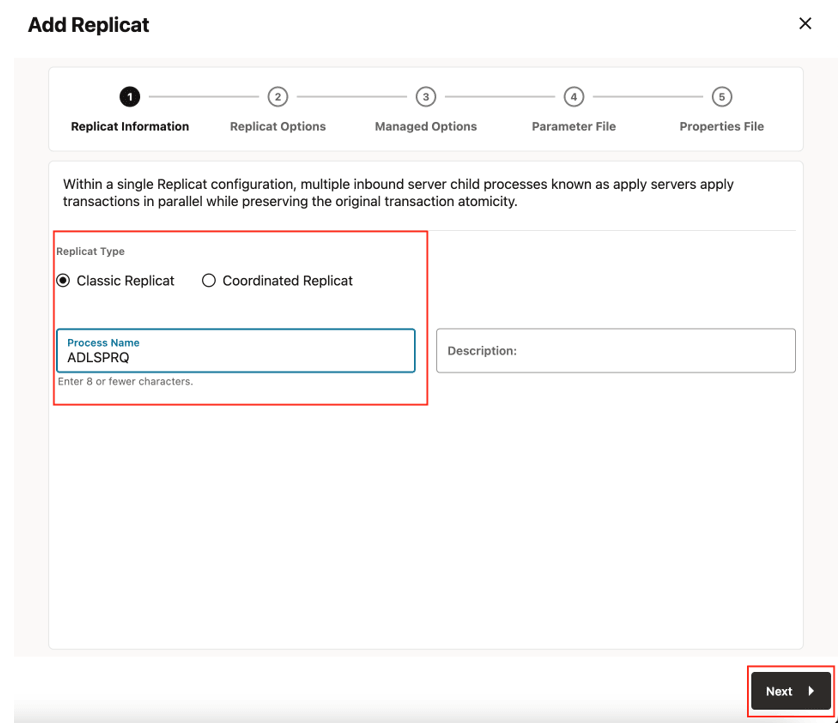
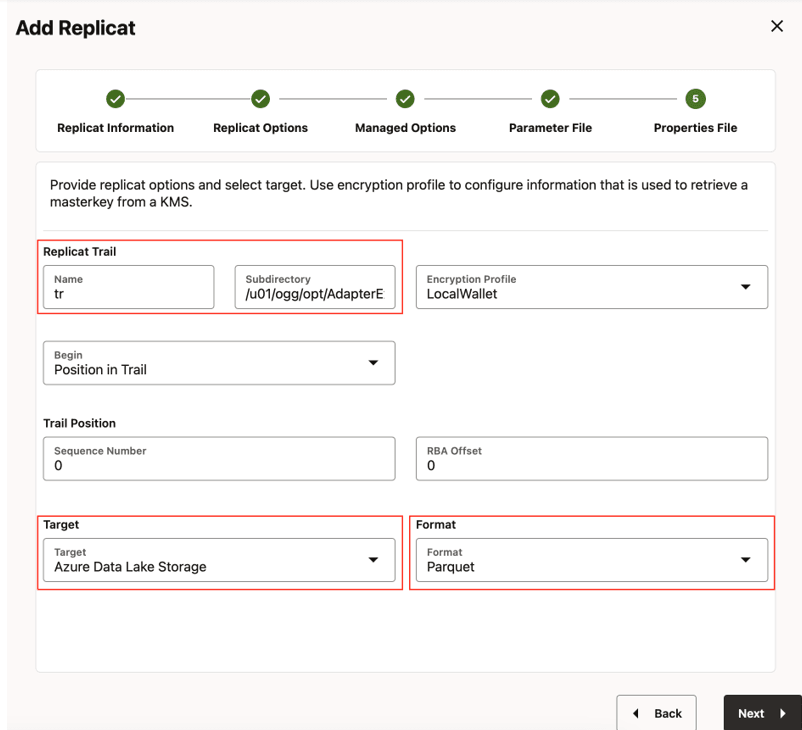
- Enter Replicat Options and click Next.
- Replicat Trail: Name of the required trail file. For sample trail,
provide
tr. - Subdirectory: Provide as
GG_HOME/opt/AdapterExamples/trail/if using the sample trail. - Target: Azure Data Lake Storage
- Format: Select the format
Figure 8-46 Replicat Options
- Replicat Trail: Name of the required trail file. For sample trail,
provide
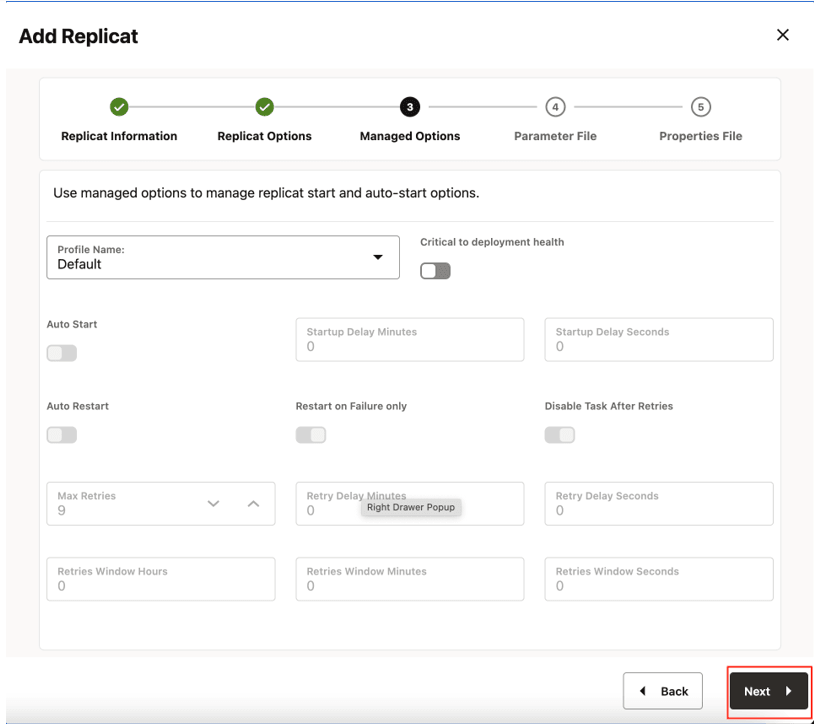
- Leave Managed Options as is and click Next.
Figure 8-47 Managed Options
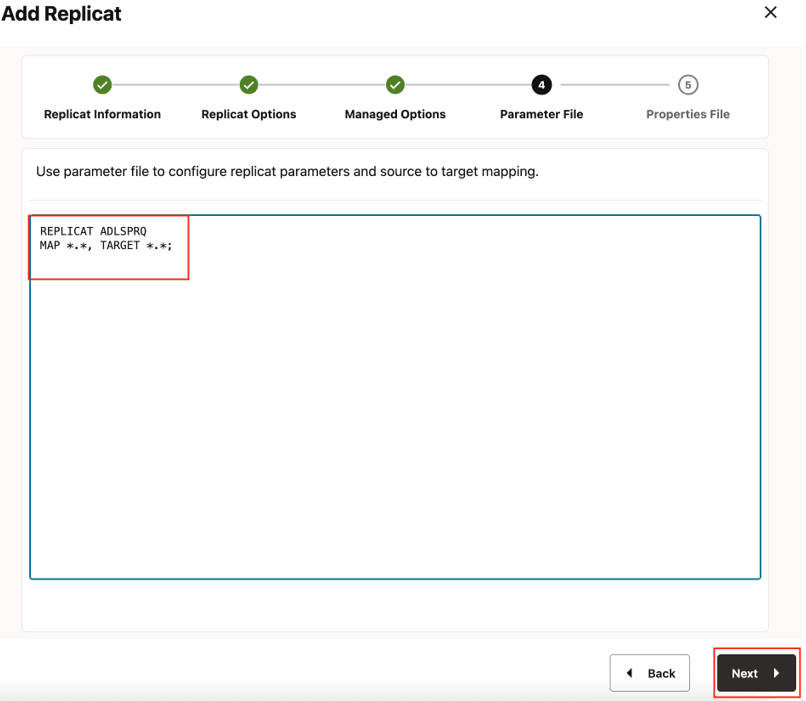
- Provide Parameter File details and click Next.
In the Parameter File, you can either specify source to target mapping or leave it as-is with a wildcard selection. If Coordinated Replicat is selected as the Replicat Type, an additional parameter needs to be provided:
TARGETDB LIBFILE libggjava.so SET property=<ggbd-deployment_home>/etc/conf/ogg/your_replicat_name.properties.Figure 8-48 Parameter File
- In the properties file, update the properties marked as #TODO and click Create
and
Run.
# Properties file for Replicat # Configuration to load GoldenGate trail operation records # into Azure Data Lake Storage by chaining # File writer handler -> Azure Blob Event handler. # Note: Recommended to only edit the configuration marked as TODO gg.target=abs #TODO: format can be 'parquet' or 'orc' or one of the pluggable formatter types. Default is 'parquet'. gg.format=parquet #TODO: Edit the Azure Blob Storage container name gg.eventhandler.abs.bucketMappingTemplate=<abs-container-name> #TODO: Edit the Azure storage account name. gg.eventhandler.abs.accountName=<storage-account-name> #TODO: Edit the Azure storage account key. #gg.eventhandler.abs.accountKey=<storage-account-key> #TODO: Edit the Azure shared access signature(SAS) to authenticate to an Azure Service. #gg.eventhandler.abs.sasToken=<sas-token> #TODO: Edit the the tenant ID of the application. gg.eventhandler.abs.tenantId=<azure-tenant-id> #TODO: Edit the the client ID of the application. gg.eventhandler.abs.clientId=<azure-client-id> #TODO: Edit the the client secret for the authentication. gg.eventhandler.abs.clientSecret=<azure-client-secret> gg.classpath=/path/to/abs-deps/*:/path/to/hadoop-deps/:/path/to/parquet_deps/* #TODO: Edit the proxy configuration. #jvm.bootoptions=-Dhttps.proxyHost=some-proxy-address.com -Dhttps.proxyPort=80 -Djava.net.useSystemProxies=true
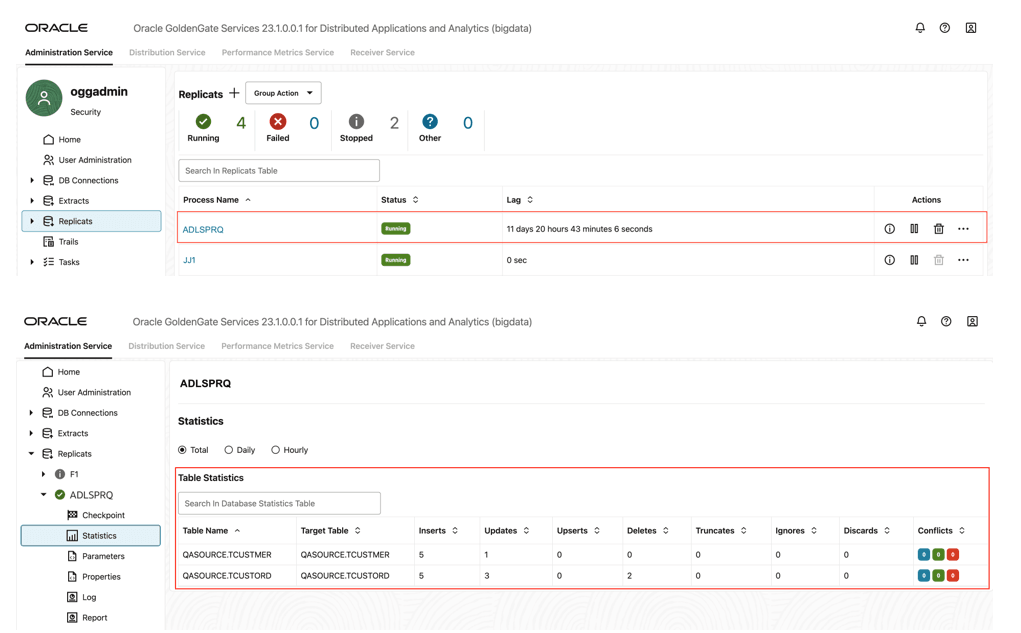
- If replicat starts successfully, it will be in running state. You can go to
replicat/statistics to see the replication statistics.
Figure 8-49 Replication Statistics
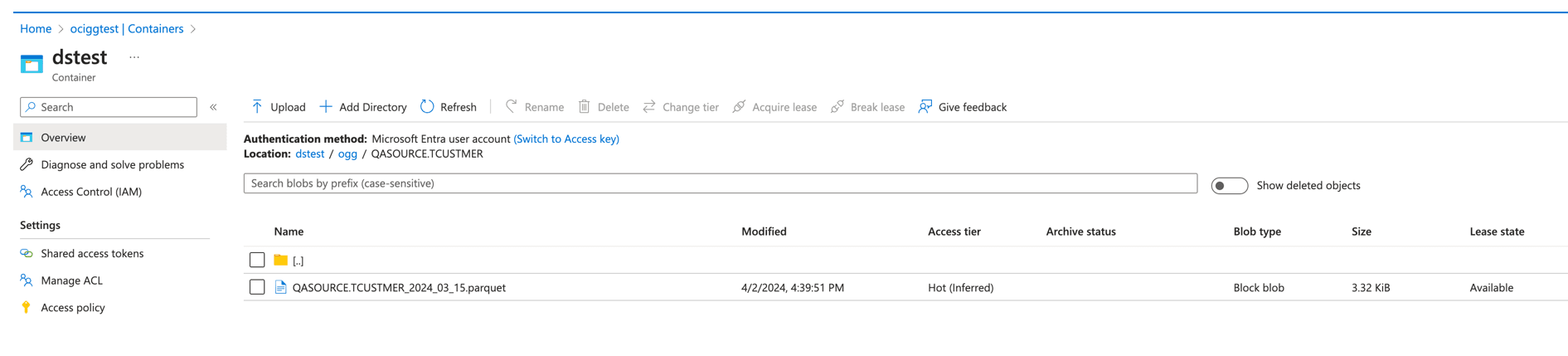
- You can go to Azure Storage console and check the container.
Figure 8-50 Azure Storage console
Note:
- If target Azure container does not exist, then it will be auto crated by GG for DAA. You can use Template Keywords to dynamically assign the container names.
- ABS Event Handler can be configured for proxy server. For more information, see Replicate Data.
- You can use different properties to control the behaviour of file writing. You can set file sizes, inactivity periods and more. For more information, see the File Writer blog post.