Using Oracle Key Vault Trail File Encryption in Oracle GoldenGate
Learn about the benefits of using Oracle Key Vault (OKV) with Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Architecture. Determine the system requirements, processes and parameters available with Oracle GoldenGate for configuring OKV with Oracle GoldenGate.
The following diagram explains the Oracle Key Vault set up and workflow in the Oracle
GoldenGate environment.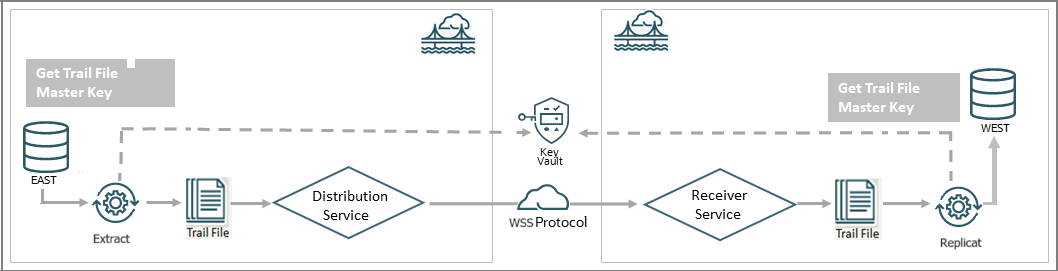
As shown in the diagram, you can select the Key Vault (OKV) as the Key
Management System while configuring the encryption profile for the deployment in Oracle
GoldenGate. This encryption profile is used by the Extract, Replicat processes to store
and apply the master keys before transferring trail files using the distribution path
and receiving the files on the other end with the RECVPATH process. The Web Secure
Socket (wss) protocol is used to validate the connection between the
DISTPATH and RECVPATH to eatablish a secure communication channel.
Oracle Key Vault Capabilities
Oracle GoldenGate 23ai and higher releases support Oracle Key Vault 21.8 for trail file encryption. The following table provides the behavior and capabilities of Oracle Key Vault (OKV).
For more information about configuring OKV, see Installing and Configuring Oracle Key Vault .
| KMS Name | KMS Type | Support Tags | Support Importing of Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Oracle Key Vault |
Keyname and custom attributes for versioning |
Yes |
Yes |
Prerequisites for Configuring GoldenGate Encryption Profile Using Oracle Key Vault
Learn the prerequisites for setting up OKV with Oracle GoldenGate.
In this section, the steps to generate the master key have been performed using the command line. Alternatively, you can use the OKV web interface to create the master key for Oracle GoldenGate. If you want to generate the master key from the OKV web interface, follow the steps provided in Create GoldenGate Master Key in the Oracle Key Vault Administrator's Guide.
The following steps are performed on the OKV configuration on the machine where the Oracle GoldenGate instance is running:
-
Download the
okvrestclipackage.zipfrom the OKV server, where Oracle GoldenGate is deployed as the same system user as the deployment. -
Enable the RESTFUL Services using the steps provided in Enabling RESTful Services in Oracle Key Vault Administrator's Guide.
-
Set the
OKV_HOMEenvironment variable.OS> setenv OKV_HOME /u01/app/oracle/OKVThe sub-directory structure contains the necessary libraries, binaries, and configuration files for the OKV environment. See Oracle Key Vault Installation and Configuration in the Oracle Key Vault Installation and Upgrade Guide for details about the configuration within the OKV server.
-
Download and install the endpoint file,
okvclient.jarfrom the OKV server, where Oracle GoldenGate is deployed as the same system user as the deployment. For example,OS> java -jar okvclient.jar -d /u01/app/oracle/OKV - Create the key. The name of the wallet is provided by the OKV
administrator. The following example show how the key is
created:
OS> okv managed-object key create [--activation-date activation date] [--algorithm algorithm] [--custom-attribute custom attribute] [--deactivation-date deactivation date] [-- extractable extractable] [--length length] [--mask mask] [--name name] [--wallet wallet] ex - okv managed-object key create --algorithm AES --length 256 --mask "ENCRYPT,DECRYPT,TRANSLATE_ENCRYPT,TRANSLATE_DECRYPT,TRANSLATE_WRAP,TRANSLATE_UNWRAP" --wallet wallet1Alternatively, you can register your own key, as shown in the following example:OKV> okv managed-object key register [--activation-date activation date] [--algorithm algorithm] [--custom-attribute custom attribute] [--deactivation-date deactivation date] [--extractable extractable] [--length length] [--mask mask] [--name name] --object object [--wallet wallet] ex - bin/okv managed-object key register --length 256 --activation-date "NOW" --object symkey.txt --algorithm AES --mask "ENCRYPT,DECRYPT,TRANSLATE_ENCRYPT,TRANSLATE_DECRYPT,TRANSLATE_WRAP,TRANSLATE_UNWRAP" --wallet wallet1 -
Activate the key as shown in the following example:
OS> okv managed-object object activate --uuid UUID -
Add the Oracle GoldenGate related key attributes (KeyName, KeyVersion) to the configuration. The key name must match the master keyname in the KMS encryption profile created within Oracle GoldenGate. The key value must match the version number of the masterkey.
OS> okv managed-object custom-attribute add --custom-attribute custom attribute --uuid uuid ex - okv managed-object custom-attribute add --custom-attribute '[ { "name": "x-OGG-KeyName", "value" : "OGG_Masterkey", "type" : "text" },{ "name": "x-OGG-KeyVersion", "value" : "1", "type" : "text"} ] ' -
Use
okvutilto list the configuration setting and check the endpoint status. As shown in the following example:OS>okvutil list -v 4The output of this command shows the configuration settings and endpoint status:okvutil version 21.12.0.0.0 Endpoint type: Oracle Database Configuration file: u01/app/oracle/OKV/conf/okvclient.ora Server: 100.70.1.1:5696 Standby Servers: Auto-login wallet found, no password needed Trying to connect to 100.70.1.1:5696 ... Connected to 100.70.1.1:5696. Unique ID Type Identifier 8BC11E57-5269-403D-9B69-A66641ADAFC7 Symmetric Key -
The next steps are managed within Oracle GoldenGate and are shown as an implementation from the Admin Client.
Client Behavior Against Different Key States for Oracle Key Vault
Following table describes the relative behavior of the of the writer (Extract) or reader (Replicat) client processes depending on the different trail encryption key states.
If the master key is non-extractable, then it implies that OKV cryptographic operations are using remote encryption. This means that the master key cannot leave or be retrieved from OKV. Commands to encrypt and decrypt in Oracle GoldenGate on the basis of once per trail file, are performed inside OKV.
| Key State | Trail Writer (encryption) | Trail Reader (decryption) |
|---|---|---|
|
Active |
Trail writer chooses the highest version number with Active state for encryption. |
Trail reader can use this key and version number to decrypt the trail. |
|
Preactive |
Trail writer ignores and does not consider the key version number with these states. |
Not Applicable |
|
Deactivated |
None |
Trail file reader retrieves and decrypts the trail if the key and version number is deactivated or compromised. |
|
Compromised |
None |
Trail file reader retrieves and decrypts the trail if the key and version number is deactivated or compromised. |
|
Destroyed |
Non |
Trail file reader generates an error and abends if the key and version number required to decrypt is in the destroyed or destroyed-compromised state. |
|
Destroyed-Compromised |
None |
Trail file reader raises an error and abends if the key and version number required to decrypt is in the destroyed or destroyed-compromised state. |