1 About the IBM RACF Advanced Connector
The IBM RACF Advanced connector integrates Oracle Identity Manager with a RACF target system.
This guide discusses the connector that enables you to use IBM RACF as a managed (target) resource of identity data for Oracle Identity Manager.
This chapter contains the following topics:
1.1 Introduction to the Connector
The connector allows information about users created or modified directly on the target system to be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager. In addition, you can use Oracle Identity Manager to perform provisioning operations on the target system.
In the IBM RACF context, the term user profile is synonymous with user account. If IBM RACF is configured as a target resource, then user profiles on IBM RACF correspond to accounts or resources assigned to OIM Users.
1.2 Certified Components
These are the software components and their versions required for installing and using the connector.
Table 1-1 Certified Components
| Item | Requirement |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Identity Manager or Oracle Identity Governance |
You can use one of the following releases of Oracle Identity Manager or Oracle Identity Governance:
|
|
JDK |
The JDK version can be one of the following:
|
|
Target systems |
IBM RACF on z/OS 2.5 and 3.1 |
|
Infrastructure requirement for the message transport layer between Oracle Identity Manager and the mainframe environment |
The infrastructure requirements can be one of the following:
|
|
Target system user account for reconciliation and provisioning operations |
IBM Authorized Program Facility (APF) authorized account with System Administrators privileges |
|
Product Libraries |
The following are the product libraries:
|
|
Pioneer and Voyager |
Pioneer and Voyager are written in single thread LE Cobol. They were developed to run above the 16M line. Options that can adversely affect these STCs are LE run options: ALL31(OFF) instead of ON STACK(,,,BELOW,,) instead of STACK(,,,ANYWHERE,,) |
|
LDAP Gateway |
The computer hosting the LDAP Gateway must run the following software:
|
1.3 Certified Languages
These are the languages that the connector supports.
-
Arabic
-
Chinese (Simplified)
-
Chinese (Traditional)
-
Danish
-
English
-
French
-
German
-
Italian
-
Japanese
-
Korean
-
Portuguese (Brazilian)
-
Spanish
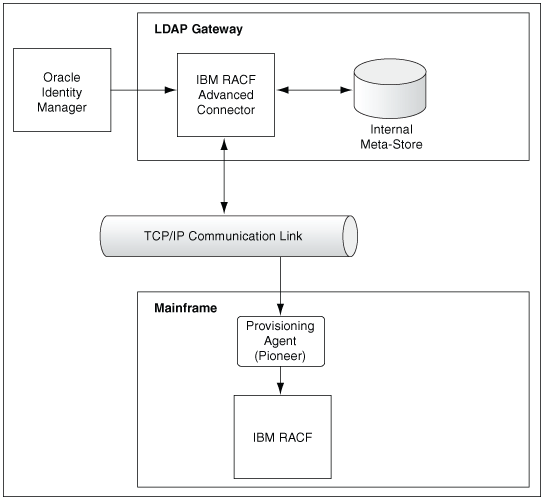
1.4 Connector Architecture
Connectors require certain architecture consisting of Gateways and Provisioning Agent.
This section contains the following topics:
1.4.1 Understanding the Connector Components
The IBM RACF Advanced connector contains the following components:
-
LDAP Gateway: The LDAP Gateway receives instructions from Oracle Identity Manager in the same way as any LDAP version 3 identity store. These LDAP commands are then converted into native commands for IBM RACF and sent to the Provisioning Agent. The response, which is also native to IBM RACF, is parsed into an LDAP-format response and returned to Oracle Identity Manager.
During reconciliation, the LDAP Gateway receives event notification, converts the events to LDAP format, and then forwards them to Oracle Identity Manager, or events can be stored in the LDAP Gateway internal store and pulled into Oracle Identity Manager by a scheduled task.
-
Provisioning Agent (Pioneer): The Pioneer Provisioning Agent is a mainframe component. It receives native mainframe IBM RACF identity and authorization change events from the LDAP Gateway. These events are processed against the IBM RACF authentication repository, in which all provisioning updates from the LDAP Gateway are stored. The response is parsed and returned to the LDAP Gateway.
Note:
At some places in this guide, the Provisioning Agent is referred to as Pioneer.
-
Reconciliation Agent (Voyager): The Reconciliation Agent captures mainframe events by using exits, which are programs run after events in IBM RACF are processed. These events include the ones generated at TSO logins, the command prompt, batch jobs, and other native events. These events are stored in the subpool cache area that is established by a supplied, standard z/OS procedure (STARTUP). The Reconciliation Agent captures these events, transforms them into LDAPv3 protocol notification messages, and then sends them to Oracle Identity Manager through the LDAP Gateway.
Note:
At some places in this guide, the Reconciliation Agent is referred to as Voyager.
-
Message Transport Layer: This connector supports a message transport layer by using the TCP/IP protocol, which is functionally similar to proprietary message transport layer protocols. In addition, the connector provides AES encryption for messages sent and received through the transport layer.
The AES encryption is performed using 128-bit cryptographic keys. In addition, Encryption and Decryption programs are supplied in the Distribution Load Library. The encryption or decryption does not require any network software or hardware.
1.4.2 Understanding the Connector Operations
Provides an overview of the provisioning and reconciliation operations.
This section contains the following topics:
1.4.2.1 Full Reconciliation Process
Full reconciliation involves fetching existing user profile data from the mainframe to Oracle Identity Manager.
If you configure the target system as a target resource, then this user profile data is converted into accounts or resources for OIM Users.
The following is a summary of the full reconciliation process:
- You set values for the attributes of the RACF Reconcile All Users scheduled task.
- You run the scheduled task. The task sends a search request to the LDAP Gateway.
- The LDAP Gateway encrypts the search request and then sends it to the Provisioning Agent on the mainframe.
- The Provisioning Agent encrypts user profile data received from RACF and then passes this data to the LDAP Gateway.
- The LDAP Gateway decrypts the user profile data. If the user profile data does not include any changes when compared to the OIM user's existing resource data, then the event is ignored and reconciliation continues with the next user on the target system. If the user profile data includes a change, then the LDAP Gateway passes the data on to Oracle Identity Manager.
- The user profile data is converted into accounts or resources for OIM Users.
1.4.2.2 Initial LDAP Population and Reconciliation Process
This reconciliation process allows for a faster reconciliation based on an Extracted file configured on the Mainframe that will be used to populate the internal LDAP store, which OIM can then use a normal scheduled task to reconcile all the data to Oracle Identity Manager.
The following is a summary of the full reconciliation process:
Note:
For detailed instructions on how to perform full reconciliation, see Performing Full Reconciliation.- Use IBM utility to EXTRACT user data to a file.
- Configure Pioneer to use this file when needed.
Once this file has been created and used by OIM it will become stale and must be deleted. The file can be generated again if needed for re-populating or updating the Internal LDAP for Oracle Identity Manager to reconcile the latest data.
- Once the above file is generated, run the RACF Reconcile Users To Internal LDAP scheduled task to populate the LDAP Gateway internal store.
- After the LDAP Gateway internal store is populated, run the RACF Reconcile All LDAP Users scheduled task with one of the following settings:
- To reconcile all users, set the value of the Last Modified Timestamp attribute to 0.
- To reconcile all users that have changed since that date, set the value of the Last Modified Timestamp attribute to a date range.
Note:
If the _internalEnt_ property, located in the LDAP_INSTALL_DIR/conf/racf.properties file, is set totrue, then the LDAP internal store will also be populated on an ongoing basis by the "real-time" event capture using Voyager and the EXITs. So after initial population and reconciliation the process will still continue to use the RACF Reconcile All Ldap Users Task scheduled job using a Date range to reconcile these "real-time" event changes from data captured in the LDAP internal store.
1.4.2.3 Provisioning Process
Figure 1-1 shows the flow data during provisioning.
The following is a summary of the provisioning process:
- Provisioning data submitted from Oracle Identity Self Service is sent to the LDAP Gateway.
- The LDAP Gateway converts the provisioning data into mainframe commands, encrypts the commands, and then sends them to the mainframe computer over TCP/IP.
- The Provisioning Agent installed on the mainframe computer decrypts and converts the LDAP message from ASCII to EBCDIC.
- The Provisioning agent executes the commands, runs them on the mainframe and within the Pioneer STC (Started Task) using the RACF API (IRRSEQ00).
- The Provisioning Agent converts the RACF API output to ASCII and encrypts the message prior to sending back to the LDAP Gateway.
- The outcome of the operation on the mainframe is displayed in Identity Self Service. A more detailed message is recorded in the connector log file.
1.5 Connector Features
The features of the connector are discussed in the following topics:
1.5.1 Full and Incremental Reconciliation
After you deploy the connector, you can perform full reconciliation to bring all existing user data from the target system to Oracle Identity Manager. After the first full reconciliation run, change-based or incremental reconciliation is automatically enabled and active. Incremental reconciliation is a real-time process. User changes on the target system are directly sent to Oracle Identity Manager or stored in the LDAP Gateway internal store.
You can perform a full reconciliation run at any time. See Configuring Incremental Reconciliation and Performing Full Reconciliation for more information.
1.5.2 Encrypted Communication Between the Target System and Oracle Identity Manager
AES-128 encryption is used to encrypt data that is exchanged between the LDAP Gateway, and the Reconciliation and Provisioning Agents on the Mainframe. This encryption is taken care by the Mainframe agents.
1.5.3 High Availability Feature of the Connector
The following are component-failure scenarios and the response of the connector to each scenario:
-
Scenario 1: The Reconciliation Agent is running and the LDAP Gateway stops responding
-
The Reconciliation Agent stops sending messages (event data) to the LDAP Gateway.
-
Messages that are not sent are stored in the subpool cache.
-
When the LDAP Gateway is brought back online, the Reconciliation Agent reads data from the subpool cache and then sends messages to the LDAP Gateway.
-
-
Scenario 2: The LDAP Gateway is running and the Reconciliation Agent stops responding
-
Event data is sent to the subpool cache.
-
When the Reconciliation Agent is brought back online, it reads data from the subpool cache and then sends messages to the LDAP Gateway.
Note:
During SHUTDOWN, there is a possibility that events that had been sent to the LDAP might be saved and re-sent again once the Agent is brought back online. This is to ensure no data lose and this process will re-list the event data to provide the most current view.
-
-
Scenario 3: The LDAP Gateway is running and the mainframe stops responding
-
Messages that are in the subpool cache are written to disk.
-
When the mainframe is brought back online, event data written to disk is again stored in the subpool cache.
-
The Reconciliation Agent reads data from the subpool cache and then sends messages to the LDAP Gateway.
Note:
During SHUTDOWN, there is a possibility that events that had been sent to the LDAP might be saved and re-sent again once the Agent is brought back online. This is to ensure no data lose and this process will re-list the event data to provide the most current view.
-
-
Scenario 4: The LDAP Gateway is running and the Provisioning Agent or mainframe stops responding
The process task that sends provisioning data to the LDAP Gateway retries the task.
-
Scenario 5: The subpool is stopped by an administrator
If the subpool is stopped by an administrator, then it shuts down the Reconciliation Agent, thereby destroying any messages that are not transmitted. However, the messages in the AES-encrypted file are not affected and can be recovered.
1.6 Connector Objects Used During Reconciliation and Provisioning
Information about connector objects used during reconciliation and provisioning are discussed in the following topics:
1.6.1 Supported Functions for Target Resource Reconciliation
The connector supports reconciliation of user data from the following events:
-
Create user
-
Modify user
-
Revoke user
-
Resume user
-
Delete user
-
Add user to group
-
Delete user from group
1.6.2 Supported Functions for Provisioning
These are the provisioning functions that the connector supports.
Table 1-2 Supported Functions for Provisioning
| Function | Description | Mainframe Command |
|---|---|---|
|
Create users |
Adds new users on IBM RACF |
ADDUSER |
|
Create groups |
Adds new group on IBM RACF |
ADDGRP |
|
Modify users |
Modifies user information on IBM RACF |
ALTUSER |
|
Change password |
Changes user passwords on IBM RACF in response to password changes made on Oracle Identity Manager through user self-service |
ALTUSER |
|
Reset passwords |
Resets user passwords on IBM RACF The passwords are reset by the administrator. |
ALTUSER |
|
Revoking user accounts |
Sets IBM RACF user to a REVOKED state |
ALTUSER |
|
Resuming user accounts |
Sets IBM RACF user to an ENABLED state |
ALTUSER |
|
Add user to group |
Connects user with an IBM RACF group |
CONNECT |
|
Remove user from group |
Disconnects user from an IBM RACF group |
REMOVE |
|
Permit user to dataset |
Permits user to be part of the data set ACL and gives them access rights to the data set |
PERMIT |
|
Remove user from dataset |
Removes user from the data set ACL |
PERMIT |
|
Permit user to access general resource |
Permits user to be part of the resource ACL and gives them access rights to the resource |
PERMIT |
|
Remove user from general resource |
Removes user from the resource ACL |
PERMIT |
|
Grant security attribute to user |
Provides non-value security attribute privileges to user |
ALTUSER |
|
Grant user to TSO segment |
Provides TSO access and information to user |
ALTUSER |
| Grant user to OMVS segment |
Provides OMVS information to users |
ALTUSER |
|
Delete user |
Deletes user from IBM RACF |
DELUSER |
1.6.3 User Attributes for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
Table 1-3 lists attribute mappings between IBM RACF and Oracle Identity Manager for target resource reconciliation and provisioning. The OnBoardRacfUser and ModifyUser adapters are used for the Create User and Modify User provisioning operations, respectively.
Table 1-3 User Attributes for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
| Process Form Field | IBM RACF Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cn | NAME | Full name
You can specify the format in which Full Name values are stored on the target system. |
| cicsOpclass | CICS_OPCLASS | Operator class |
| cicsOpident | CICS_OPIDENT | Operator ID |
| cicsOpprty | CICS_OPPRTY | Operator priority |
| cicsRslkey | CICS_RSLKEY | Resource key 0–99 |
| cicsTimeout | CICS_TIMEOUT | Timeout value |
| cicsTslkey | CICS_TSLKEY | Type key 1–99 |
| cicsXrfsoff | CICS_XRFSOFF | Transaction off (Force|NoForce) |
| dfltGrp | DEFAULT-GROUP | Default group for the user |
| instdata | DATA | Installation-defined data for the user |
| netviewConsname | NETVIEW_CONSNAME | Console name |
| netviewCtl | NETVIEW_CTL | Control |
| netviewDomains | NETVIEW_DOMAINS | Domain name |
| netviewIc | NETVIEW_IC | Command|Command List |
| netviewMsgrecvr | NETVIEW_MSGRECVR | Message receiver |
| netviewNgmfadmn | NETVIEW_NGMFADMN | Administration (Y|N) |
| netviewNgmfvspn | NETVIEW_NGMFVSPN | View span |
| netviewOpclass | NETVIEW_OPCLASS | Operator class |
| omvsAssizemax | OMVS_ASSIZEMAX | Address space size |
| omvsAutouid | OMVS_AUTOUID | Generate auto user identifier |
| omvsCputimemax | OMVS_CPUTIMEMAX | CPU time |
| omvsFileprocmax | OMVS_FILEPROCMAX | Files per process |
| omvsHome | HOME | Homelocation |
| omvsMemlimit | OMVS_MEMLIMIT | Non-shared memory size |
| omvsMmapareamax | OMVS_MMAPAREAMAX | Memory map size |
| omvsProcusermax | OMVS_PROCUSERMAX | Processes per UID |
| omvsProgram | PROGRAM | Program |
| omvsShared | OMVS_SHARED | Shared user identifier |
| omvsShmemmax | OMVS_SHMEMMAX | Shared memory size |
| omvsThreadsmax | OMVS_THREADSMAX | Threads per process |
| omvsUid | UID | UID |
| owner | OWNER | Owner of the user profile |
| resumeDate | RESUME DATE | Future date from which the user will be allowed access to the system |
| revokeDate | REVOKE DATE | Future date from which the user's access to the system will be revoked |
| revoke | REVOKE|RESUME | Status of the user |
| tsoAcctNum | ACCTNUM | Default TSO account number on the TSO/E logon panel |
| tsoCommand | COMMAND | Command to be run during TSO/E logon |
| tsoDest | DEST | Default SYSOUT destination |
| tsoHoldclass | HOLDCLASS | Default hold class |
| tsoJobclass | JOBCLASS | Default job class |
| tsoMaxSize | MAXSIZE | Maximum region size the user can request at logon |
| tsoMsgclass | MSGCLASS | Default message class |
| tsoProc | PROC | Default logon procedure on the TSO/E logon panel |
| tsoSize | SIZE | Minimum region size if not requested at logon |
| tsoSysoutclass | SYSOUTCLASS | Default SYSOUT class |
| tsoUnit | UNIT | Default UNIT name for allocations |
| tsoUserdata | USERDATA | TSO-defined data for the user |
| uid | User | Login ID |
| userPassword | PASSWORD | Password used to log in |
| waaccnt | WAACCNT | Account number for APPC or IBM z/OS processing |
| waaddr1 | WAADDR1 | Address line 1 for SYSOUT delivery |
| waaddr2 | WAADDR2 | Address line 2 for SYSOUT delivery |
| waaddr3 | WAADDR3 | Address line 3 for SYSOUT delivery |
| waaddr4 | WAADDR4 | Address line 4 for SYSOUT delivery |
| wabldg | WABLDG | Building for SYSOUT delivery |
| wadept | WADEPT | Department for SYSOUT delivery |
| waname | WANAME | User name for SYSOUT delivery |
| waroom | WAROOM | Room for SYSOUT delivery |
1.6.4 GROUP Attributes for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
The connector supports reconciliation and provisioning of the GROUP multivalued attribute. For any particular user, a child form is used to hold values of the GROUP attributes listed in the table. The AddUserToGroup and RemoveUserFromGroup adapters are used for GROUP provisioning operations.
Table 1-4 lists GROUP attribute mappings between IBM RACF and Oracle Identity Manager.
Table 1-4 GROUP Attribute Mappings for IBM RACF Connector
| Child Form Field | IBM RACF Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
MEMBER_OF |
GROUP |
UID Of the group being assigned to User |
1.6.5 Security Attributes for Provisioning
The connector supports provisioning of the SECURITY ATTRIBUTE multivalued attribute. For any particular user, a child form is used to hold values of the SECURITY ATTRIBUTE attributes listed in the table.
The following list shows the bit flag security attributes that are supported for provisioning operations between Oracle Identity Manager and IBM RACF:
- ADSP
- AUDITOR
- CICS
- DCE
- DFP
- EXPIRED
- GRPACC
- NETVIEW
- OIDCARD
- OMVS
- OPERATIONS
- OPERPARM
- OVM
- PROTECTED
- PROXY
- RESTRICTED
- SPECIAL
- TSO
- UAUDIT
Table 1-5 Security Attribute for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning
| Child Form Field | IBM RACF Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ATTRIBUTE | Security Attribute | Attribute access authority for user |
1.6.6 DATASET Profile Attributes for Provisioning
The connector supports provisioning of the DATASET multivalued attribute. For any particular user, a child form is used to hold values of the DATASET attributes listed in the table.
Table 1-6 lists DATASET attribute mappings between IBM RACF and Oracle Identity Manager.
Table 1-6 DATASET Attribute Mappings for IBM RACF Advanced Connector
| Child Form Field | IBM RACF Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Dataset Name |
PROFILE NAME |
Prodile ID |
|
Dataset Access |
ACCESS |
User's access level to the dataset |
|
Dataset Generic |
GENERIC |
Treat the dataset as a generic name |
1.6.7 Resource Profile Attributes for Provisioning
(The connector supports reconciliation and provisioning of the RESOURCE PROFILE multivalued attribute. For any particular user, a child form is used to hold values of the RESOURCE PROFILE attributes listed in the table.
Table 1-7 Resource Profile Attributes for Target Resource Provisioning
| Child Form Field | IBM RACF Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RESOURCE PROFILE ID | RESOURCE PROFILE NAME& CLASS NAME | Profile ID and class name combinations |
| RESOURCE ACCESS | RESOURCE ACCESS | User's access level to resource profile |
1.6.8 Reconciliation Rule
During target resource reconciliation, Oracle Identity Manager tries to match each user fetched from IBM RACF with existing IBM RACF resources provisioned to OIM Users. This is known as process matching. A reconciliation rule is applied for process matching. If a process match is found, then changes made to the user on the target system are copied to the resource on Oracle Identity Manager. If no match is found, then Oracle Identity Manager tries to match the user against existing OIM Users. This is known as entity matching. The reconciliation rule is applied during this process. If an entity match is found, then an IBM RACF resource is provisioned to the OIM User. Data for the newly provisioned resource is copied from the user profile.
The following is the reconciliation rule for target resource reconciliation:
Rule name: IdfReconUserRule
Rule element: User Login Equals uid
In this rule element:
-
User Login is the User ID field on the process form and the OIM User form.
-
uid is the USER attribute on IBM RACF.
After you deploy the connector, you can view this reconciliation rule by performing the following steps:
- On the Design Console, expand Development Tools and then double-click Reconciliation Rules.
- Search for and open the IdfReconUserRule rule.
1.6.9 Reconciliation Action Rules
Reconciliation action rules specify actions that must be taken depending on whether or not matching IBM RACF resources or OIM Users are found when the reconciliation rule is applied. Table 1-8 lists the reconciliation action rules.
Table 1-8 Reconciliation Action Rules for IBM RACF Advanced Connector
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
None |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
1.6.10 Viewing the Reconciliation Action Rules for IBM RACF Advanced Connector
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation action rules for target resource reconciliation by performing the following steps:
- On the Design Console, expand Resource Management and then double-click Resource Objects.
- Search for and open the OIMRacfResourceObject resource object.
- Click the Object Reconciliation tab, and then click the Reconciliation Action Rules tab. The Reconciliation Action Rules tab displays the action rules defined for this connector. Reconciliation Action Rules shows the reconciliation action rule for target resource reconciliation.