4 Planning and Creating Projects
This chapter describes how to plan and create a project in Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (Oracle BAM).
This chapter includes the following sections:
4.1 Planning a Project
A project is a BAM entity that groups other related BAM entities.
Other BAM entities that you can add to or create in a project are:
-
Data Objects, which contain the data to be monitored, such as external databases or streams of data from ongoing business processes. See Working with Data Objects for more information.
-
Business Queries, which fetch and analyze the data to be monitored, such as sales figures for different countries. See Creating Business Queries for more information.
-
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which fetch and analyze especially important measures, such as current production rates. See Creating KPIs for more information.
-
Business Views, which display data fetched by queries and KPIs in various formats, such as charts, tables, and gauges. See Creating and Using Business Views for more information.
-
Parameters, which filter fetched data according to user input, such as the country for which to view sales figures. See Creating Parameters for more information.
-
Alerts, which notify users of out-of-range fetched data, such as a spike in the average wait time at a call center. See Creating Alerts for more information.
-
Dashboards, which display collections of related views, such as a pie chart of sales by country and a bar graph of sales by salesperson. See Creating Dashboards for more information.
These entities operate together to achieve a business monitoring goal. Before you create a project, you should plan what the entities in the project will do.
Note:
You can add any data object to which you have access to any project. You cannot move or copy other entities from one project to another. However, you can export a project to a ZIP file and import it into another BAM server. See Using Commands with Oracle BAM for more information.
4.2 Choosing Bottom-Up or Top-Down Project Building Steps
You can create a project from the bottom up or from the top down, as long as certain aspects of the project are bottom up.
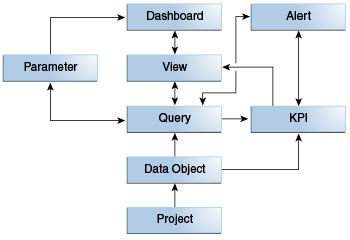
Figure 4-1 illustrates the steps for creating a project:
Some aspects of building projects are always bottom-up. You must create your project and add data objects to it first. You cannot configure a query or a realtime KPI before you add a data object. Likewise, you cannot configure a scheduled KPI before you create the query on which it is based. You cannot create a KPI from a view. You cannot create a parameter from a dashboard.
However, other aspects of project building can be either bottom-up or top-down. You can create a dashboard, then a view, then a query, or you can create a query, then a view, then a dashboard. You can create a parameter before or after you create a query that uses it. You can create a query or KPI that triggers an alert action. Or you can create a stand-alone alert, then create an alert action in a query or KPI to trigger the stand-alone alert.
4.3 Creating a Project
This section outlines the detailed procedure to create a Project.
Use the following procedure to create a project.
To create a project:
4.4 Opening a Project
This section outlines the steps to open a Project.
Use the following procedure to open a project.
To open a project:
4.5 Renaming a Project
This section outlines the procedure to rename a project.
Use the following procedure to change the Display Name of a project.
The Display Name is case sensitive and may contain any characters except the forward slash (/), which indicates a folder path. It may have up to 128 characters. It can be changed at any time.
To rename a project:
4.6 Deleting a Project
This section outlines the procedure to delete a Project.
Use the following procedure to delete a project. All entities in the project except data objects are also deleted.
To delete a project:
4.7 Securing a Project
This section outlines the procedure to secure a project.
By default, BAM entities inherit security settings from the project in which they are created.
To change security settings for a project:
-
Go to the Designer page.
The project name appears in the top left corner of the BAM window.
Process Analytics is the initial and default project in BAM if BPM is configured in the same domain.
-
Click the down arrow to the right of the project name.
-
Select Security from the pop-up menu.
The security tab for the project opens.
-
To add a role or group to whom you can explicitly grant or deny permissions, follow these steps:
-
Click the Add icon in the Grant Permissions or Deny Permissions table.
The Add Application Roles, Groups, and Users dialog opens.
See Managing Oracle BAM Users for information about how to add users to roles and groups.
-
Type a Name for the role or group you are adding.
-
Select from the drop-down List: Application Role or Group.
-
Click Search to populate the Available Members list.
-
To add a member to the Selected Members list, select the member and click the single right arrow.
-
To add all members to the Selected Members list, select the member and click the double right arrow.
-
To remove members from the Selected Members list, use the single and double left arrows.
-
When the Selected Members list is final, click OK.
The Add Application Roles, Groups, and Users dialog closes, and the Name you specified appears in the table.
-
-
To remove a role or group, select the table row and click the Remove icon.
-
To grant permissions, select Read, Write, Remove, or Security for the users, roles, and groups listed in the Grant Permissions table.
-
To deny permissions, select Read, Write, Remove, or Security for the users, roles, and groups listed in the Deny Permissions table.
-
Click Save.
4.8 Copying a Project
-
In order to Clone a project, download the
bam-impexp.copyproject.jarandcopyproject.shfiles from Oracle Tech Network and copy them to the<FMW_HOME>/soa/bam/liband<FMW_HOME>/soa/bam/binlocations respectively. -
If your project has KPIs, you must apply Patch 19153993 as a fix for bug 18897246. Previously, the KPI Watchlist Data Control entry did not have the project name in its ID which meant that if you had two or more projects with the same KPI watchlist names, the KPI watchlists and business views would not function correctly for the new cloned project. The patch has produced a fix for this issue.
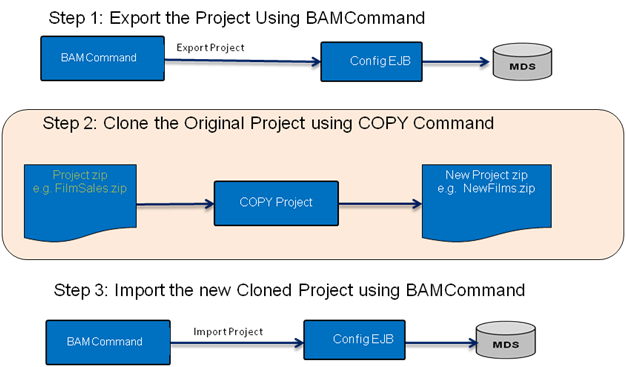
Cloning a Project
Cloning a project is a three-step process as shown in the following image.
To copy a project:
4.9 Managing Changes in a Project
Changing an entity in a project might affect other entities that are dependent on the changed entity. For example, deleting a query breaks views based on that query.
When you delete an entity, any dependent entities are listed, and you are asked to confirm the deletion.
If an entity is broken because an entity it depends on no longer exists or is also broken, its icon in the left navigation pane changes to a red circle with a white X:
You can open and edit the entity to fix it. For example, if a view is broken because the query it is based on no longer exists, you can select a different query or create a new query for the view.
Deleting a view removes it from any dashboards that reference it, and the dashboard icons do not change to a red circle with a white X.