24 Working With Image and Video Conversions
The Digital Asset Manager feature is used to define and provide images, videos, and audio files in specified formats and sizes for download by the people in your organization who need them. This helps organizations maintain consistent standards for branding and digital content use.
For Digital Asset Manager to work, the following components must be installed and enabled on the correct server as noted.
| Component Name | Component Description | Enabled on Server |
|---|---|---|
|
DAMConverter |
Enables Oracle WebCenter Content: Inbound Refinery to convert digital assets into multiple renditions. |
Inbound Refinery Server |
|
DamConverterSupport |
Enables the Content Server to support digit asset management features. This component is highly dependent on the ZipRenditionManagement Component. |
Content Server |
|
DigitalAssetManager |
Enables the user interface for digital asset management in tight integration with components used to create and manage renditions and zip file archives. This component is highly dependent on the ContentBasket Component. |
Content Server |
|
ContentBasket |
Enables users to select renditions of content items and place them in a personal storage space called the Content Basket. |
Content Server |
|
ZipRenditionManagement |
Enables Content Server access to digital asset renditions created and compressed into a ZIP file by Inbound Refinery. |
Content Server |
This section discusses the following topics:
24.1 Understanding Digital Asset Manager
Digital Asset Manager creates multiple formats of digital assets automatically when an image or video is checked into Content Server, and lists the formats under one content ID. This ensures that the asset, such as a corporate logo or promotional video, maintains a standard size and quality in the multiple formats required by an organization, while providing the content management features of Content Server. For example, one person can bundle and download images of the logo for use on a web-site, and another can download and bundle images of the same logo for use in office presentations or print collateral, all from a single digital asset checked into Content Server.
Digital assets are valuable electronic images and videos to be made available within an organization in multiple output formats, called renditions. The quantity and type of renditions are defined by the system administrator in rendition sets. A user selects a rendition set used to create renditions of a digital asset at the time the asset is checked into Content Server. Once checked in, a digital asset is routed to Inbound Refinery and converted using the specified conversion application.
This section discusses the following topics:
24.1.1 Supported Conversion Applications
By default, Inbound Refinery supplies rendition sets for use with Oracle Outside In Image Export to convert images. For additional image conversion options, a stand-alone graphics conversion application can be installed. Oracle does not supply or support any specific third-party conversion engine. Sample configurations for additional image conversion engines can be accessed from the Oracle WebCenter Content Oracle Technology Network pages. For additional information, see the "Integrating the Inbound Refinery with 3rd Party Image Converters" blog.
To convert videos, a stand-alone video conversion application must be installed. Digital Asset Manager is currently configured to work with Telestream’s Vantage. A supported version of Vantage must be obtained from Telestream and is available from their website (http://www.telestream.net).
Digital Asset Manager is designed and tested on fully functioning implementations of third-party conversion applications. Demonstration versions of conversion applications are not recommended or supported.
24.1.2 Supported Streaming Servers
For streaming digital video, Digital Asset Manager currently supports the following streaming servers:
-
Windows Streaming Media: versions for supported Windows operating systems
-
QuickTime Streaming Media: Darwin and QuickTime Streaming Server version 10.4
-
RealMedia: Helix DNA Server version 11
24.1.3 Supported Input Formats
Supported input formats are determined by the graphic or video conversion application being used. Digital Asset Manager can use several graphic conversion engines. Only Oracle Outside In Image Export is included with Inbound Refinery. Formats supported by Oracle Outside In Image Export can be found on Oracle's website at http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/webcenter/content/oit-all-085236.html.
Third-party conversion engines may offer additional support to graphics format. Third-party conversion engines must be obtained independently of Inbound Refinery and are not officially supported by Oracle.
Graphics formats supported by compatible conversion engines include the following:
-
JPG/JPEG (Joint Photographic Expert Group)
-
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
-
BMP (Bitmap)
-
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
-
TIFF (Tag Image File Format)
-
PSD (PhotoShop)
-
AI (Adobe Illustrator)
-
PDF (Portable Document Format)
For a comprehensive listing of formats supported, view the documentation that came with your chosen graphic conversion engine.
24.1.4 Supported Output Formats
Output formats are determined by the conversion application. Formats supported by Oracle Outside In Image Export can be found on Oracle's website at http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/webcenter/content/oit-all-085236.html.
Viewing of renditions in your browser is limited to what can be displayed effectively in your browser. For images, only formats supported by your web browser can be displayed. For video, only formats that have browser plug-ins are available for viewing in your web browser, such as output formats supported by Windows Media Player, Real Player, QuickTime Player, and Flash. Any image or video assets rendered in a format not supported for viewing in a browser will still be managed by Content Server, but will be available only for download.
Video Manager currently supports the following output formats:
-
MPEG Layers 1, 2, and 4 (.mpg, .mpeg, .mp2, .mp4)
-
MPEG Layer 3 Audio (.mp3)
-
Adobe Flash (.flv)
-
QuickTime (.mov)
-
Audio Video Interleave (.avi)
Due to the extensive number of formats supported by Telestream’s Vantage, Windows Media Player, Real Player, QuickTime Player, and Adobe Flash, and the difficulty in configuring all the possible combinations, Video Manager officially supports a limited subset of these formats. You can configure Digital Asset Manager to accept additional formats and test them as needed.
Note:
If using Microsoft IIS to serve conversions, unrecognized MIME types generate a 404 error. To ensure that the browser properly displays supported formats, check that all MIME types being used are registered in IIS.
For more information, see the IIS documentation and the Microsoft article at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc725608%28WS.10%29.aspx.
24.2 Configuring Digital Asset Manager
The following configuration files must be modified to configure Digital Asset Manager for image and video conversion:
-
Content Server
config.cfgfile, located in theIntradocDir/config/directory -
Inbound Refinery
intradoc.cfgfile, located in theDomainDir/ucm/ibr/bindirectory
This section details the necessary configuration steps.
24.2.1 Configuring for Image Conversion
Digital Asset Manager requires a conversion application to create renditions of an image. Default rendition sets for use with Oracle Outside In Image Export are provided and no configuration is necessary.
Default Rendition Sets
Default rendition sets are defined in the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda file, which is located in the refinery IdcHomeDir/components/DAMConverter/resources/ directory. This file should never be altered because upgrades to the component overwrite any changes. For information about defining and using rendition sets other than the default sets included in the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda, see Creating and Configuring Image Rendition Sets.
The following default rendition sets are included in the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda file installed with Digital Asset Manager.
| Rendition Set Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
ThumbnailOnly |
Creates one 72 dpi PNG rendition exactly 80 pixels high |
|
BasicRenditions |
Creates the following renditions:
|
|
MultipleFormats |
Creates the following renditions:
|
Alternate Conversion Applications
If needed, an alternate conversion application can be used. To use a conversion application other than Oracle Outside In Image Export, obtain and install the application and define rendition sets suitable for the application.
Note:
For best performance rendering images, install the image conversion application on the same server as the Inbound Refinery instance used for Digital Asset Manager. For best performance rendering videos, see the recommendations of the video conversion application.
Additional rendition sets should be defined in a new file called extraRendition_definitions.hda which must be created in the /data/configuration/dam/ directory. For information about creating additional rendition sets, see Creating and Configuring Image Rendition Sets.
24.2.2 Modifying the Content Server Configuration File
A default value must be set for the VideoRenditions and ImageRenditions metadata fields to prevent errors if a rendition set is not selected at time of check-in. To modify the configuration file:
Digital Asset Manager allows a user to bundle and download assets to a local or shared file system. Edit the following variables to set the maximum allowable size of a download can be specified, either in megabytes or number of files:
-
MaxRenditionBundleInMegabytes=Maximum size of bundle in megabytes. -
MaxRenditionFileEntries=Maximum number of files in the bundle, expressed numerically.
Note:
The DefaultVideoConversionSet identifies the rendition set to be used if a user does not specify a video rendition set when checking in a video. The DefaultPackedConversionSet identifies the rendition set to be used if a user does not specify an image rendition set when checking in an image. They must be set in the config.cfg file, and not in the Default Value field of the Content Manager applet.
24.2.3 Associating File Formats and Mapping File Extensions
Content Server identifies content items as digital assets based on the extension of the file checked in. The following file formats must be associated with Digital Asset Manager and the file extensions mapped to the correct format.
24.2.3.1 Image Formats
-
JPEG (.jpeg; .jpg)
-
GIF (.gif)
-
AI (.ai)
-
PSD (.psd)
-
BMP (.bmp)
-
PNG (.png)
-
TIFF (.tiff; .tif)
24.2.3.2 Video Formats
-
MPEG Layers 1, 2, and 4 (.mpg, .mpeg, .mp2, .mp4)
-
QuickTime (.mov)
-
Audio Video Interleave (.avi)
-
Flash Video (.flv)
Because the conversion engine passes rendition information to the third-party conversion application, any additional format must be supported by the third-party conversion application.
Note:
When converting one type of digital asset, images or videos, only associate the formats for that type of asset.
24.2.4 Associating a File Format
To associate a format with the Digital Asset Manager conversion engine:
-
Log in as an administrator to Content Server.
-
From the main menu, choose Administration then Admin Applets.
-
From the Applets list, choose Configuration Manager.
-
On the Configuration Manager applet, choose Options then File Formats.
-
On the File Formats page, associate the format with the Digital Asset Manager conversion engine.
If the format is listed in the File Formats (upper) section of the File Formats page:
-
Select the format from the list. For example select,
image/jpegfor JPEG images orvideo/mpegfor MPEG videos. -
Click Edit.
-
On the Edit File Format page, select Digital Media Graphics for image formats and Digital Media Video for video formats from the Conversion choice list. Digital Media Graphics and Digital Media Video are the names of the Digital Asset Manager conversions.
-
If needed, modify the description. The description is displayed in the Configuration Manager and is not displayed in the Content Server interface.
-
Click OK.
If the format is not listed in the File Formats (upper) section of the File Formats page:
-
Click Add.
-
On the Add New File Format page, enter the type of format in the Format field. The type can be any value and is displayed on the Content Information and Rendition Information pages of Content Server. For help in choosing the correct type, see Identifying MIME Types.
-
Select Digital Media Graphics for images or Digital Media Video for videos from the Conversion choice list. Digital Media Graphics and Digital Media Video are the names of the Digital Asset Manager conversions.
-
If needed, add a description. The description is displayed in the Configuration Manager and is not usually displayed in the Content Server interface.
The description can be displayed in the user interface if the configuration variable
IsOverrideFormatis set equal to true in the Content Server configuration file. SettingIsOverrideFormat=truein the Content Server configuration file enables a choice list on the check-in page that allows a user to select a conversion format for a specific file, bypassing the assigned format. -
Click OK.
-
24.2.5 Mapping File Extensions
After a format is associated with the appropriate Digital Media conversion engine, the appropriate file extensions must be mapped to the file format in Configuration Manager. All files with a file extension mapped to a format associate with Digital Media Graphics or Digital Media Video are sent to Inbound Refinery for conversion.
To map a file extension to a file format associated with the Digital Asset Manager conversion engine:
-
Log in as an administrator to Content Server.
-
From the main menu, choose Administration then Admin Applets.
-
From the Applets list, choose Configuration Manager.
-
Choose Options then File Formats.
-
On the File Formats page, map the extensions to the appropriate format:
If the extension is listed in the File Extensions (lower) section of the File Formats page:
-
Select the extension from the list.
-
Click Edit.
-
On the Edit File Extension page, select the appropriate format from the Map to Format choice list.
-
Click OK.
If the format is not listed in the File Formats (upper) section of the File Formats page:
-
Click Add.
-
On the Add File Extensions page, enter the file extension in the Extension field. Do not enter the dot of the file extension.
-
Select the appropriate format from the Map to Format choice list.
-
Repeat steps a through c for each extension to be associated with the format. For example,
pspimagecould also be associated withapplication/PaintShop. -
Click OK.
-
Click Close.
-
Close Configuration Manager.
After associating a format to the appropriate Digital Asset Manager conversion (Digital Media Graphics or Digital Media Video), and mapping the appropriate file extensions to the format, all files with those extensions checked into Content Server are passed to Inbound Refinery for processing through the conversion application.
-
24.3 Setting Up and Managing Image Conversions
This section discusses the following topics:
24.3.1 Understanding Image Rendition Sets
When a digital asset is checked in to Content Server, Digital Asset Manager creates multiple renditions of that asset. The criteria for each image rendition is defined in one of two files.
The default renditions set is defined in the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda file and it should not be modified. Custom rendition sets can be added to the extraRendition_definitions.hda component resource file. This file can be created with a standard text editor and must be located in a new directory named dam in the refinery IntradocDir/data/configuration/ directory. The full file path should be:
IntradocDir/data/configuration/dam/extraRendition_definitions.hda
For videos, the criteria is defined in the video conversion application.
24.3.1.1 About Image Asset Rendition Definition
The criteria defining the default rendition sets at installation are in the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda file in the IdcHomeDir/components/DAMConverter/resources/ directory. This file should not be edited.
The definitions are grouped into rendition sets which correspond to rendition sets available to contributors on the content check-in form when a image asset is checked in. It includes the following predefined rendition sets:
-
ThumbnailOnly
-
BasicRenditions
-
MultipleFormats
The included rendition sets are examples that work with Outside In Image Export. If they are not needed, remove them from the option list on the check-in page using the Configuration Manager. Do not edit the resource file to remove the sets. Any changes made are lost when a component is updated.
Additional rendition sets can be added the extraRendition_definitions.hda file, which can be created with a standard text editor. It must be stored in a new directory named dam in the refinery IntradocDir/data/configuration/ directory.
Digital Asset Manager merges damconverter_basedefinitions.hda and extraRendition_definitions.hda when running, with the second file taking precedence over the resource file. For example, if you create a new rendition in your file with the same name as one in the resource file but with different parameters, the new parameters are used.
24.3.1.2 About Defining Image Rendition Sets
When a contributor checks a digital asset into Content Server, a rendition set is selected on the check-in form. For image files, that rendition set matches a rendition set defined in either the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda file or the extraRendition_definitions.hda file.
Image rendition sets defined in the extraRendition_definitions.hda file contain the options for converting digital assets into the image renditions specified in the set. The default renditions sets are in the component resource file, which should not be changed. Any additional rendition sets should be added to the extraRendition_definitions.hda. In that file, the top properties section contains the file path to a third-party conversion application. The bottom section contains the rendition set options, organized into sets, called rendition result sets.
When a file is checked into Content Server, the format of the file determines if it is a digital asset. If it is an image file, Content Server passes the file to Inbound Refinery, which calls rendition options from the extraRenditions.hda file and pass them to the image conversion application. The resulting renditions are then passed back through Inbound Refinery to Content Server or other specified location, where they are managed under a single content ID and made available to your organization.
For image assets, the names of the rendition sets defined for the choice list in the PackagedConversions metadata field in the Configuration Manager applet must match exactly to the names of the rendition sets defined in the extraRendition_definitions.hda file.
When modifying or adding renditions, it is important to remember that a contributor will only see the name of the rendition set when checking in a digital asset. The rendition set name should be descriptive. Rendition names and descriptions are displayed on the content information and rendition information pages.
Spaces and other characters reserved for Idoc Script tags or are illegal for use in URLs, such as spaces, cannot be used in rendition names.
24.3.2 Creating and Configuring Image Rendition Sets
To add, modify, or delete image renditions and rendition sets, edit the IntradocDir/data/configuration/dam/extraRendition_definitions.hda file. To successfully modify the extraRendition_definitions.hda file, you should be aware of basic HDA file structure. For more detailed information, see Developing with Oracle WebCenter Content.
This section discusses the following topics:
24.3.2.1 extraRendition_definitions.hda File Structure
When defining additional rendition sets, the extraRendition_definitions.hda file must contain a header line and two section types.
Section Types
The extraRendition_definitions.hda file has two section types using the following format:
@section_type section_name Section data @end
The two section types are:
-
Properties Section
-
ResultSet Section
In the extraRendition_definitions.hda file, there is one properties section and multiple result set sections. All rendition sets are organized in result sets.
Comments are not allowed within a section of an HDA file. However, comments can be placed in the HDA file before the first section, between sections, or after the last section.
Blank lines within a section of an HDA file are interpreted as a NULL value. Blank lines before the first section, between sections, or after the last section are ignored.
Properties Section
The properties section of the extraRendition_definitions.hda file defines the path to an external conversion application. In the default file, it also declares the values of Idoc Script variables defining conversion options used by the default rendition result sets.
Default Idoc Script variables in the properties section are used by the default rendition sets. They are not required for any additional rendition sets you define and are not discussed in this guide. Conversion options can be specified directly within the result sets. For more information on working with Idoc Script, see Developing with Oracle WebCenter Content.
Result Set Sections
Two types of result sets are in the extraRendition_definitions.hda file, listed here in order of display in the file:
-
Rendition Result Sets
-
ExtensionFormatMap
Rendition result sets organize rendition sets and contain information about creating renditions. There can be many rendition result sets, in any order. They can be added, modified, or deleted, but each name must be unique.
The ExtensionFormatMap is an optional result set that lists file extension/format pairs, so Inbound Refinery can return the correct file format to Content Server for use internally. This is not a required set, as Inbound Refinery uses a different system to map extensions to mime types, but if this result set is defined, the mapping specified in it takes precedence.
24.3.2.2 Adding a Rendition Set
The simplest way to add a rendition set to the extraRendition_definitions.hda file is to copy an existing rendition result set and modify it. To successfully modify an existing set, be aware of basic set structure.
Modifications made to a component resource such as damconverter_basedefinitions.hda are overwritten if Digital Asset Manager is updated to a newer version. Do not edit the damconverter_basedefinitions.hda manually. Additional rendition sets should be added to the extraRendition_definitions.hda file created in the IntradocDir/data/configuration/dam. Digital Asset Manager uses both files when running.
Rendition Result Set Structure
HDA files are ordered using simple name/value pairs, representing tabular data in an ASCII text format. The first line of a ResultSet section declares the set with the command @ResultSet, and then specifies the name of the set. The second line specifies the number of columns in a table, and the following lines name and populate the columns based on their order in the result set. The last line closes the result set with the command @end.
For example, the SampleGraphicSet rendition result set has the following format:
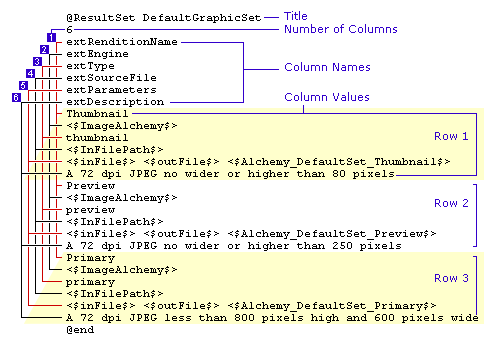
The first line of the rendition result set declares it as a result set by starting with @ResultSet, and the last line closes the set, with @end. The first line also gives the set a name. In this case, the name is ThumbnailOnly.
The name used should be descriptive, but spaces and other characters reserved for Idoc Script tags or illegal for use in URLs, such as spaces, cannot be used in rendition names.
The second line identifies how many columns are in the result set. In rendition result sets for Digital Asset Manager, there are 6 columns.
Each column has the following name and description.
| Column Name | Column Description |
|---|---|
|
extRenditionName |
The name of the rendition displayed on the Rendition Information page. This can be any descriptive name. Do not use Primary or Alternate for rendition names. These terms are reserved for internal use by Content Server. |
|
extEngine |
The path to the conversion engine used. By default, this is expressed as an Idoc Script variable declared in the properties section of the extraRendition_definitions.hda file. If you are using Image Export to create the rendition, use |
|
extType |
How the rendition is being used.
|
|
extSourceFile |
The file path to the asset checked into for conversion expressed as Idoc Script. |
|
extParameters |
The options passed to the conversion engine defining how the source file is rendered. By default, this is expressed as Idoc Script variables declared in the properties section of the extraRendition_definitions.hda file, but it can be expressed as a literal string.
|
|
extDescription |
The description for the rendition displayed on the Rendition Information page. |
For more information about working with .hda files, see Developing with Oracle WebCenter Content.
To add a new rendition result set:
-
Open the
extraRendition_definitions.hdafile in a standard text editor. -
Copy and paste an existing rendition result set.
-
Select a rendition result set to copy, starting at the
@ResultSetline and ending at the@endline, and copy it. -
Position the cursor between any two existing rendition result sets in the
extraRendition_definitions.hdafile. -
Paste the rendition result set into the file.
Blank lines between result set sections are ignored. To help visually organize the
extraRendition_definitions.hdafile, it is useful to insert a blank line before and after the new rendition result set. -
-
Change the name of the new rendition result set, listed next to
@ResultSet. For example,@ResultSet NewName.The name used should be descriptive. Do not use spaces or other characters reserved for Idoc Script tags or which are illegal for use in URLs, such as spaces.
-
Change rendition information for each rendition to keep in the result set.
-
Change the name of the rendition, listed in the extRenditionName column. Rendition names may have spaces.
-
Change the type of the rendition, listed in the extType column. Each rendition can multiple types, for example, preview, web.
-
Change the conversion options for rendering, listed in the extParameters column. Conversion options are dependent on which third-party conversion application being used.
-
Change the description of the rendition, listed in the extDescription column. The description can be anything, and is displayed on the Rendition Information page.
Do not change the
<$InFilePath$>variable used in the extSouceFile column.
-
-
Delete any extraneous renditions in the result set.
-
Save the
extraRendition_definitions.hdafile.
24.3.2.3 Enabling a Rendition Set
After a rendition set is added to the extraRendition_definitions.hda file, it must be made available as an option in the Image Rendition Set field on the Content check-in Form, using Configuration Manager.
To add the name of the rendition set as an option in Configuration Manager:
24.3.3 Working with XMP and EXIF Data
Most digital images have data associated with them by the hardware or software used to create them. For example, digital photographs have the date they were created and the camera used to create them associated with them, among other things. Digital files such as those created with Adobe Photoshop have a greater set of metadata associated with them. The metadata associated with digital photographs is called EXIF data, which stands for Exchangeable Image File Format. It is a subset of the type of data created by computer applications such as Adobe Photoshop. The application metadata is called XMP data, which stands for EXtensible Metadata Platform.
By default, Inbound Refinery is now configured to send EXIF and XMP data to Content Server, where it is indexed and available for searching as text.
24.3.3.1 Searching XMP and EXIF Data in Content Server
By default, XMP schema and EXIF data are extracted by Inbound Refinery and passed to Content Server. Content Server then displays the data on the Image Data tab of a digital asset.
If OracleTextSearch is installed and enabled, the data is indexed and available for searching through a full-text search. To enable searching on a specific criteria in the XMP or EXIF metadata, a placeholder field must be enabled on the Content Server user interface and the search collection must be rebuilt. When done, users can search for content using the specific criteria in the data.
To enable an XMP or EXIF data field on the user interface and make the specific criteria available for searching:
24.4 Setting Up and Managing Video Conversions
Digital Asset Manager requires a third-party conversion application to render video assets checked in to Content Server. Digital Asset Manager is designed to work with Telestream’s Vantage (http://www.telestream.net/vantage/overview.htm). You can also use command-line interface tools to create video rendition sets.
This section has the following topics:
24.4.1 Installing Vantage
The instructions to install Vantage are available on the Telestream website.
Visit http://www.telestream.net/ for information on how to install Vantage.
Note:
Visit http://www.telestream.net/ for the latest information relating to Vantage.
Due to the demand on computer resources required for rendering video assets, it is recommended that Vantage and Inbound Refinery be installed on separate server-class systems. For ease of access, it is also recommended that both servers have a duplicate user list of administrators.
The Vantage license must include:
-
Metadata handling
-
Closed captioning handling and analysis
-
Any in or out transcoding requirements
24.4.2 Setting the Shared Directory Path for Vantage
If you have three Vantage workflows: WMV, WebSmall, and WebBig, create the following directories:
-
For WMV:
The Watch action should watch:
\\\\VantageServer\\DAMRenditions\\WMV\in\The Deploy action should deploy to:
\\\\VantageServer\\DAMRenditions\\WMV\out\ -
For WebSmall:
The Watch action should watch:
\\\\VantageServer\\DAMRenditions\\WebSmall\in\The Deploy action should deploy to:
\\\\VantageServer\\DAMRenditions\\WebSmall\out\ -
For WebBig
The Watch action should watch:
\\\\VantageServer\\DAMRenditions\\WebBig\in\The Deploy action should deploy to:
\\\\VantageServer\\DAMRenditions\\WebBig\out\
24.4.3 Setting Media Locations
By default, Content Server uses the weblayout directory as the media location. This only requires setting a configuration variable in Inbound Refinery to point to the Content Server weblayout directory in order to use it as the media location for video.
However, video renditions can be placed in a variety of locations, such as the Content Server weblayout directory, placed on a file system for access outside of Content Server, or sent to a streaming server.
Note:
When streaming rendered videos, install and configure a supported media server based on the instructions from the media server, and set the conversion application to deliver the correct streaming format. Currently Digital Asset Manager supports Darwin Streaming Server (QuickTime), Helix Streaming Server (HelixMedia), and Windows Media Server
This section discusses the following topics regarding media locations:
24.4.3.1 Placing Renditions Within Content Server
Using the weblayout directory as the media location keeps assets within Content Server, but prevents assets from being accessed outside of Content Server. Assets stored outside Content Server can be sent to multiple locations with different access rights and different backup schedules, for example, or can be served from different media servers or web servers.
Setting Placement Location Configuration Variables details the procedure for setting configuration variables needed to specify media locations. Example 24-1 shows the configuration necessary for storing media renditions in the Content Server weblayout directory.
Example 24-1 Storing Media Renditions in the Content Server Weblayout Directory
Content Server Settings
No Content Server configuration variables need to be set when storing everything in the weblayout directory.
Inbound Refinery Settings
Set the following variable in the Inbound Refinery UCM_server1_intradoc.cfg file to point to the Content Server weblayout directory:
DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot-agentName=agentWeblayoutDir
where agentName is the IDC_Name of the Content Server and agentWeblayoutDir is the weblayout directory of Content Server, relative to the Inbound Refinery.
If Content Server is using partitions set up using File Store Provider, a configuration entry must be made for each partition. For example, if the Content Server has a partition defined as damPartition on root $#env.WeblayoutDir$/damPartition/, then the entry would be:
DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot-agentNameOnpartitionName=agentdamPartitionPath
where agentName is the IDC_Name of Content Server, partitionName is the name of the partition, and agentdamPartitionPathName is the path to the partition root, relative to Inbound Refinery.
24.4.3.2 Placing Renditions Outside Content Server
Placing assets outside of Content Server allows renditions to be accessed by other servers, such as a streaming media server or a web server. When placing assets outside of Content Server, the location of assets must be set in the configuration files of both Inbound Refinery and Content Server. A URL root must also be set in the configuration file for Content Server. The following example shows the configuration necessary for storing media renditions outside Content Server.
Note:
Both Content Server and Inbound Refinery must have physical access to the placement locations. To access any renditions outside of Content Server a separate web server must be installed and configured.
Note:
Make sure that the URL rootDefaultMediaUrlRoot is specified in lowercase otherwise the assets may not work correctly.
Example 24-2 Storing Media Renditions Outside Content Server
Content Server Settings
The following configuration setting must be set
in the Content Server intradoc.cfg file to specify
the physical and URL roots of the media location:
DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot=\\\\mediaServer/ucmmedia/ DefaultMediaUrlRoot=http://mediaServer/media/
If Content Server is using partitions set up
with File Store Provider, then each partition is a subdirectory of
the root location set in DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot. By default, Content Server will store the media to the location
specified in the DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot setting appended with the
partition name.
For example, if DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot=\\\\mediaServer/ucmmedia/ then media would be stored at:
\\\\mediaServer/ucmmedia/partitionName
Similarly, the default for the URL root set in DefaultMediaUrlRoot would be automatically appended with
the partition name. For example, if DefaultMediaUrlRoot=http://mediaServer/media/, then the media would be accessed at:
http://mediaServer/media/partitionName
A File Store Provider partition can optionally
be defined to be used as the physical and URL root by setting DefaultMediaPhysicalRootOnpartitionName and DefaultMediaUrlRootOnpartitionName. For example:
DefaultMediaPhysicalRootOnpartitionName=\\\\mediaServer2/ucmparition/ DefaultMediaUrlRootOnpartitionName=http://mediaServer2/ucmparition/
Inbound Refinery Settings
Set the following entry in the Inbound Refinery intradoc.cfg file:
DefaultMediaPhysicalRoot-agentName=\\\\mediaServer/ucmmedia/
where agentName is the IDC_Name of Content Server.
If DefaultMediaPhysicalRootOnpartitionName was set in the Content Server intradoc.cfg file, then it must also be set in the Inbound
Refinery intradoc.cfg file, so that both settings
resolve to the same location:
DefaultMediaPhysicalRootOnpartitionName=\\\\mediaServer2/ucmparition/
24.4.3.3 Placing Renditions Within and Outside Content Server
In some situations it may be useful to use the weblayout directory as the media location for most renditions but place a particular format outside Content Server. For example, you may want a .MOV rendition stored within Content Server but have the .WMV and .WMA renditions placed outside Content Server for access by a streaming media server. The following example shows the configuration necessary for storing media renditions both inside and outside Content Server.
Note:
Both Content Server and Inbound Refinery must have physical access to the placement locations.
Example 24-3 Storing Media Renditions Inside and Outside Content Server
Content Server Settings
Follow the examples specified in the Content Server section of Example 24-2 to specify the physical and URL roots of the media.
Set the following variable to specify that the .WMV and .WMA files are to be treated differently from other renditions:
WinMediaSupportEnabled=true
Set the following variable in the Content Server intradoc.cfg file to specify where to locate the .WMV and .WMA files:
WinMediaPhysicalRoot=\\\\winmediaServer/ucmRenditions/windowsMedia/ WinMediaUrlRoot=rstp://winmediaServer/ucmRenditions/windowsMedia/
Inbound Refinery Settings
Follow the examples specified in the Inbound Refinery section of Example 24-2 to specify the physical root of the media.
Set the following variable in the Inbound Refinery intradoc.cfg file to specify that the .WMV and .WMA files are to be treated differently from other renditions:
WinMediaSupportEnabled=true
Use the following variable to specify what formats to place outside Content Server:
WinMediaFormats=wmv|wma
Set the following variable to specify the location for the .WMV and .WMA files:
WinMediaPhysicalRoot-agentName=\\\\winmediaServer/ucmRenditions/windowsMedia/
Procedures for setting locations for specific formats are detailed in Configuring Specific Media Format Placement Locations.
24.4.3.4 Setting Placement Location Configuration Variables
To set the asset placement locations:
If all rendered video assets are to go to the set locations, then setting the variables in the configuration files are that is needed. To send some media formats to other locations (for example all .ra files to a streaming server or all .mpg files to an external storage system), then the locations for those formats must also be configured.
24.4.3.5 Configuring Specific Media Format Placement Locations
Different locations can be specified for differing video renditions based on the media format. Media categories are available to define physical and URL roots for different formats:
-
WinMedia
-
DarwinMedia
-
HelixMedia
-
QuickTimeMedia
-
RealMedia
These category names serve as labels only, and any format can be grouped under any category label.
In order to specify different locations for different formats, edit the intradoc.cfg files for both Inbound Refinery and Content Server to:
-
enable a category
-
specify the formats handled by the category
-
set the physical root specific to the category
For Content Server only:
-
set the URL root specific to the category
Note:
Both Content Server and Inbound Refinery must have physical access to the placement locations.
To set a different location for a specific format:
24.4.4 Using Streaming Servers
Depending on how media conversions are set, categories, and URL root variables, renditions can be served out of a web server or streaming media server. The following actions must be performed to stream rendered videos:
-
install and properly configure a supported media server based on the instructions that came with the media server
-
set the conversion application to deliver the correct streaming format
-
configure a category to deliver the rendition to the correct place
-
configure the web URL root with the proper protocol and syntax for the streaming server
Digital Asset Manager supports Darwin Streaming Server (QuickTime), Helix Streaming Server (RealMedia), and Windows Media Server. For information about protocols used with streaming media, see the media server documentation.
24.4.5 Defining Video Rendition Sets
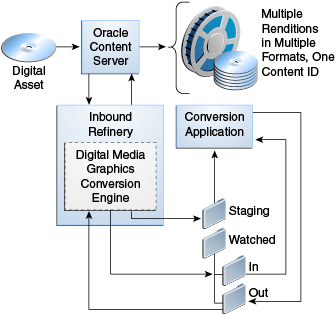
When a file is checked into Content Server, the format of the file determines if it is a digital asset. If it is a video file, Content Server passes the file to Inbound Refinery, which notifies the video conversion application a file is there to convert. The resulting renditions are then passed back through Inbound Refinery to Content Server or other specified locations, where they are managed under a single content ID and made available to the organization.
See Setting Up and Managing Video Conversions for more information about video renditions. See the Downloading Specific Video Renditions in WebCenter Content blog for information about downloading video renditions.
Figure 24-1 Rendering a Video Asset
24.4.6 Importing the WindowsMediaWorkflow.xml File
After installing Vantage, it is recommended that you import the WindowsMediaWorkflow.xml file located in the IdcHomeDir/components/DAMConverter/Vantage folder. This workflow creates all the variables, labels and style sheets required by the Digital Asset Manager integration.
-
Start the Vantage Workflow Designer.
-
Go to File, Import Workflows...
-
Select or create a category for the workflow.
-
Verify that the paths on the initial Watch Action and the final two Deploy Actions are valid in your environment.
-
Activate the workflow.
This workflow produces up to three renditions:
-
A Windows Media (wmv) rendition of the input
-
A set of keyframes for the storyboard
-
If the input has closed captions, a W3C TTML file is produced.
24.4.7 Understanding the Vantage Workflow
This section describes the main steps in the Vantage workflow for Digital Asset Manager. Each Digital Asset Manager video rendition set must be created with a separate Vantage workflow.
Each workflow starts with a Watch action. The Watch action is configured to watch the “in” directory for each rendition. After the Watch action picks up the job, the workflow splits into multiple parts. In this section, we’ll discuss the workflow for media files with both audio and video streams.
Producing the video rendition
The following is an overview of this process:
-
A Flip action creates every rendition in the rendition set. Each Flip action must set the Vantage variable "Rendition Name." This variable is the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Rendition name in the WebCenter Content user interface.
To set the Vantage variable “Rendition name”:
-
Right-click the action and select Add Variables... .
-
In the Add Variable dialog, add the "Rendition Name" variable.
-
-
Each Flip action that produces video renditions has two Identify actions; these actions identify properties about the rendition. In one Identify action the attributes for the following variables are identified:
Variable Description Movie Duration
Identifies the content duration
Video Width
Identifies the video width
Video Height
Identifies the video height
Video Framerate
Identifies the video frame rate
Video Bitrate
Identifies the video bit rate
-
The second Identify action identifies the following variable:
Variable Description File name
Identifies the file name
-
The Identify Actions feeds a Populate action. The Populate action populates variables identified by the Identify action into the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Renditions Metadata Label. The WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Renditions Metadata Label has the following fields:
Field Description RenditionName
Populated by the Vantage variable “Rendition Name”. Both video rendition and Keyframes renditions use this for identification.
FileName
Populated by the Vantage variable “File Name”. Used by video renditions.
Bitrate
Populated by the Vantage variable “Bitrate”. Used by video renditions.
Duration
Populated by the Vantage variable “Duration”. Used by video renditions.
Framerate
Populated by the Vantage variable “Framerate”. Used by video renditions.
Height
Populated by the Vantage variable “Height”. Used by video renditions.
Width
Populated by the Vantage variable “Width”. Used by video renditions.
CaptureInterval
Populated by the Vantage variable “Capture Interval”. Used by Keyframe renditions.
-
The label created by the Populate action feeds a Transform action to transform the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Renditions Metadata Label into the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Style Sheet. Inbound Refinery reads this XML attachment to get information for each video rendition of the set.
-
All Transform and/or Examine actions feed a Deploy action that copies the rendition and files created by the workflow to the "out" directory for the rendition set.
-
After the Deploy action, a Delete action deletes the original file from the "in" directory. When the workflow deletes the original file, Inbound Refinery knows the workflow is complete.
Note:
Ensure that the Delete action is set to execute regardless of the state: Right-click and select Perform On, then Any. This ensures the original file gets deleted even if the workflow has an error. In case of a workflow error, check Vantage for error message details.
Note:
Every time Inbound Refinery finishes a workflow, it checks the "in" and "out" directories for old files and deletes them. By default any file more that 1 day old is deleted. This can be changed by setting the “WatchedWorkflowOldJobCleanup'' variable. This variable accepts an integer value and one of the following suffixes: "year", "month", "week", "day", "hour", "minute", "second". For example, if you want files to be considered old after 3 hours, set WatchedWorkflowOldJobCleanup to 3hour.
Producing the optional storyboard
The following is an overview of this process:
-
A Flip: JPEG Keyframe action is needed to produce the storyboard. This Flip action sets the following variables:
Variable Description Rendition Name
Set to Keyframes.
KeyFrameInterval
Set to the interval to capture the image. For example, if the storyboard on the user interface should have an image every 5 seconds, set this variable to 00:00:05:00 29.97 fps.
Configure JPEG Setting
Capture Mode must be set to "Repeating Keyframes" and the Capture Interval must be bound to the "KeyFrameInterval" variable.
-
The Flip: JPEG Keyframe feeds a Populate action. The Populate action populates variables identified by the previous action into the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Renditions Metadata Label. Note that not all the variable in the label are used.
-
The label created by the Populate action feeds a Transform action to transform the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Renditions Metadata Label into the WebCenter Content Digital Asset Manager Style Sheet. Inbound Refinery reads this XML attachment to get information about the story board for the rendition set.
Producing the optional closed captions
If the rendition set is expected to produce text from the closed captions, an Examine action is required following the Watch action. An Examine: Examine media video and audio action produces a W3C TTML attachment that is deployed by the Deploy action.
24.4.8 Managing Video Conversion
Content Server identifies content items as digital assets based on the extension of the file checked in. At installation, Digital Asset Manager checks to see if the file formats exist in the Content Server Configuration Manager applet.
This section discusses the following topics:
24.4.8.1 Editing the Video File Type Configuration Table
If you add a file format and map the extension to the Digital Media Video conversion engine, and need that format to play in an embedded player (such as on the Rendition Information page), the extension must exist in the Video File Type configuration table of the IdcHomeDir/components/DAMConverter/resources/dam_cfg_tables.htm file.
The format must exist in the Video File Type configuration table only for the file to play in an embedded player. If the format is not in the table, the rendition can still be opened and played in a standalone player that supports the rendered format.
To verify that the added format exists in the Video File Type configuration table, open the dam_cfg_tables.htm file in a standard browser and review the file extensions listed. If the file extension does not exist, write a custom component listing the extension and additional necessary information and merge the tables. For more information about creating custom components, see Developing with Oracle WebCenter Content.

The following table lists the columns of the Video File Type configuration table and their function.
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
|
fileExtension |
The extension of the file formats to be supported played in the embedded players. |
|
formatName |
The name of the format associated with the extension. This value corresponds to the values in the Video Format Prefs table, which is configurable, and is displayed in the choice lists of the embedded players. |
|
player |
The player that supports the added format extension. The values are case-sensitive. Currently only three values are allowable:
|
|
metafileExtension |
The metafile extension associated with the format extension, used to determine what embedded player will play a streaming version of the format. There must be a value in this field if the format is streamed. |
24.4.8.2 Setting the Default Video Format Preferences
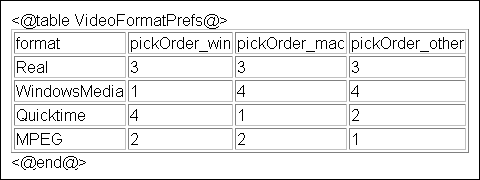
Embedded players are displayed on the Rendition Information page or when a web-viewable link is clicked. The format chosen to play in the embedded player is based on a table of user preferences regarding available rendition format options, set on the Video Preferences page. Prior to user input, default preferences are based on values set in the Video Format Preferences table of the IdcHomeDir/components/DigitalAssetManager/dam_cfg_tables.htm file.
IdcHomeDir/components/DigitalAssetManager/
To add new settings or modify default preferences, create a custom component containing the new or modified settings and merge the custom data table into the corresponding default data table. For more information about creating custom components, see Developing with Oracle WebCenter Content.
Note:
Do not edit a standard Content Server component resource directly. Always create a custom component to merge changes into Content Server or Inbound Refinery.
Modifications made to a component resource are overwritten if Digital Asset Manager is updated to a newer version.
The following table lists the columns of the Video Format Preferences table and their function:
| Column Name | Definition |
|---|---|
|
format |
Configurable name displayed in the choice list of an embedded player. |
|
pickOrder_win |
Determines the order a format is selected on a Windows operating system. |
|
pickOrder_mac |
Determines the order a format is selected on a Macintosh operating system. |
|
pickOrder_other |
Determines the order a format is selected on an operating system other than Windows or Macintosh. |
24.4.9 Using the Command-Line Interface (CLI) Tool for Video Rendition Sets
Starting with the 12c release, Digital Asset Manager allows the use of command-line interface (CLI) tools to produce video rendition sets.
To produce video rendition sets, define the video renditions in the file IntradocDir/data/configuration/dam/extraRendition_definitions.hda just like image renditions. For more information, see Creating and Configuring Image Rendition Sets.
This section contains the following topics:
24.4.9.1 Creating Video Renditions with CLI Tool
To produce video rendition sets, define the video renditions in the file IntradocDir/data/configuration/dam/extraRendition_definitions.hda just like image renditions.
The following is an example extraRendition_definitions.hda that defines a WMV rendition set that uses FFmpeg to create a Windows Media rendition and a set of keyframes that are 4 seconds apart:
@Properties LocalData
FFMpegPath=/path/ffmpeg.exe
@end
@ResultSet WMV
6
extRenditionName
extEngine
extType
extSourceFile
extParameters
extDescription
WinMedia
<$FFMpegPath$>
video|outputExtension=wmv
<$InFilePath$>
-i "<$inFile$>" "<$outFile$>.wmv"
Windows Media
StoryBoard
<$FFMpegPath$>
keyframes|frameIntervalSeconds=4,outputExtension=png
<$InFilePath$>
-i "<$inFile$>" -vsync 1 -r 0.25 -s 320x240 -f image2 "<$outDir$>\keyframe%03d.png"
unused description
@end24.4.9.2 Gathering Video Metadata Using CLI Tool
You can get the video properties of each video rendition using the command-line interface (CLI) tool. This ensures that Inbound Refinery and Digital Asset Manager return all the data about a video rendition that the Content Server user interface expects to display.
The following is an example extraRendition_definitions.had file:
@Properties LocalData
MediaRenditionInfoPath=D:/3rdParty-Bin/MediaInfo_CLI_0.7.67_Windows_i386/MediaInfo.exe
MediaRenditionInfoParameters=--Output=XML -f <$mediaPath$>
MediaRenditionInfoNodeMap=MediaInfoNodeMap
@end
@ResultSet MediaInfoNodeMap
2
mediaInfoKey
mediaXmlNodeName
bitrate
Bit_rate
duration
Duration
framerate
Frame_rate
height
Height
width
Width
@end