Per-CPU Data for Aggregations
DTrace offers the option to gather per-CPU data for aggregations. This capability can be useful when the combined aggregation data does not provide sufficient resolution. For example, the intrstat command uses per-CPU aggregation data to report statistics about CPUs that handle interrupts for each device. You can enable the collection of per-CPU aggregation data by setting the aggpercpu option.
When per-CPU aggregation data is collected, the dtada_percpu array in the dtrace_aggdata structure references the location to store the collected data. The dtada_data member of that structure references the location to store the total aggregation data. The following figure shows the per-CPU aggregation.
Using Per-CPU Data for Aggregations
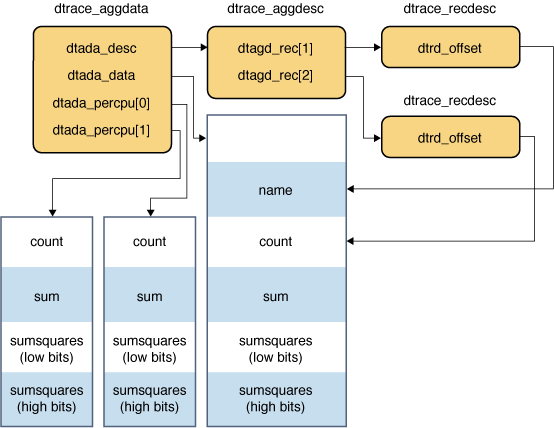
You do not need an offset to index these buffers because the first two fields in the dtada_data buffer are not duplicated in the per-CPU buffers. You can add the following code to the end of the Using the walk() Function, to examine the data in the per-CPU buffers.
if (!data->dtada_percpu)
fatal("No per-cpu data\n");
for (i = 0; i < g_max_cpus; i++) {
if (!g_present[i])
continue;
count = *((uint64_t *)(data->dtada_percpu[i]) + 0);
sum = *((uint64_t *)(data->dtada_percpu[i]) + 1);
sumsquares = *((uint64_t *)(data->dtada_percpu[i]) + 2);
avg = (double)sum / count;
avgsquares = (double)sumsquares / count;
stddev = sqrt (avgsquares - avg * avg);
if (count)
printf("%11s %2d %10lu %17.3f %17.3f\n", "CPU", i,
count, avg, stddev);
else
printf("%11s %2d %10lu %17s %17s\n", "CPU", i,
count, "-", "-");
}
printf("\n");The variable g_max_cpus is set to make a call to the sysconf() function. Because the value might be larger than the number of CPUs present, the entries in the g_present array are set to indicate whether a particular CPU is present. The function iterates over the set of possible CPU IDs. If a CPU is present, the function extracts and processes this data from the per-CPU buffer.
When this version of the consumer is run by using a D program to measure the standard deviation of system call latency, the output displays the overall values and the per-CPU breakdowns; as shown in the following example.
NAME COUNT AVG STDDEV
brk 30 3811.167 3460.861
CPU 0 16 3350.438 2969.729
CPU 1 14 4337.714 3881.644
clock_gettime 3 1694.000 501.488
CPU 0 3 1694.000 501.488
CPU 1 0 - -
close 5 5091.800 1613.886
CPU 0 0 - -
CPU 1 5 5091.800 1613.886
fchmod 1 3994.000 0.000
CPU 0 0 - -
CPU 1 1 3994.000 0.000
fcntl 3 1445.333 482.400
CPU 0 0 - -
CPU 1 3 1445.333 482.400
fsat 3 31520.000 6722.756
CPU 0 0 - -
CPU 1 3 31520.000 6722.756
fstat64 3 2520.667 537.064
CPU 0 0 - -
CPU 1 3 2520.667 537.064