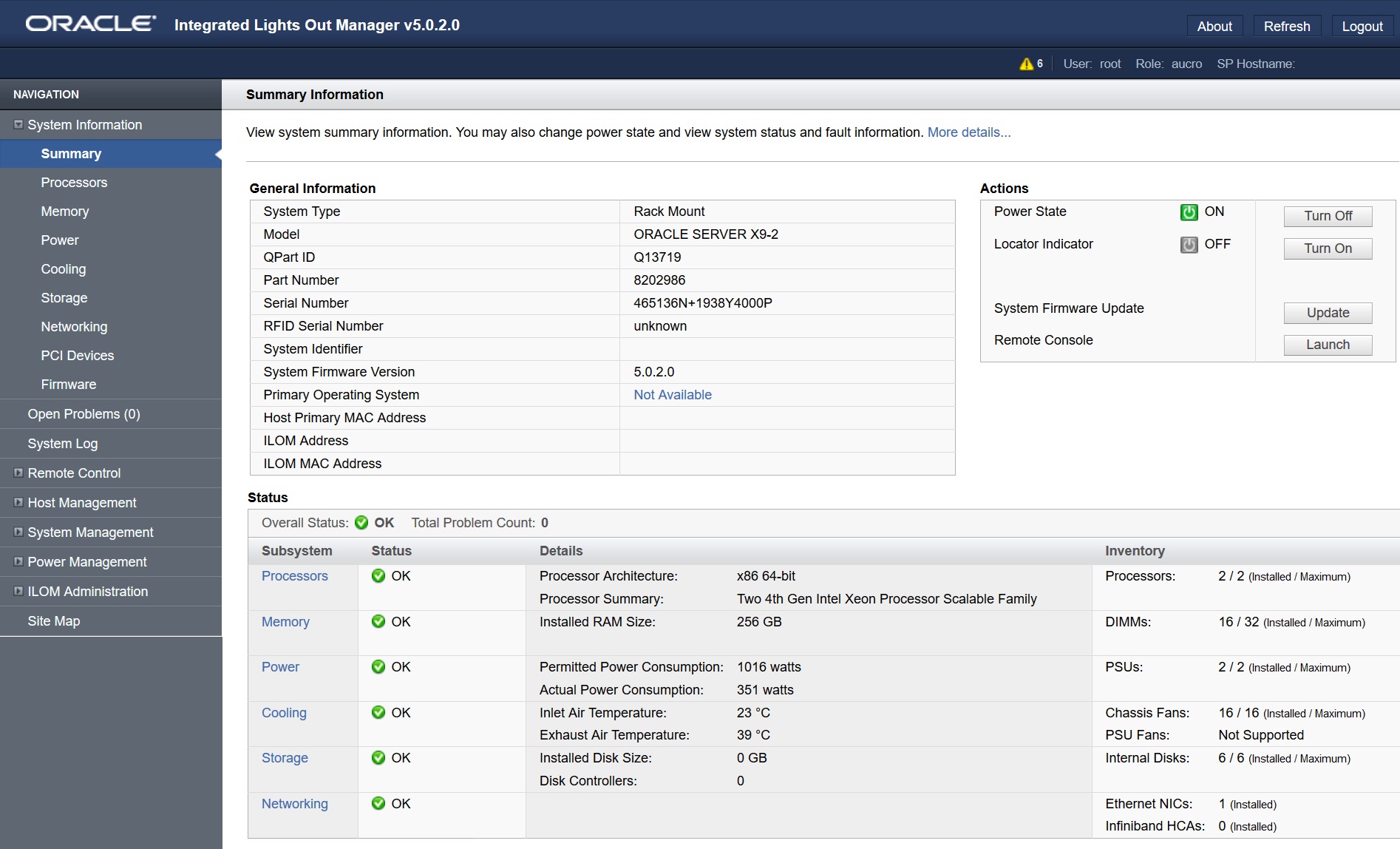
Using Oracle ILOM
Oracle ILOM can be used to configure the system and to monitor the health of the system. It is firmware embedded on the service processor, and does not need to be installed. You can access Oracle ILOM any time the system is connected to power, whether the host is operational or not.
You can access Oracle ILOM locally or remotely using a web interface or a command-line interface (CLI). To get started, see the following sections:
Oracle ILOM Connection Options
Before you can access Oracle ILOM, you must cable the server for a remote network management connection or a local serial management connection. You have the following options for establishing a management connection to the server service processor.
| Management Connection | Management Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Dedicated Local Management Connection |
SER MGT |
|
|
Dedicated Network Management Connection |
NET MGT |
|
|
Shared Sideband Network Management Connection |
NET0–NET3 Note: The number of ports varies depending on the server model. |
|
|
Host-to-ILOM Interconnect |
Internal |
A communication channel known as the Host-to-ILOM Interconnect enables communication between the host OS and Oracle ILOM without the use of the network management port. The Host-to-ILOM Interconnect is particularly useful when you want to perform these Oracle ILOM tasks locally:
|
Logging In to Oracle ILOM
You can physically connect to the SP using a serial connection or a network connection. The network connection can be configured to use a static IP address or DHCP (the default). Optionally, the servers can use an in-band network connection to the service processor, rather than the default out-of-band NET MGT port.
You can log in to the Oracle ILOM command-line interface (CLI) locally using the RJ-45 serial management port (SER MGT). You also can log in to the Oracle ILOM web interface or CLI remotely using one of the network ports on the server.
To log in to Oracle ILOM, follow these procedures:
Note:
Oracle ILOM is shipped with a default administrator account and password that allows first-time login and access. The default account isroot and the password is changeme. To build a secure environment and to enforce user
authentication, you must change the default password for this account. If this default
Administrator account has since been changed, contact your system administrator for an
Oracle ILOM user account with Administrator privileges.
Note:
To prevent unauthorized access to Oracle ILOM, create user accounts for each user. For details, see Establishing User Accounts and Roles.