Learn About Using Rackware for Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer Workloads
Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer is a fully managed, rack-scale infrastructure that is available in a cloud connected OPEX model. Oracle Private Cloud Appliance is a rack-scale engineered system – CAPEX, that you can purchase with the same OCI APIs, SDKs, compute, storage, and networking just like Compute Cloud@Customer and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Both these systems enable you to develop once and deploy anywhere while also meeting data residency requirements.
In this solution, you learn how configure backup and recovery for your Compute Cloud@Customer workloads for these use cases:
- Migrate one or more virtual machines (VMs) from older Private Cloud Appliances to the latest machines.
- Back up one or more virtual machines from Private Cloud Appliance to Compute Cloud@Customer.
- Configure disaster recovery (DR) between two Compute Cloud@Customer environments.
Note:
This content is provided for informational purposes and self-supported guidance only. Consultancy or other assistance related to the content is not covered under the Oracle Support contract or associated service requests. If you have questions or additional needs, then please reach out to your Oracle Sales contact directly.About Rackware
Rackware CloudMotion and CloudProtect deliver the capabilities to perform one-time migration of systems from both bare metal and virtual machines to virtual machines located in any cloud environment as well as the ability to perform single system backup/restore operations as well as complete disaster recovery preparation and restore capabilities.
Rackware CloudProtect is a highly automated cloud management and disaster recovery solution that allows enterprises to assess, migrate, and protect workloads in cloud and hybrid cloud environments. Rackware capabilities include migration of Linux and Windows workloads to and from a wide variety of cloud environments including Compute Cloud@Customer, Private Cloud Appliance, and OCI.
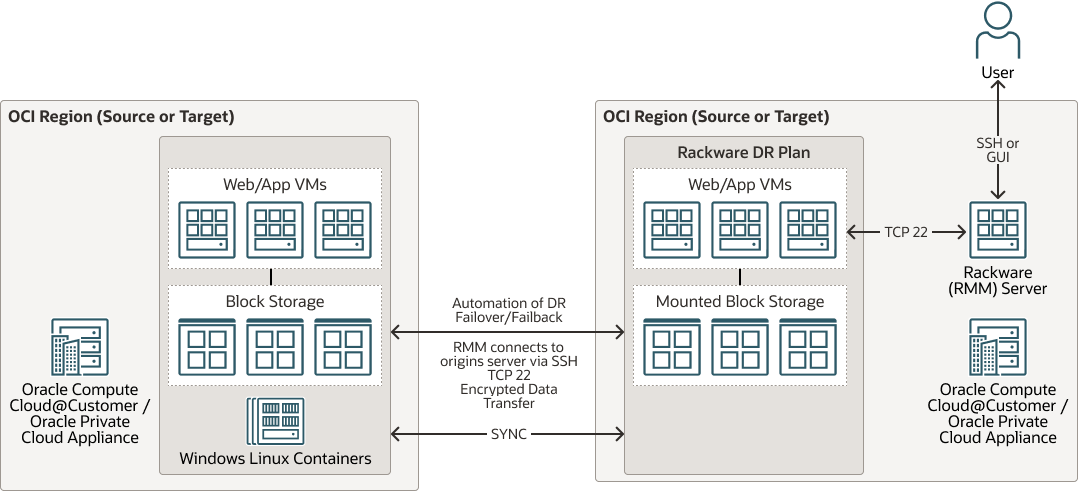
Architecture
This architecture shows the topology and ports that must be opened when RMM
performs a migration and a Capture/Sync operation to a
physical or virtual server in the target environment.
This architecture supports the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
Rackware allows seamless interoperability, migration, backup, and disaster recovery between any Oracle Cloud environments, including:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer
- Oracle Private Cloud Appliance
- Oracle Cloud Machine (or Oracle Cloud@Customer Gen 1)
RMM provides other features like selective filesystem syncs, file and folder
exclusions, enabling cloud-init, and custom post-scripts.
You can protect data using simple backup and recovery as well as more complex complete disaster recovery scenarios. Rackware CloudProtect features include:
Disaster Recovery: CloudProtect facilitates disaster recovery by providing the ability to replicate and recover critical workloads and data in cloud environments. This ensures business continuity in the event of on-premises outages or disasters.
Multicloud Support: Rackware supports multiple cloud platforms as well as on-premises and hybrid cloud configurations, allowing organizations to adopt a multicloud, multipremise strategies. This flexibility enables you to choose the solution that best suits your business needs.
Automated Cloud Migration: CloudProtect offers automation tools for migrating workloads from on-premises environments to the cloud. This includes features for optimizing resource allocation and ensuring a smooth transition.
Orchestration and Automation: Orchestration features enable the automation of complex workflows, making it easier to manage and deploy applications across hybrid cloud and multisite environments.
Backup and Recovery: CloudProtect includes converged backup and recovery capabilities to protect data and applications. This involves regular backup schedules and the ability to restore data to specific points in time.
Considerations
Backup and disaster recovery are related concepts but serve different purposes in ensuring the continuity and protection of data and systems. The key differences between backup and disaster recovery are as follows:
Purpose
- Backup: Create a copy or snapshot of data at a specific point in time. Backups are intended to provide a means of restoring data in case of accidental deletion, data corruption, or other data loss events.
- Disaster Recovery: Restore an entire system or environment in the event of a significant disruption or disaster. It involves more comprehensive planning and strategies to ensure the continuity of business operations.
Scope
- Backup: Backup typically involves copying and storing data, files, or configurations. It may include regular, incremental, or full backups of specific data sets or systems. It is often restricted in scope to a single machine, or a view.
- Disaster Recovery: Disaster recovery encompasses a broader scope, involving the restoration of entire data centers, systems, networks, and applications. You can recover the overall IT infrastructure to a functional state after a major incident.
Timeframe
- Backup: Backups are often performed regularly, ranging from daily to more frequent intervals, depending on your organization's policies and data criticality.
- Disaster Recovery: Disaster recovery plans are designed to be implemented in the aftermath of a significant incident. It involves a more extended timeline compared to the relatively quicker process of restoring individual files from backups.
Data Retention
- Backup: Backups are usually retained for a specified period, providing a historical record of data changes over time. Older backups may be archived or rotated based on retention policies.
- Disaster Recovery: While data retention is a consideration in disaster recovery planning, the focus is on the recovery of the most recent and consistent version of the entire system to minimize downtime.
Recommendations
Business Impact Assessment
- Evaluate the criticality of data and systems to the business.
- Understand the financial, operational, and reputational impact of potential data loss.
Data Classification and Prioritization
- Classify data based on importance and sensitivity.
- Prioritize systems and data with higher business impact for more frequent backups and lower RPO.
Compliance Requirements
- Identify regulatory and compliance standards applicable to the organization.
- Ensure RPO and RTO objectives align with compliance requirements for data protection and recovery.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
- Consider the time required to restore systems and data (RTO).
- Align RPO and RTO objectives to achieve comprehensive recovery planning.
Application and System Dependencies
- Understand dependencies between applications and systems.
- Coordinate RPO and RTO objectives to maintain consistency across interconnected components.
Resource Constraints
- Assess the available resources for backup and recovery processes.
- Balance RPO and PIT objectives with resource limitations, considering costs and infrastructure capacity.
Data Change Rates
- Analyze the rate at which data changes within systems.
- Adjust backup frequency and RPO based on the dynamic nature of data to minimize potential loss.
Technology Stack
- Consider the technology stack and infrastructure in use.
- Ensure compatibility between backup solutions, system architecture, and the chosen RPO and RTO objectives.
Testing and Validation
- Regularly test backup and recovery processes.
- Validate that RPO and PIT objectives are achievable and effective in real-world scenarios.
Communication and Stakeholder Involvement
- Engage key stakeholders, including business leaders and IT teams.
- Communicate RPO and RTO objectives clearly and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
Continuous Improvement
- Establish a framework for continuous review and improvement.
- Adapt RPO and RTO objectives based on evolving business needs, technological advancements, and lessons learned from past incidents.
The design and philosophy of Rackware's CloudProtect software embodies these principals. At the lowest level, Rackware's CloudProtect replicates a single machine which maps to a one-time backup. You can then group multiple VM instances together into a Wave to for a wide use, once, point-in-time copy of your data and systems. You can then build waves into several end solutions such as one-time migration or one-time backup.Then combine these waves with disaster recovery policies such as schedule, frequency, retention policies, failure or success notifications to create DR Waves. DR Waves implement regular backup and synchronization between an origin and target environment.
Consider these factors to design and implement a useful set of both Backup policies and a complete DR plan for your enterprise. The integration of new technologies such as Distributed Cloud in the form of Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer, Oracle Private Cloud Appliance, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and complete solutions such as Rackware's CloudProtect into your existing policies can make your strategy robust and resilent.
Note:
The design and construction of backup policies and disaster recovery best practices is outside the scope of this solution playbook.About Required Services and Roles
This solution requires the following services and roles:
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
-
Oracle Private Cloud Appliance
-
Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer
- Oracle Linux 7.x and 8.x
- Oracle Database 19C
- Rackware Management Module (RMM)
These are the roles needed for each service.
| Services Name: Role | Required to... |
|---|---|
Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure: sysdba |
Close, shutdown, and unmount the standby database in the cloud. |
Oracle Private Cloud Appliance: Compute Enclave |
Create network, compute, and storage constructs. |
Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer: administrator |
User on Oracle Compute Cloud@Customer with Administrator permissions to configure and deploy Oracle Linux Instances, complete access to resources such as compute, network, observability and management services. |
Rackware Management Module (RMM):
administrator |
Install and migrate workloads into RMM. |
OCI: administrator |
Complete access to resources such as compute, network, observability and management services, including the configuration of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage utilized by this solution. |
OCI: security administrator |
Inspect access to resources such as compute, network, and complete access to observability and management services. |
Oracle Database: root |
Configure the primary and standalone database, instantiate and configure the standby database. |
Oracle Linux: root or user with sudo
privileges
|
Prepare origin and target environments on Oracle Linux. |
Windows: system or local user with
administrator privileges
|
Prepare origin and target environments on Windows. |
See Oracle Products, Solutions, and Services to get what you need.