ColdFusion, Java-based Edtech Platform Deployment on Oracle Cloud
After moving its student information system (SIS) to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), ComSpec has helped students, faculty, and college administrators at over 50 schools worldwide to process registrations and financial aid applications, to conduct degree audits, and to run reports up to two times faster than when the platform ran on-premises.
Deploying their platform on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure also enabled ComSpec to reduce downtime to meet software license agreements (SLAs) and contractual commitments to their customers.
Founded in 1983 in Bingham Farms, Michigan, ComSpec International works closely with college administrators, higher education consultants, and educational software managers to prepare the architecture, implementation, features, and interfaces of the company's flagship Edtech platform, EMPOWER.
Architecture
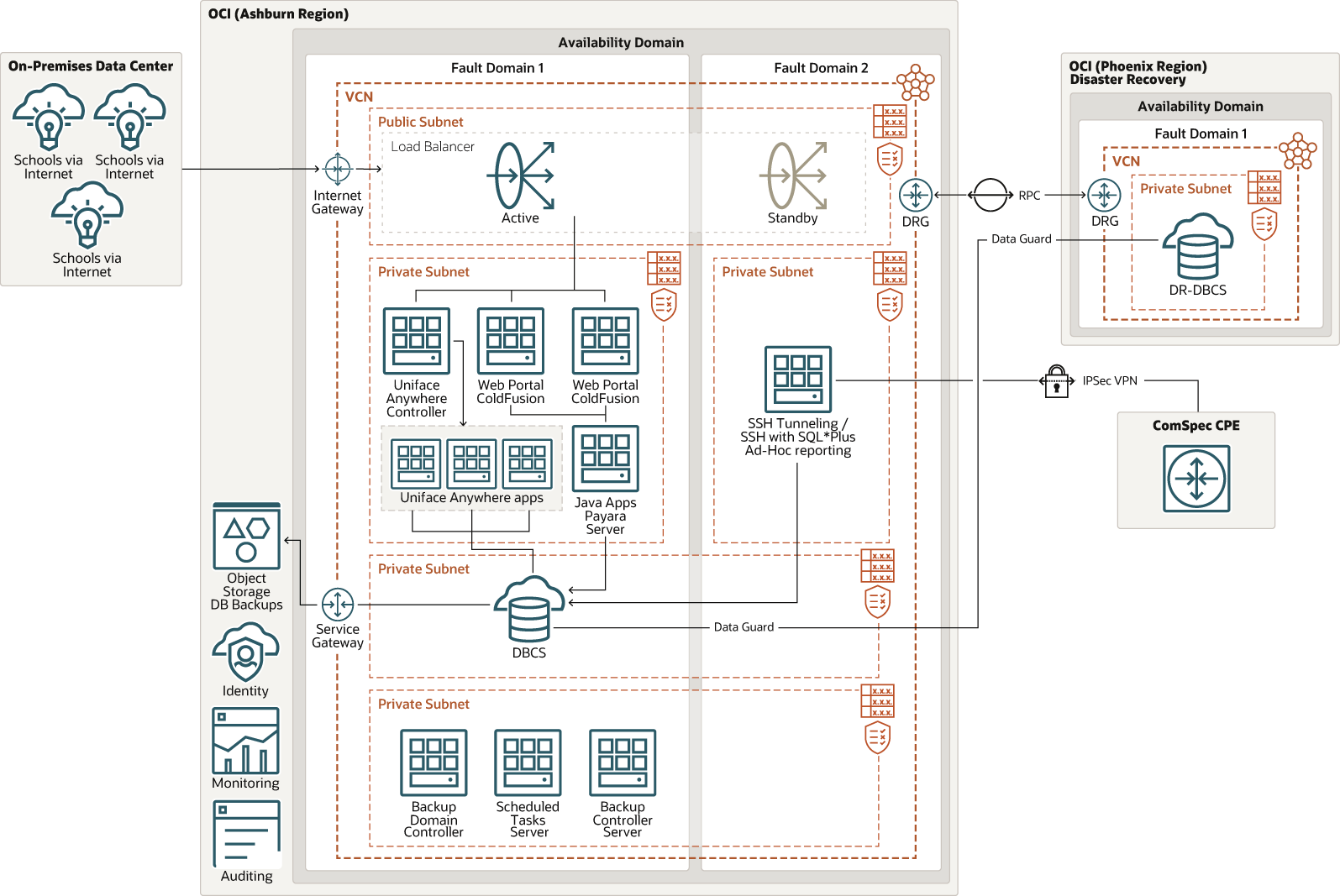
End users access the Empower SIS application through the public load balancer, which restricts access and routes the request to the servers running inside a private network.
To access ComSpec's student information system (SIS) on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, university personnel are authenticated by logging into a Uniface Anywhere controller. As users are authorized, they can then access ComSpec's three Uniface Anywhere application servers, which transfer data to and from an Oracle Database running on Oracle Database Cloud Service.
Students and university personnel can access ComSpec's web portal, ColdFusion applications, and Java applications, which also transfer data to and from the Oracle Database Cloud Service.
For reporting jobs, university personnel can log into ComSpec's ad hoc reporting server, which pulls data directly from the Oracle Database Cloud Service.
To manage this platform, ComSpec administrators connect to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure through a virtual private network (VPN) over an IPsec secure network protocol using a WatchGuard network appliance.
In ComSpec's primary site, which runs in the Oracle Cloud region in Ashburn, ComSpec has a backup domain controller, a backup controller server, a scheduled tasks server (for backup cron jobs), a database backup, and a database backup copy. For high availability, ComSpec uses Oracle Data Guard to create a replicated version of its Oracle Database in a disaster recovery site located in an Oracle Cloud region in Phoenix.
comspec-oci-architecture-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the access control plane for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Cloud Applications. The IAM API and the user interface enable you to manage identity domains and the resources within the identity domain. Each OCI IAM identity domain represents a standalone identity and access management solution or a different user population.
- Audit
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit service automatically records calls to all supported Oracle Cloud Infrastructure public application programming interface (API) endpoints as log events. Currently, all services support logging by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit.
- Monitoring
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring service actively and passively monitors your cloud resources using metrics to monitor resources and alarms to notify you when these metrics meet alarm-specified triggers.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domain
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Remote peering
Remote peering allows the VCNs' resources to communicate using private IP addresses without routing the traffic over the internet or through your on-premises network. Remote peering eliminates the need for an internet gateway and public IP addresses for the instances that need to communicate with another VCN in a different region.
- Load balancer
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing provides automated traffic distribution from one entry point to multiple servers reachable from your virtual cloud network (VCN). The service offers a load balancer with your choice of a public or private IP address and provisioned bandwidth.
A load balancer improves resource utilization, facilitates scaling, and helps ensure high availability. You can configure multiple load balancing policies and application-specific health checks to ensure that the load balancer directs traffic only to healthy instances. The load balancer can reduce your maintenance window by draining traffic from an unhealthy application server before you remove it from service for maintenance. You can create a public load balancer with a public IP address that is accessible from the internet or a private load balancer with an IP address from the hosting subnet, which is visible only within your VCN.
- Virtual Machine
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service enables you to provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it.
- Oracle Database Cloud Service
Oracle Database Cloud Service is a fully managed database service that lets developers quickly develop and deploy secure, cloud native applications. Oracle automates all tasks, such as backup and recovery, database and operating system patching, updates, and data encryption.
- Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
Get Featured in Built and Deployed
Want to show off what you built on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure? Care to share your lessons learned, best practices, and reference architectures with our global community of cloud architects? Let us help you get started.
- Download the template (PPTX)
Illustrate your own reference architecture by dragging and dropping the icons into the sample wireframe.
- Watch the architecture tutorial
Get step by step instructions on how to create a reference architecture.
- Submit your diagram
Send us an email with your diagram. Our cloud architects will review your diagram and contact you to discuss your architecture.