Design Network Architecture for Data and Application Integration Workloads on OCI
Deploy Oracle Cloud Infrastructure data integration and application integration solutions based on key networking considerations and supported architecture patterns.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is Oracle’s next-generation cloud platform that delivers a comprehensive suite of services across infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS). It offers enterprise-grade computing, storage, networking, and security capabilities, designed to support scalable, high-performance, and secure cloud solutions. Built with a focus on hybrid and multicloud strategies, OCI enables organizations to seamlessly run AI, analytics, databases, and integration workloads across diverse environments.
The OCI Integration stack encompasses data integration, application integration, and real-time replication capabilities.
- Data integration: Oracle Data Integrator on Oracle Cloud Marketplace, Oracle Integration, and Oracle Data Transforms
- Application integration: Oracle Integration
- Real-time replication: OCI GoldenGate
This tutorial will delve into key networking considerations and supported architecture patterns for deploying data integration and application integration solutions.
Integration methodologies
Data integration involves extracting data from diverse sources, applying necessary transformations, and loading it into a centralized data warehouse commonly following Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) or Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) methodologies. Once centralized, the data becomes readily accessible for analysts to drive insights using analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools.
Application integration, on the other hand, ensures real-time synchronization between disparate applications. It enables seamless communication and automated workflows by leveraging APIs, allowing systems to respond to data changes or business events in a coordinated and consistent manner.
The Oracle Integration stack encompasses a complete set of tools for enabling data and application workflows, categorized as follows:
- Oracle Data Integrator combines infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) with a pre-configured middleware environment, offering a streamlined deployment experience for data integration needs. As a powerful ELT tool, ODI is engineered for handling large-scale data integration, utilizing metadata-driven transformations and real-time synchronization to ensure seamless data flow across diverse environments.
- OCI Data Integration service is a fully-managed, cloud-native platform (PaaS) designed for seamless data ingestion, transformation, and orchestration. With its intuitive no-code interface, it empowers users to streamline complex workflows while leveraging event-driven processing for efficient, automated data movement across diverse environments.
- Oracle Data Transforms is a fully-managed PaaS solution integrated with Autonomous Data Warehouse, revolutionizing data integration with its intuitive browser-based interface. Designed for seamless cloud-based operations, it offers deep Oracle service integration, delta share support, and simplified workflows to streamline data transformation across diverse environments.
- Oracle Integration is a fully managed PaaS solution designed to streamline application and API integration. It features an extensive suite of pre-built adapters, enabling seamless connectivity across enterprise systems. With workflow automation, secure API management, and AI-powered decision-making, Oracle Integration enhances business agility by optimizing integrations and orchestrating intelligent processes.
Each tool serves distinct use cases, from data transformation and cloud pipelines to seamless application connectivity and automation.
Networking foundations
OCI Networking delivers a resilient, secure, and scalable networking foundation critical for running data and application integration workloads. These network services support both hybrid and multicloud configurations with minimal latency and high reliability. The core networking components include the following.
- Virtual cloud networks (VCNs) are customizable, logically isolated networks in OCI where you define IP ranges, subnets, route tables, and security policies.
- Dynamic routing gateways (DRGs) enables private connectivity between VCNs, on-premises networks, and third-party clouds, and acts as a centralized hub for routing traffic.
- OCI FastConnect is a dedicated, high-bandwidth connection that bypasses the public internet to connect on-premises environments or partner clouds to OCI.
- OCI Site-to-Site VPN provides encrypted IPsec tunnels for secure communication between on-premises networks and OCI over public internet.
- Remote peering connection allows secure, private communication between VCNs in different OCI regions without traversing the public internet.
- Service gateways allow VCN resources to privately access Oracle services (for example, OCI Object Storage, Autonomous Database) without internet egress.
- VCN peering enables traffic flow between two VCNs in the same region and tenancy using route tables and security lists.
For multicloud interconnect, OCI supports private connectivity to other cloud providers via integrated architectures:
- OCI to Amazon Web Services (AWS) → OCI FastConnect + AWS Direct Connect
- OCI to Microsoft Azure → OCI FastConnect + Azure ExpressRoute.
- OCI to Google Cloud → OCI FastConnect + Google Partner Interconnect
These configurations ensure secure, low-latency, and compliant data movement across cloud platforms, helping enterprises achieve true cloud interoperability.
Architecture
The provided architecture patterns, deployment steps, and connectivity models offer a blueprint for implementing efficient and future-ready cloud integration strategies.
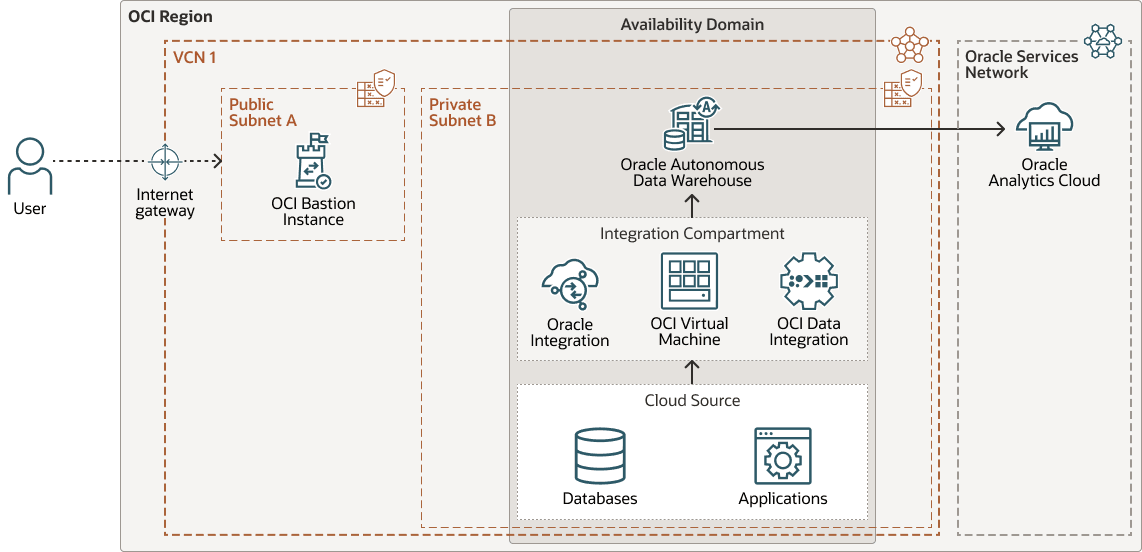
Architecture pattern 1
The source system, data integration tool, and target system are all deployed within the same subnet, either public or private, inside a single VCN in OCI. The advantages include:
- Simplified network configuration and setup
- Low-latency communication between components
- Optimized data transfer performance
- Minimal security management due to co-location
- Ideal for high-throughput, intra-VCN integration workloads
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
integration-architecture-pattern-1-oracle.zip
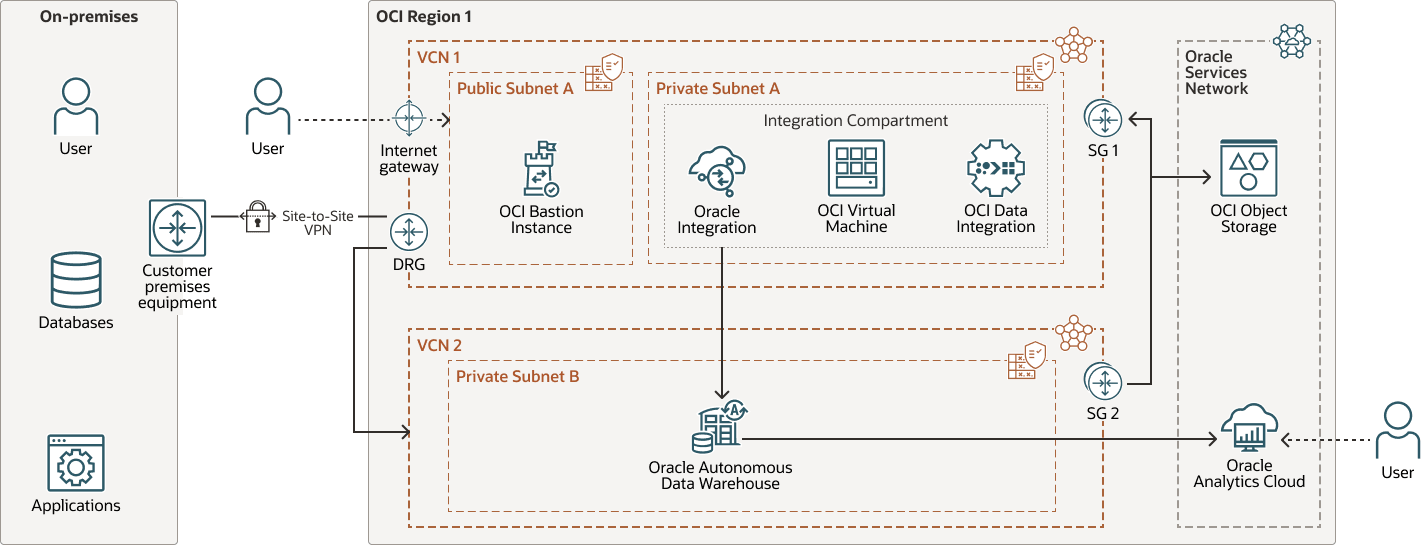
Architecture pattern 2
The source system is located on-premises, the data integration tool is deployed in a private subnet within VCN 1, and the target system resides in a private subnet within VCN 2. Both VCNs are part of the same OCI tenancy. Connectivity between the on-premises environment and OCI is established using OCI FastConnect or VPN, while VCN peering or a dynamic routing gateway (DRG) enables communication between VCN 1 and VCN 2. The advantages include:
- Support for hybrid cloud integration with secure on-premises connectivity
- Network segmentation and resource isolation across VCNs
- Secure and efficient data flow between components
- Dedicated or encrypted links for consistent performance
- Scaling for multi-tier or distributed integration workloads
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
integration-architecture-pattern-2-oracle.zip
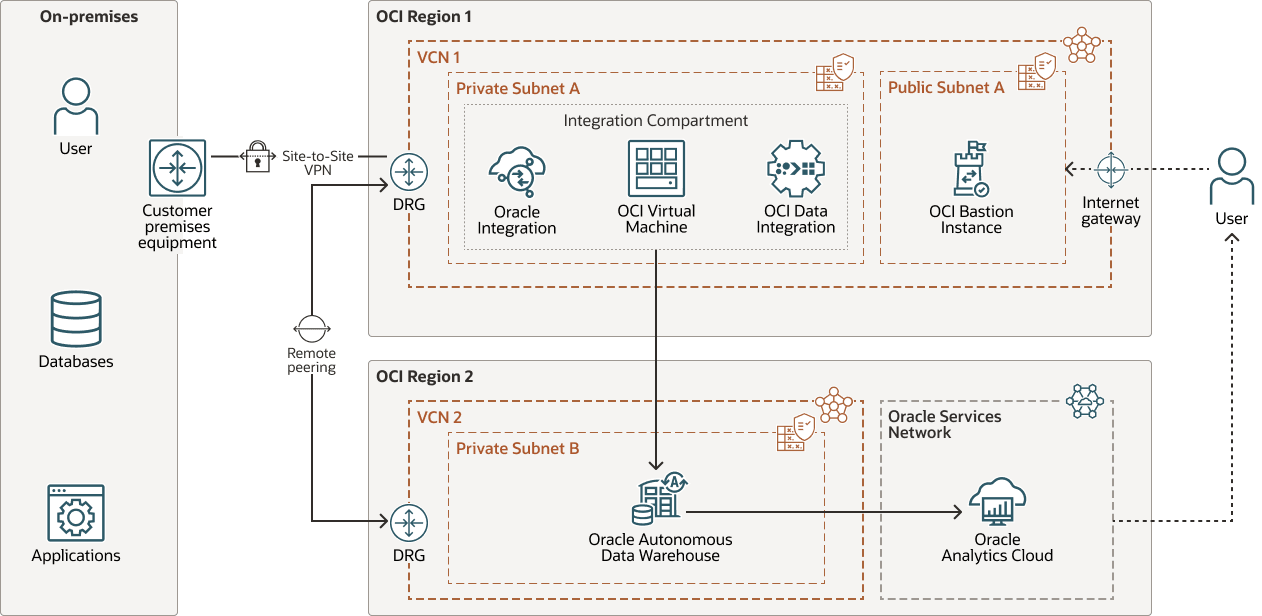
Architecture pattern 3
The source system is hosted on-premises in region 1. The data integration tool is deployed in a private subnet within VCN 1 located in region 1, while the target system and Oracle Integration reside in a private subnet within VCN 2. To enable secure communication across these distributed environments, a remote peering connection (RPC) is used to link the VCNs across different OCI regions. A DRG facilitates the routing and management of this inter-region traffic. The advantages include:
- Secure, private connectivity between different regions and tenancies
- Preventative exposure to the public internet for inter-VCN communication
- Support for high-availability, multi-region deployment models
- Scalable architecture for global integration solutions
- Network isolation while enabling seamless data exchange
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
integration-architecture-pattern-3-oracle.zip
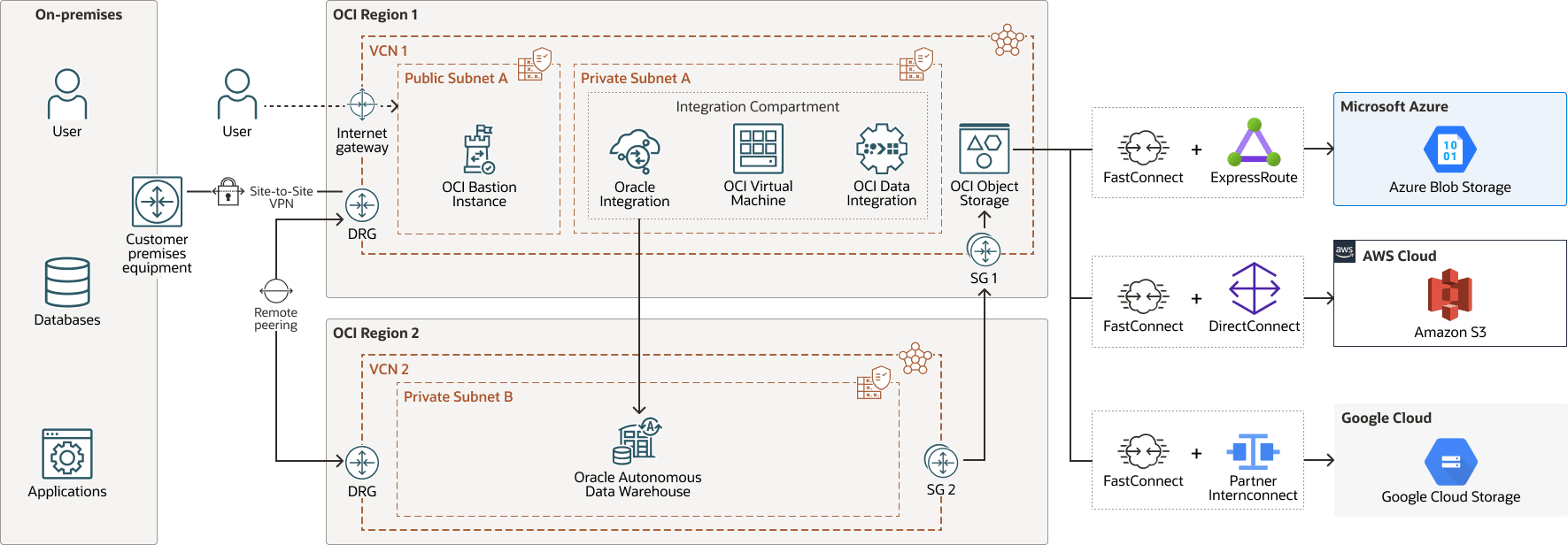
Architecture pattern 4
The source system is located on-premises in region 1. The data integration tool is deployed in a private subnet within VCN 1 in region 1, while the target system resides in a private subnet within VCN 2. The source system resides in a multicloud environment, spanning providers such as Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Seamless and secure connectivity between OCI and these cloud platforms is achieved using dedicated interconnect solutions:
- OCI to Google Cloud: OCI FastConnect + Google Partner Interconnect ensures a private, low-latency link between OCI and Google Cloud.
- OCI to Azure: OCI FastConnect + Azure ExpressRoute (private peering) enables direct, secure connectivity while bypassing the public internet.
- OCI to AWS: OCI FastConnect + AWS Direct Connect (private) provides dedicated network paths for optimized data transfer between OCI and AWS.
The advantages include:
- High-performance, private connectivity across multiple cloud platforms
- Low-latency, secure data transfer between OCI and third-party clouds
- Compliance and governance by avoiding public internet routing
- Scalable, distributed integration architectures
- Flexibility for deploying cross-platform enterprise workloads
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
integration-architecture-pattern-4-oracle.zip
OCI delivers a comprehensive and flexible integration framework supporting data and application synchronization across hybrid, multi-region, and multi-cloud deployments. By leveraging its enterprise-grade services such as Oracle Data Integrator, Oracle Data Transforms, and Oracle Integration and pairing them with robust networking constructs like DRGs, OCI FastConnect, and RPCs, organizations can implement highly secure, scalable, and resilient architectures.
The architecture has the following components:
- Dynamic routing gateway
(DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another OCI region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- OCI FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect creates a dedicated, private connection between your data center and OCI. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Internet
gateway
An internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- Local
peering
Local peering allows two VCNs within the same OCI region to communicate directly using private IP addresses. This communication does not traverse the internet or your on-premises network. Local peering is enabled by a Local Peering Gateway (LPG), which serves as the connection point between VCNs. Configure an LPG in each VCN and establish a peering relationship to allow instances, load balancers, and other resources in one VCN to securely access resources in another VCN within the same region.
- Network security group
(NSG)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of OCI you control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of virtual network interface cards (VNICs) in a single VCN.
- OCI virtual cloud
network and subnet
A virtual cloud network (VCN) is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an OCI region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Service
gateway
A service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and does not traverse the internet.
- OCI Site-to-Site VPN
OCI Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs on OCI. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Oracle
Analytics Cloud
Oracle Analytics Cloud is a scalable and secure public cloud service that empowers business analysts with modern, AI-powered, self-service analytics capabilities for data preparation, visualization, enterprise reporting, augmented analysis, and natural language processing and generation. With Oracle Analytics Cloud, you also get flexible service management capabilities, including fast setup, easy scaling and patching, and automated lifecycle management.
- Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse
Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse is a self-driving, self-securing, self-repairing database service that is optimized for data warehousing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. OCI handles creating, backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
- Bastion host
The bastion host is a compute instance that serves as a secure, controlled entry point to the topology from outside the cloud. The bastion host is provisioned typically in a demilitarized zone (DMZ). It enables you to protect sensitive resources by placing them in private networks that can't be accessed directly from outside the cloud. The topology has a single, known entry point that you can monitor and audit regularly. So, you can avoid exposing the more sensitive components of the topology without compromising access to them.
- OCI Data Integration
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Integration is a fully-managed, serverless service for designing and executing data pipelines. It enables seamless extraction, transformation, and loading of data into OCI targets like Autonomous Data Warehouse and OCI Object Storage. Users can build integration flows through a codeless, intuitive interface that auto-scales execution environments. It supports both ETL with Spark-based processing and ELT using SQL Pushdown for performance and efficiency. The service also offers tools for data preparation and protects against schema drift with rule-based handling.
- Oracle Integration
Oracle Integration is a fully-managed, preconfigured environment that allows you to integrate cloud and on-premises applications, automate business processes, and develop visual applications. It uses an SFTP-compliant file server to store and retrieve files and allows you to exchange documents with business-to-business trading partners by using a portfolio of hundreds of adapters and recipes to connect with Oracle and third-party applications.
Recommendations
Use the following recommendations when deploying data and application integration workloads on OCI.
- Architecture pattern selection
When deploying integration workloads on OCI, selecting the right architecture pattern is essential to ensure optimal performance, scalability, and security.
- Pattern 1 suits low-latency, high-throughput use cases with all components deployed within a single VCN, enabling efficient intra-cloud communication.
- Pattern 2 supports hybrid integrations, connecting on-premises systems to OCI via OCI FastConnect or VPN, with inter-VCN traffic managed through VCN peering or a DRG.
- Pattern 3 enables multi-region and multi-tenancy deployments with RPCs and DRGs, providing high availability and private connectivity across distributed environments.
- Pattern 4 is designed for multicloud scenarios, ensuring secure, low-latency integration between OCI and third-party clouds like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud using dedicated interconnect solutions.
- Networking best practices
To build a robust and scalable network architecture on OCI, it is essential to incorporate network isolation and resilient connectivity. This involves using customized VCNs with segmented subnets (public or private) to logically separate workloads and enforce access control. For secure communication, leverage OCI FastConnect for high-bandwidth, low-latency links, or OCI Site-to-Site VPN for encrypted internet tunnels. Use a DRG and RPCs for cloud-to-on-premises or inter-VCN routing, while OCI Service Gateway enable private access to Oracle services without internet exposure. Enforce security through well-defined route tables and security lists, minimizing lateral movement and safeguarding critical resources.
- OCI-managed integration services
OCI offers a robust suite of fully-managed integration services designed to address both data and application integration requirements.
- Oracle Data Integrator provides a powerful ELT framework within a pre-configured IaaS environment, ideal for high-volume data processing.
- Data Integration delivers a cloud-native, no-code platform for designing complex, event-driven data pipelines across diverse sources.
- Oracle Data Transforms, seamlessly integrated with Autonomous Data Warehouse, simplifies data transformations through an intuitive browser interface.
- For application integration, Oracle Integration enables API-driven workflows, offers a wide range of pre-built adapters, and incorporates AI-powered automation, accelerating enterprise integration initiatives.
Together, these services enable organizations to build secure, scalable, and intelligent integration flows without the burden of infrastructure management.
- Security and governance considerations
Security is a foundational element of OCI’s reference architectures, implemented through a defense-in-depth approach to safeguard data across hybrid, multi-region, and multi-cloud environments. Deployments should prioritize private connectivity using OCI FastConnect, DRGs, and RPCs to avoid exposure to the public internet and minimize risk. Network isolation via private subnets and segregated VCNs enhance access control and resource protection.
Security is further reinforced through OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM), network security groups (NSGs), and firewall policies, allowing granular access control across all layers. Adopting OCI’s Cloud Adoption Framework and well-architected design principles ensures compliance, governance, and sustained operational security.
- Monitoring, automation, and cost optimization
To ensure operational excellence, organizations should integrate continuous monitoring, logging, and automation throughout the deployment lifecycle. Utilizing OCI Monitoring's alarms, teams can proactively identify and address performance or availability issues. Regular end-to-end connectivity validation ensures seamless interaction between source, integration, and target systems, supported by optimized network configurations.
For cost efficiency, OCI recommends using the Oracle Cloud Cost Estimator for accurate budget forecasting and capacity planning, aligning resource usage with business objectives. Deployments should be routinely evaluated against the Well-Architected Framework to maintain a cost-effective, resilient, and scalable architecture. Automating reporting, alerting, and governance processes further enhances operational agility while minimizing manual errors.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Performance
The reference architectures are designed to deliver high-performance data and application integration across OCI environments. Deployments within the same VCN, particularly under architecture pattern 1, benefit from low-latency, high-throughput communication due to proximity and reduced network traversal.
In hybrid and multicloud scenarios (patterns 2 through 4), dedicated connectivity solutions such as OCI FastConnect and third-party equivalents like AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute ensure sustained bandwidth and reduced jitter, ideal for enterprise-grade ETL and ELT workloads.
Additionally, the use of event-driven orchestration in Data Integration and Oracle Integration facilitates responsive, real-time data handling. These services are architected to auto-scale and optimize parallel data flow, ensuring consistent performance even during peak data loads or process-intensive scenarios.
- Security
Security is foundational to the deployment of integration workloads on OCI, and each reference architecture integrates OCI’s layered security model.
Network isolation is achieved through private subnets and logically segmented VCNs, while secure communication is enforced using encrypted tunnels via VPN Connect or private connections via OCI FastConnect. Architecture patterns leveraging multi-region or multicloud strategies implement RPCs and DRGs to enable private, controlled traffic flow, eliminating exposure to the public internet.
Access control is fine-tuned using IAM policies, NSGs, and firewall rule sets, ensuring that only authorized users and services can interact with critical resources. This comprehensive security posture aligns with industry best practices and compliance mandates for data sovereignty and governance.
- Availability
High availability is a key design principle across all recommended architecture patterns. OCI's globally distributed infrastructure allows for resilient deployments that span multiple fault domains, availability domains, and even regions. Architecture patterns 3 and 4 exemplify this with inter-region VCN communication via RPC and DRG, enabling disaster recovery setups and geographically redundant architectures.
The use of managed services such as Oracle Integration, Autonomous Database, and Data Integration ensures enterprise-grade availability, with built-in monitoring, auto-restart, and fault tolerance. Additionally, the deployment can be further hardened by configuring health checks, fail-over routing policies, and leveraging OCI Monitoring and OCI Logging to proactively detect anomalies and ensure uninterrupted service delivery.
- Cost
Cost optimization is integral to OCI’s reference architecture strategy. By leveraging cloud-native services and deploying workloads within the same VCN (pattern 1), organizations can significantly reduce interconnect and egress costs.
OCI's pay-as-you-go pricing model, combined with tools like the Oracle Cloud Cost Estimator and the Well-Architected Framework, enables informed financial planning and architecture rightsizing. Customers are encouraged to monitor usage patterns, automate cost reporting, and explore reserved capacity or universal credits where applicable, ensuring both performance efficiency and fiscal accountability across their OCI integration deployments.
Deploy
Configure, provision, validate, and enable these architectures.
You can deploy these reference architectures on OCI by following these steps.
- Sign in to the OCI Console using your Oracle Cloud credentials.
- Set up the networking infrastructure as illustrated in the reference
architecture. This typically includes configuring components such as:
- VCNs
- Subnets (public and private as required)
- DRGs
- Route tables
- Security lists
- Service gateways
- OCI FastConnect or VPN for hybrid or multi-cloud connectivity
- Provision the required OCI services, including:
- Data Integration
- Oracle Application Integration
- Autonomous Database
- Oracle Analytics Cloud (if part of the solution)
- Validate the end-to-end connectivity between the source and target systems from within the deployed services. Fine-tune VCN settings, routing rules, and security policies based on your specific use case or access requirements.
- Enable OCI Monitoring, OCI Logging, and alarms to maintain system health. Use the Cost Estimator for growth planning and regularly review your architecture against the Well-Architected Framework for optimal performance and efficiency.
Explore More
Enhance your understanding of Oracle Cloud services and best practices with the following curated resources.
Review these additional resources:
- Oracle Data Integrator
- Data Integration in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation
- Oracle Data Transforms
- Oracle Integration 3
- Networking in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation
- Multicloud Interconnect in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation
- Multicloud Resource Hub
- Well-architected framework for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Oracle Cloud Cost Estimator
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Documentation
- Cloud Adoption Framework
- Comparing Oracle ETL/ELT Tools (blog)
Change Log
This log lists significant changes:
| November 24, 2025 | Updated diagrams and descriptions for each of the four architecture patterns to show that Oracle Integration is always deployed within Oracle Services Network (OSN):
|