Deploy Oracle E-Business Suite with Palo Alto Networks Firewall and Exadata Cloud Services
Cloud deployments of Oracle E-Business Suite provide an array of benefits, both from a technology and a business perspective. The top benefits of cloud computing, as often touted in the marketplace, are support for growth, performance and availability; thus resulting in increased business agility. It also offers lower costs and a more secure system.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) solution and certified database services offer several clear advantages over other cloud solutions. For example, Oracle provides Oracle E-Business Suite cloud automation (Cloud Manager Tool for Oracle E-Business Suite Life Cycle management) for OCI and associated database services (such as Virtual Machine DB Systems, Exadata Cloud Services or Exadata Cloud@Customer) that are not available from other vendors.
Moving Oracle E-Business Suite workloads or extending your current OCI tenancy with Oracle E-Business Suite workload on Oracle Cloud with Palo Alto Network VM-Series virtual, next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), enhances the native security options provided by OCI.
Architecture
This reference architecture describes a highly-available multi-node deployment wherein Oracle E-Business Suite Database is running on Oracle Exadata Cloud Services.
Note:
If you are just beginning your OCI journey, further details for moving your E-Business Suite workload in OCI can be found in the My Oracle Support (MOS) note Getting Started with Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Doc ID 2517025.1, referenced in the "Explore More" topic.In this architecture, an Oracle E-Business Suite workload has been deployed in a hub and spoke network topology where traffic is routed through a central hub and is connected to multiple distinct networks (spokes VCNs). The hub VCN connects to the spoke VCNs through Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG). In this scenario, hub is the combination of both the DRG and the firewall VCN.
Here, the application tier contains multiple instances of the application, in order to provide high availability. The database tier uses an Oracle Real Application Clusters database running on a Oracle Exadata Cloud Services.
The following diagram illustrates this architecture:
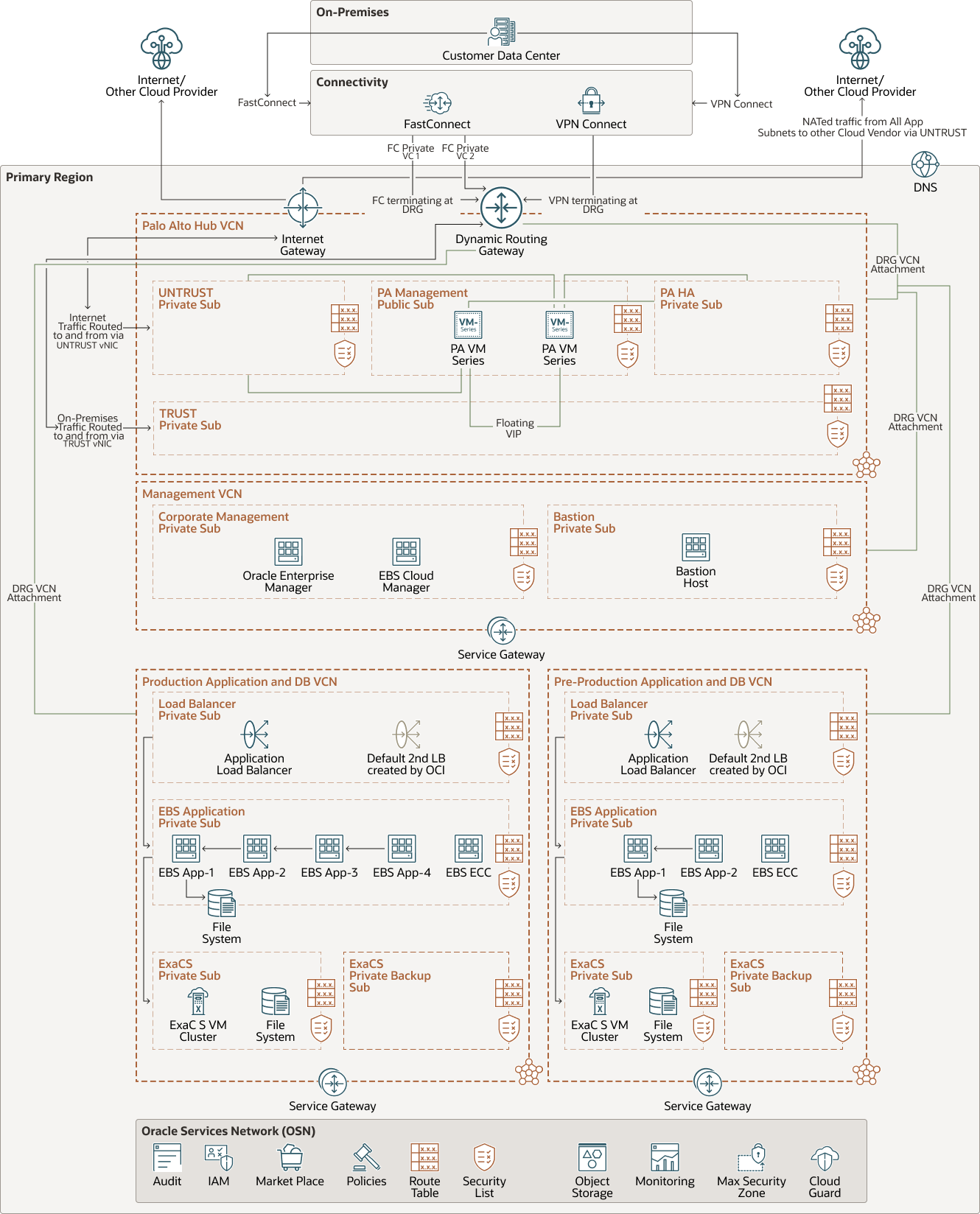
Description of the illustration ebs-pan-exacs.png
To strengthen the security posture of the tenancy, Palo Alto Networks VM Series is deployed. This will allow you to protect your workload and monitor both North-South (traffic entering your cloud network) and East-West (traffic moving within your cloud environment between VCNs) traffic. All traffic that flows either between the spoke VCNs, to-and-from the Internet, to-and-from the on-premises data center, or to the Oracle Services Network, will be routed through the hub VCN and inspected by Palo Alto Networks VM Series Firewall’s multilayered threat prevention technologies.
Logical traffic flows are depicted below:
North-South Traffic Flow Inbound:
This illustration depicts the inbound north-south traffic flow emanating from the Internet into an OCI region:

Description of the illustration ns-inbound-inet-spoke.png
ns-inbound-inet-spoke-oracle.zip
This illustration depicts the inbound north-south traffic flow emanating from the customer's on-premise data center into an OCI region:

Description of the illustration ns-inbound-prem-spoke.png
ns-inbound-prem-spoke-oracle.zip
North-South Traffic Flow Outbound:
This illustration depicts the outbound north-south traffic flow emanating from an OCI region to the Internet:
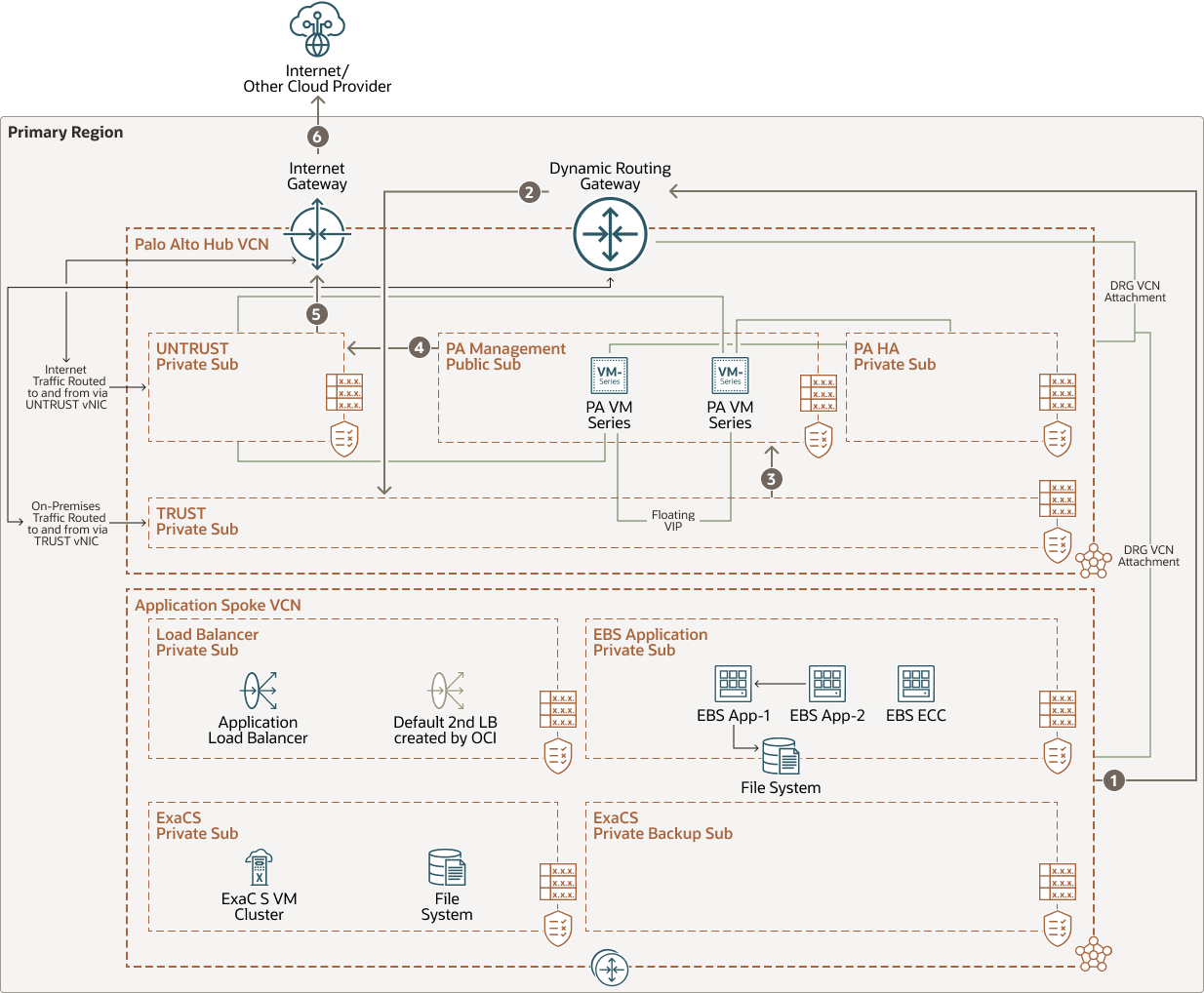
Description of the illustration ns-outbound-spoke-prem.png
ns-outbound-spoke-prem-oracle.zip
This illustration depicts the outbound north-south traffic flow emanating from an OCI region to the customer's on-premises data center:

Description of the illustration ns-outbound-inet.png
East-West Traffic Flow:
This illustration depicts the east-west traffic flow within an OCI VCN:
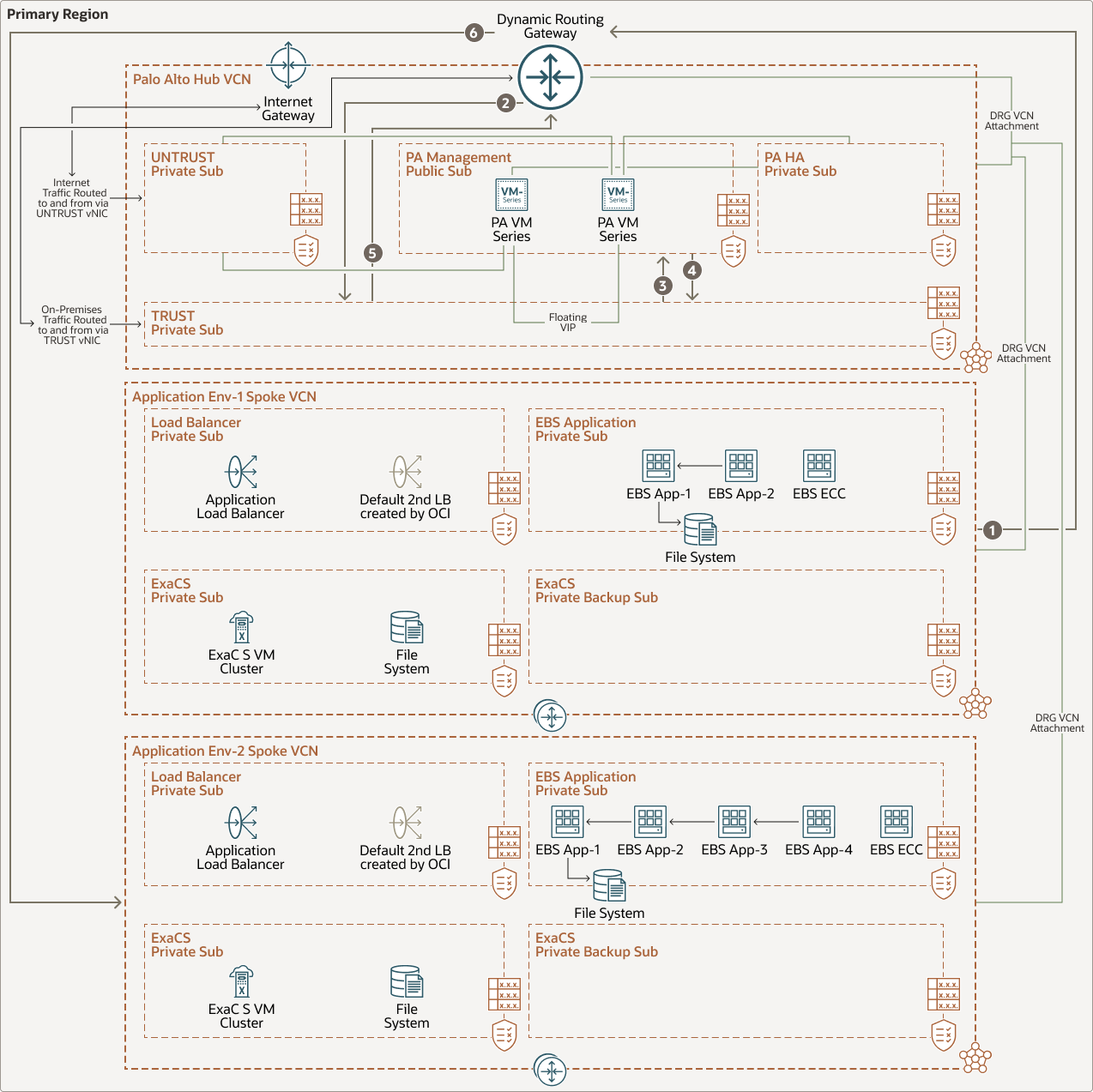
Description of the illustration ew-vcns.png
- Tenancy
When you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Oracle creates a tenancy for your company, which is a secure and isolated partition within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure where you can create, organize, and administer your cloud resources.
-
Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents). Most Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources are either region-specific, such as a virtual cloud network, or availability domain-specific, such as a compute instance.
-
Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
-
Availability domains (AD)
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
-
Fault domains (FD)
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
-
Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can either be in a single availability domain or span all the availability domains in the region (recommended). Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
-
Hub VCN
The hub VCN is a centralized network where Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewalls are deployed. It provides secure connectivity to all spoke VCNs, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services, public endpoints and clients, and on-premises data center networks.
-
Application tier spoke VCN
The Application tier spoke VCN contains a private subnet to host the Oracle E-Business Suite application stack. It also has Exadata Client and backup subnets.
-
Load balancer (LB)
The OCI Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
-
Security list (SL)
Security Lists act as virtual firewalls for your compute instances. A security list consists of a set of ingress (connections initiated from the internet) and egress (connections initiated from within the VCN) security rules that apply to all the VNICs in any subnet with which the security list is associated.
-
Route Table (RT)
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways outside a VCN (for example, to the internet, to your on-premises network, or to a peered VCN).
-
Service gateway (SG)
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to Oracle Services travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
-
Internet Gateway (IGW)
An internet gateway is an optional virtual router you can add to your VCN to allow traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
-
Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
With the new enhancement features of DRG, you can now attach the following resources:- VCNs
- Remote peering connections
- Site-to-Site VPN IPSec tunnels
- OCI FastConnect virtual circuits
-
Virtual network interface card (VNIC)
The services in OCI data centers have physical network interface cards (NICs). Virtual machine instances communicate using virtual NICs (VNICs) associated with the physical NICs. Each instance has a primary VNIC that's automatically created and attached during launch and is available during the instance's lifetime. DHCP is offered to the primary VNIC only. You can add secondary VNICs after instance launch. You should set static IPs for each interface.
-
Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
-
FastConnect (FC)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Virtual circuit (VC)
A virtual circuit is a layer-2 or layer-3 Ethernet VLAN that runs over one or more physical network connections to provide a single, logical connection between the router on the edge of your network and the Oracle router. Each virtual circuit is made up of information shared between the customer and Oracle, as well as an Oracle FastConnect partner (if you're connecting through an Oracle FastConnect partner). Private virtual circuits support private peering, while public virtual circuits support public peering.
-
Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall
Provides all the capabilities of physical next generation firewalls in a virtual machine form, delivering inline network security and threat prevention to consistently protect public and private clouds.
With the VM-Series on OCI, you can protect and segment your workloads, prevent advanced threats, and improve visibility into your applications as you move to the cloud.- The management subnet uses the management interface to allow end users to connect to the user interface.
- The untrust subnet is used to direct external traffic to or from the Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Firewall.
- The trust subnet is used to direct internal traffic to or from the Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Firewall.
- The high availability (HA) subnet ensures that VM-Sseries firewalls are in high availability.
-
E-Business Suite Application Tier
An Oracle E-Business Suite application is composed of servers and file system. In this reference architecture, it is deployed with multiple application tier nodes and caters to the application. When deploying an Oracle E-Business Suite application tier with multiple nodes, you can use either a shared or non-shared application tier file system. This architecture adopts a shared application tier file system, which reduces disk space requirements and eliminates the need to apply patches to each node in the environment.
-
Enterprise Command Centers (ECC)
Enterprise Command Centers provide information discovery along with visualization and exploration capabilities embedded within Oracle E-Business Suite user interfaces. The Oracle Enterprise Command Center Framework lets you create business dashboards in different functional areas. Oracle E-Business Suite users navigate transactional information by using interactive visual components and guided discovery capabilities allowing exploratory data analysis. Mobility and responsive design are built into the Oracle Enterprise Command Center Framework, and all dashboards automatically adjust the layout to better fit a desktop or mobile device form factor.
Oracle Enterprise Command Center Framework, including the dashboard content, automatically adheres to existing Oracle E-Business Suite security context and security. Enterprise Command Centers help Oracle E-Business Suite users to identify and act on priority transactions without custom operational reporting. ECC release V7 includes 32 command centers comprising 121 dashboards across Oracle E-Business Suite.
-
Oracle E-Business Suite database tier - Exadata Cloud Service
Exadata Cloud Services enable you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. You can provision flexible X8M systems that allow you to add database compute servers and storage servers to your system as your needs grow. X8M systems offer RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) networking for high bandwidth and low latency, persistent memory (PMEM) modules, and intelligent Exadata software. You can provision X8M systems by using a shape that's equivalent to a quarter-rack X8 system, and then add database and storage servers at any time after provisioning.
In order to provision an Exadata Cloud Services database, first you have to provision Exadata Cloud Services infrastructure and VM cluster resources separately. Along with the Infrastructure, a VM cluster, an initial database home, and database are created. You can create additional database homes and databases at any time by using the Console or the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure API.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks. When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
Oracle recommends using regional subnets because they’re more flexible. They make it easier to efficiently divide your VCN into subnets while also designing for availability domain failure.
- Security
In order to strengthen the security posture of your OCI tenancy, Oracle recommends using Cloud Guard and Security zones. You must enable Cloud Guard before you create Security zones. Cloud Guard helps you detect policy violations in existing resources that were created before the Security zone.
Cloud Guard
Cloud Guard is a cloud-native service that helps customers monitor, identify, achieve, and maintain a strong security posture on Oracle Cloud. Use the service to examine your OCI resources for security weaknesses related to configuration, and your OCI operators and users for risky activities. Upon detection, Cloud Guard can suggest, assist, or take corrective actions, based on your configuration. The following list summarizes what you need to know to get started planning for Cloud Guard:- Target: Defines the scope of what Cloud Guard checks. All compartments within a target are checked in the same way and you have the same options for processing problems that are detected.
- Detector: Performs checks to identify potential security problems based on activities or configurations. Rules followed to identify problems are the same for all compartments in a target.
- Responder: Specifies actions that Cloud Guard can take when detectors identify problems. Rules for how to process identified problems are the same for all compartments in a target.
Security zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use Security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a Security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys.When you create and update resources in a Security zone, OCI validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
- Load balancer bandwidth
While creating the load balancer, you can either select a predefined shape that provides a fixed bandwidth, or specify a custom (flexible) shape where you set a bandwidth range and let the service scale the bandwidth automatically based on traffic patterns. With either approach, you can change the shape at any time after creating the load balancer.
- E-Business Suite Cloud Manager Tool
Oracle E-Business Suite Cloud Manager is a web-based application that drives all the principal automation flows for Oracle E-Business Suite on OCI, including provisioning new environments, performing lifecycle management activities on those environments, and restoring environments from on-premises.
Oracle highly recommends all customers who intend to move their Oracle E-Business Suite workload to OCI to use this automation tool for lift and shift, provisioning, and lifecycle management. However, if our current automation offerings do not meet your specific requirements, you may use a manual procedure.
Explore More
Learn more about deploying Oracle E-Business Suite with a Palo Alto Networks firewall and Exadata Cloud Services.
Review these additional resources:
- Product and product-related documentation:
- Best practices framework for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Secure application workloads with Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Firewall
- Deploy Exadata Cloud Service with Data Guard in multiple regions
- Manage multiple Oracle E-Business Suite customers across tenancies
- Oracle E-Business Suite Cloud Manager Guide
- Overview of Enterprise Command Centers
- Basic Routing Scenarios For The Enhanced DRG
- My Oracle Support Notes:
- Getting Started with Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (Doc ID 2517025.1)
- Installing Oracle Enterprise Command Center Framework, Release 12.2 (Doc ID 2495053.1)
- Standards Used by the Oracle E-Business Suite Cloud Manager for Provisioning Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (Doc ID 2656874.1)