Deploy a MongoDB Database
MongoDB is a document-oriented database program. MongoDB is classified as a NoSQL database program and uses JSON-like documents with schema.
Architecture
This reference architecture deploys three MongoDB nodes and one MongoDB Ops Manager on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
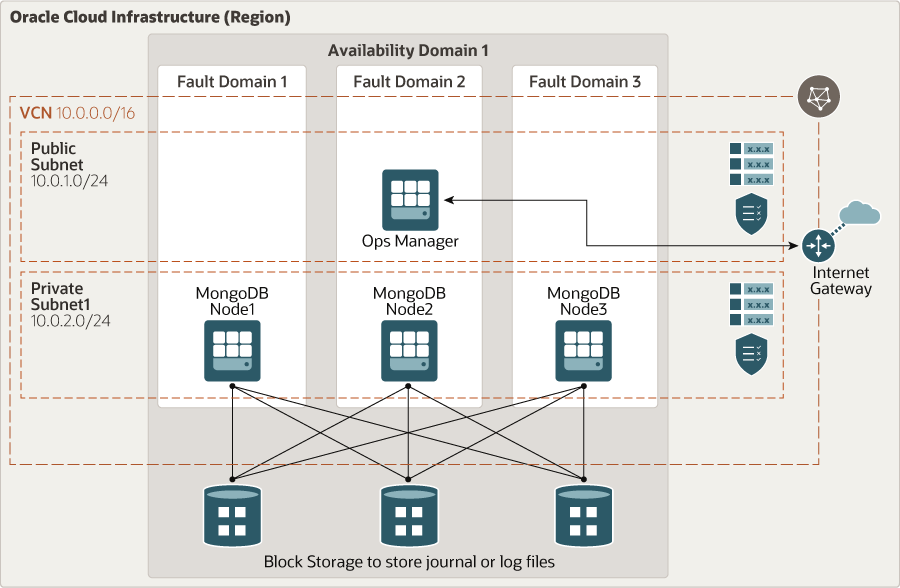
Description of the illustration mongodb-oci.png
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnet
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domain
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Ops Manager
Ops Manager manages the MongoDB deployment. It provides features that enable you to optimize clusters and reduce operational risks.
- MongoDB node
These are the Compute nodes running MongoDB.
- Block volume
With block storage volumes, you can create, attach, connect, and move storage volumes, and change volume performance to meet your storage, performance, and application requirements. After you attach and connect a volume to an instance, you can use the volume like a regular hard drive. You can also disconnect a volume and attach it to another instance without losing data.
You can use the same architecture in a region with multiple availability domains.
Recommendations
Your requirements might differ from the architecture described here. Use the following recommendations as a starting point.
- Compute shape, Ops Manager
Use a VM.Standard2.24 or higher shape (at least two virtual network interface cards, or VNICs) for higher throughput. This setup provides sufficient CPU and memory to efficiently host the Ops Manager.
- Compute shape, MongoDB node
Use a VM.DenseIO2.24 shape, which provides locally attached storage for higher I/O operations per seconds (IOPS) and up to 24.6 Gbps of networking bandwidth. Use RAID configuration (RAID 10) for better data protection on locally attached disks.
- Block volume
In addition to locally attached storage, use at least three block volumes (32 TB) using the multiple-attached feature. This addition provides more storage.
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
Use regional subnets for your deployment, regardless of the number of availability domains.
- Security lists
Use security lists to define ingress and egress rules that apply to the entire subnet.
For example, this architecture allows ICMP internally for the entire private subnet.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
- Security Zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
Considerations
- Performance
To get the best performance, choose the correct Compute shape with appropriate bandwidth.
- Availability
Consider using a high-availability option based on your deployment requirements and region. Options include using multiple availability domains in a region and fault domains.
- Cost
A DenseIO instance provides higher performance on I/O operations for a higher cost. Evaluate your requirements to choose the appropriate Compute shape.
- Monitoring and alerts
Set up monitoring and alerts on CPU and memory usage for your nodes, so that you can scale the shape up or down as needed.