About this Architecture
This architecture describes how to set up Oracle Integration 3 instances for development, test, and production and focuses on the security aspects of an implementation. See "Explore More" at the end of this playbook for a link to Set up a landing zone architecture with Oracle Integration, which focuses on Oracle Integration 3's specific services.
Set Up OCI IAM Identity Domains for Your Oracle Integration 3 Environment
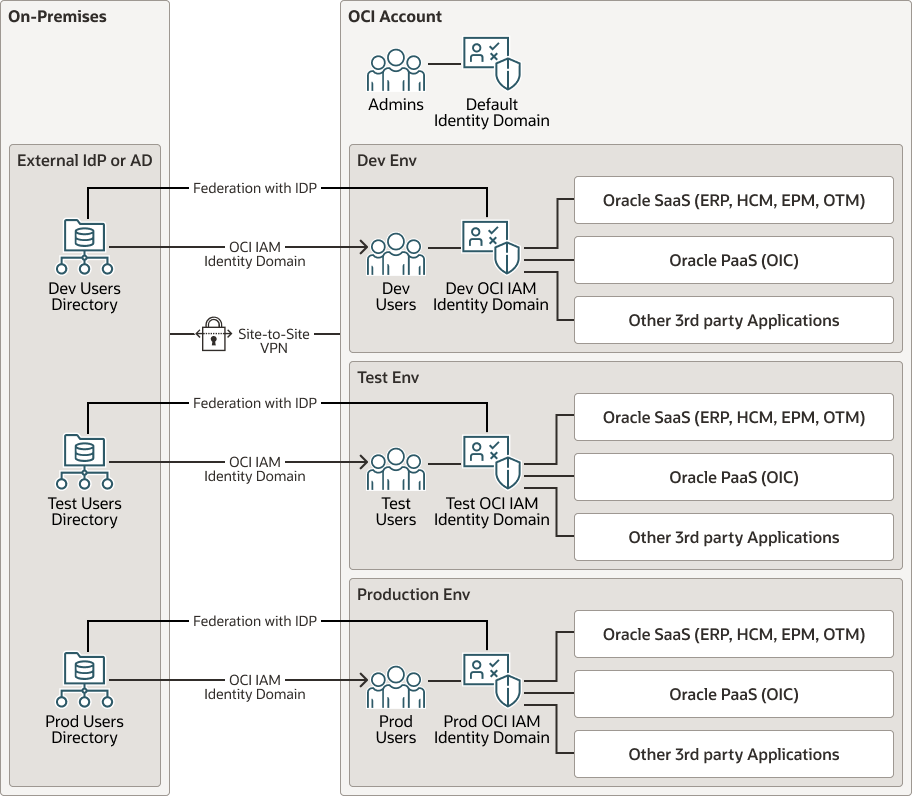
Description of the illustration oi3-ss-lz.png
You should dedicate the default OCI IAM Identity Domain to your OCI administrators, as it is not for daily use. The default OCI IAM Identity Domain, rather, is used for OCI-tenancy-level administrative tasks. Additional development, test, and production OCI IAM Identity Domains further separate the necessary environments.
The default OCI IAM Identity Domain instance is integrated with OCI services, ensuring that users and groups in your organization can authenticate and access OCI resources according to the identity policies set up in the OCI IAM Identity Domain. The cloud account administrator owns the Default OCI IAM Identity Domain and can create one or more secondary OCI IAM Identity Domain instances. In this case the development, test, and production OCI IAM Identity Domain instances for an Oracle Integration 3 deployment.
The default OCI IAM Identity Domain contains the groups created during the deployment of a landing zone.
In addition to the resources created by the landing zone, you also need to create the groups and compartments necessary to handle Oracle Integration 3 instances. The setup will distinguish between administrators allowed to create and delete an Oracle Integration 3 instance or change the compartment of an Oracle Integration 3 instances and administrators who can stop, start, and update Oracle Integration 3 instances. This setup ensures that individuals at the development, test, or production environment level cannot create or delete an Oracle Integration 3 instance. These administrators can only start, stop, or update the instances in their own compartment.
Set Up the OCI IAM Identity Domains for Your Instances
As mentioned in the overview section, in order to deploy Oracle Integration 3, you need to set up a set of OCI IAM Identity Domains for your Oracle Integration 3 instances. Within these OCI IAM Identity Domain instances, you will have specific groups with varying levels of permissions.
Understand the Naming Conventions
The naming convention within an administrator's OCI IAM Identity Domains are
oci-iam-id-dev, oci-iam-id-test,
and oci-iam-id-prod. Note that you can customize your
organization’s exact group names and permissions based on your organization’s
requirements and the specific naming conventions you follow.
Create User Groups
Within these OCI IAM Identity Domain instances, create user groups that will get different levels of permissions. The groups needed for the purpose of OCI deployment are shown in the following table.
| Group Name | Description | Permissions | Ref. in policies for comp. |
|---|---|---|---|
| xxx-oi3-admin-grp | Oracle Integration3 Administrators | Create, Delete, Change Compart. | xxx-oi3-admin-cmp |
| xxx-oi3- operator-dev-grp | Oracle Integration 3 Operators group for Development | Update, Start, Stop | xxx-oi3- operator-dev-cmp |
| xxx-oi3- operator-test-grp | Oracle Integration 3 Operators group for Testing | Update, Start, Stop | xxx-oi3- operator-test-cmp |
| xxx-oi3- operator-prod-grp | Oracle Integration 3 Operators group for Production | Update, Start, Stop | xxx-oi3- operator-prod-cmp |
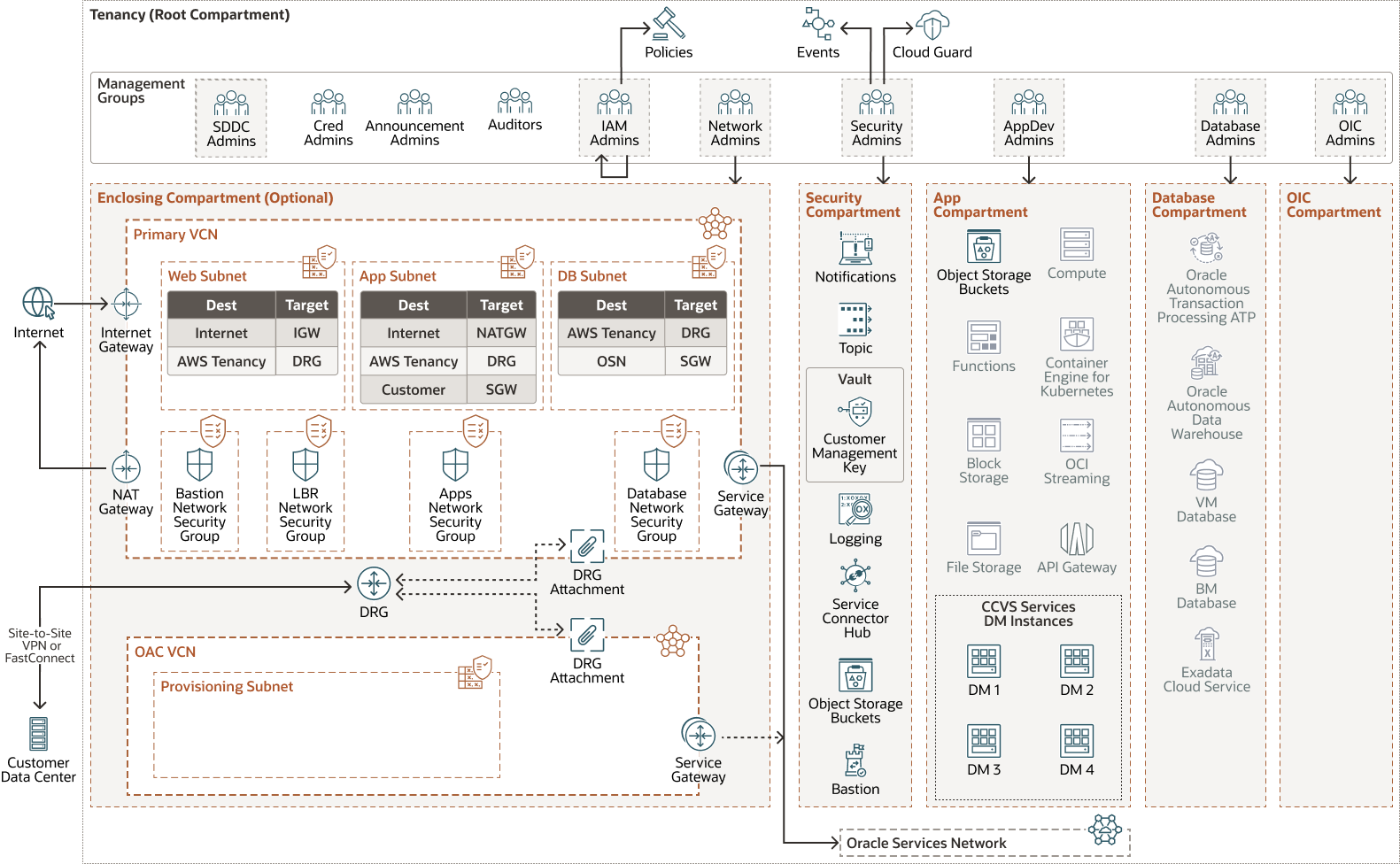
Architecture
The following diagram illustrates the architecture of an Oracle Integration 3 deployment on top of OCI Landing Zone:
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-regional logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize, control access, and set usage quotas for your Oracle Cloud resources. In a given compartment, you define policies that control access and set privileges for resources.
- OCI IAM Identity Domain
Identity and Access Management (IAM) uses identity domains to provide identity and access management features such as authentication, single sign-on (SSO), and identity lifecycle management for Oracle Cloud as well as for Oracle and non-Oracle applications, whether SaaS, cloud hosted, or on premises.
- Bastion
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Bastion provides restricted and time-limited secure access to resources that don't have public endpoints and that require strict resource access controls, such as bare metal and virtual machines, Oracle MySQL Database Service, Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP), Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine (OKE), and any other resource that allows Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) access. With OCI Bastion service, you can enable access to private hosts without deploying and maintaining a jump host. In addition, you gain improved security posture with identity-based permissions and a centralized, audited, and time-bound SSH session. OCI Bastion removes the need for a public IP for bastion access, eliminating the hassle and potential attack surface when providing remote access.
- Oracle
Services Network
The Oracle Services Network (OSN) is a conceptual network in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure that is reserved for Oracle services. These services have public IP addresses that you can reach over the internet. Hosts outside Oracle Cloud can access the OSN privately by using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect or VPN Connect. Hosts in your VCNs can access the OSN privately through a service gateway.
Understand the Compartment Structure
The following diagram shows the compartment structure for deployed development, test, and production Oracle Integration 3 instances:
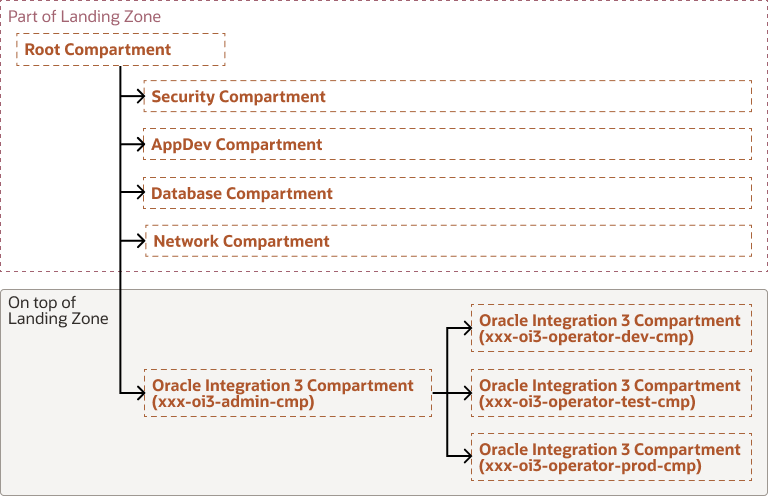
Description of the illustration oi3-compartment-structure.png
oi3-compartment-structure-oracle.zip
The diagram shows a compartment called Oracle Integration 3 Compartment
(using a naming convention of xxx-oi3-admin-cmp where
xxx is a three letter, lower case customer
abbreviation). This compartment is for admins who have permissions to create Oracle Integration 3 instances. In the sub-compartment Oracle Integration 3 Development Compartment
(xxx-oi3-operator-dev-cmp), users have permissions
through a group membership that allows you to stop and start Oracle Integration 3 development instances. Test and production instance are separate compartments.
The compartments are mentioned in table 1. (See above)
Each compartments needs to have policies configured to allow the administrators to do the actions on the Oracle Integration 3 instance. See "Deploy Oracle Integration 3", below, for more information about these policies.