Protect Your Siebel Workloads by Deploying a Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Firewall on Oracle Cloud
Protect and segment your Oracle Siebel workloads, prevent advanced threats, and improve applications visibility by using Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Palo Alto VM-Series is the virtualized form factor of the Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewall, it enables you to meet the following goals:
- Reduce attack surface and insert threat prevention.
- Network security automation ensuring safe and on-demand scalability.
- Managing the network security consistently across different deployments.
Architecture
This architecture shows an Oracle Siebel deployment that uses Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Palo Alto Networks (PAN) VM is deployable directly from the Marketplace in the OCI Console. It's important that you work directly with Palo Alto Networks to validate your design using this reference architecture as a guidance.
Palo Alto Networks and multiple OCI VCN deployment as depicted in the architecture diagram allows you to control north-south and east-west traffic:
- North-South Traffic: Palo Alto Networks VM secures traffic entering your cloud network from an untrusted source or your cloud network to reach an untrusted source.
- East-West Traffic: Palo Alto Networks VM secures traffic moving within your cloud environment between Virtual Cloud Networks (VCNs).
While Palo Alto Networks recommends segmenting the network using a hub and spoke topology, where traffic is routed through a central hub and is connected to multiple distinct networks (spokes), In the architecture below, all North-South and East-West traffic is considered to be going through the PAN VM Series firewall for additional security. This depends on the company's security standards and requirements.
All Oracle Siebel internal and external traffic should pass through the Palo Alto Networks VM. There is no local peering setup between VCNs, which means any traffic flows between the Siebel application subnet and the Siebel database subnet should pass through the Palo Alto Networks VM for more advanced and enhanced security.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
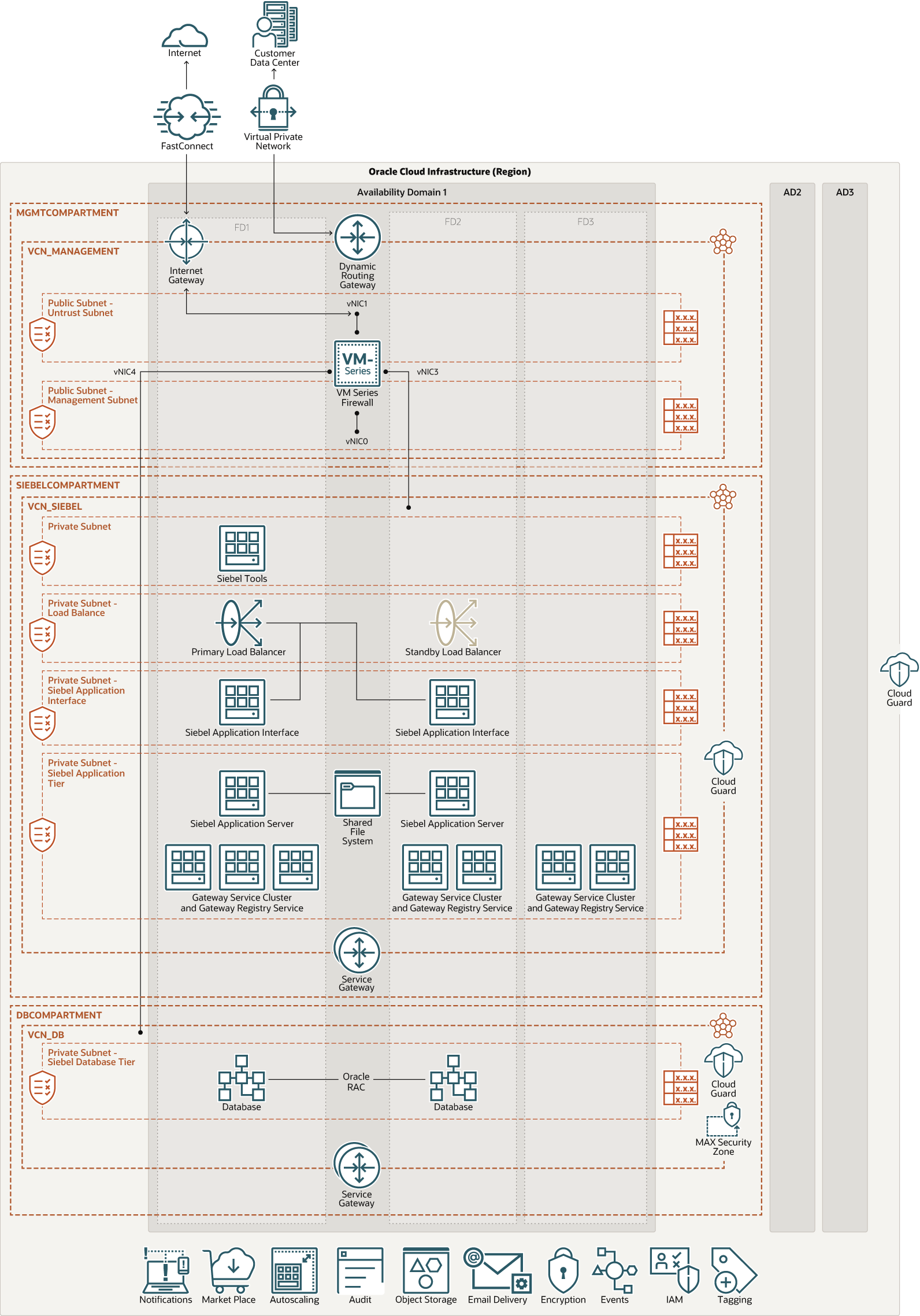
Description of the illustration deploy-siebel-palo-alto-vm-firewall.png
deploy-siebel-palo-alto-vm-firewall-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
To deploy the VM-Series firewall in OCI, your VCN must have at least three virtual network interfaces cards (VNICs) for the management interface and two data interfaces.
- PAN VM Series Firewall
The Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall is the virtualized form of the Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewall. It is positioned for use in a virtualized or cloud environment where it can protect and secure east-west and north-south traffic.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from one entry point to multiple servers reachable from your VCN. The service offers a load balancer with your choice of a public or private IP address, and provisioned bandwidth. A load balancer improves resource utilization, facilitates scaling, and helps ensure high availability. You can configure multiple load balancing policies and application-specific health checks to ensure that the load balancer directs traffic only to healthy instances. The load balancer can reduce your maintenance window by draining traffic from an unhealthy application server before you remove it from service for maintenance. The Load Balancing service enables you to create a public or private load balancer within your VCN. A public load balancer has a public IP address that is accessible from the internet. A private load balancer has an IP address from the hosting subnet, which is visible only within your VCN. Dedicated subnets will be created for Private or Public Load Balancers for future requirements. OCI Public load balancer with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall (WAF) will be considered for any internet-facing web application or HTTP-based API.
- Application Tier
The application tier includes compute instances for the Oracle Siebel 2021 application. In this design, applications are deployed in Virtual Machines, all compute instances in the application tier are attached to a private subnet. So, the applications are isolated at the network level from all the other resources in the topology, and they are shielded from unauthorized network access. The NAT gateway enables the private compute instances in the application tier to access hosts outside the cloud (for example, to download application patches or for any external integrations). Through the NAT gateway, the compute instances in the private subnet can initiate connections to the internet and receive responses, but won’t receive any inbound connections initiated from hosts on the internet. The service gateway enables the private compute instances in the application tier to access a Yum server within the region to get operating-system updates and additional packages. The service gateway also enables you to back-up the applications to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage within the region, without traversing the public internet. The components in the application tier have access to shared Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage, for storing shared binaries and data generated by Oracle Siebel applications.
- Database Tier
The database tier contains Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Database instances. VM Database/IaaS machine or Oracle Database Exadata Cloud Service depends on the database requirements. The service gateway enables you to backup the databases to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage within the region, without traversing the public internet.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Network address translation (NAT) gateway
A NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Cloud Guard
You can use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
- Security Zone
Security zones ensure Oracle's security best practices from the start by enforcing policies such as encrypting data and preventing public access to networks for an entire compartment. A security zone is associated with a compartment of the same name and includes security zone policies or a "recipe" that applies to the compartment and its sub-compartments. You can't add or move a standard compartment to a security zone compartment.
Oracle Maximum Security Zone is Oracle’s most stringent recipe with strict policy enforcement.
- Gateway Service Cluster and Gateway Registry Service
Oracle Siebel Gateway provides the dynamic address registry for Siebel Servers and server components, and also for Siebel Application Interface and other modules. The Siebel Application Interface and Siebel Gateway work together to provide Siebel Server load balancing. The Siebel Gateway also includes persistent storage in the registry for configuration information for Siebel Server, Siebel Application Interface, and other installable components.
Oracle Siebel CRM supports an optional native clustering feature for Siebel Gateway to provide high availability benefits to Siebel CRM customers. This feature works at the software level and is the preferred and recommended approach for clustering the Siebel Gateway. The clustering feature supports both the Siebel Gateway service (application container) and the Siebel Gateway registry.
Recommendations
- VCN
-
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
-
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
-
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
-
Use regional subnets.
-
Private subnets are recommended to have individual route tables to control the flow of traffic within and outside of VCN.
-
- Security
Use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure proactively. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
- Security Zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
- Load balancer bandwidth
While creating the load balancer, you can either select a predefined shape that provides a fixed bandwidth, or specify a custom (flexible) shape where you set a bandwidth range and let the service scale the bandwidth automatically based on traffic patterns. With either approach, you can change the shape at any time after creating the load balancer.
Considerations
When deploying Oracle Siebel CRM and Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), consider the following.
- VCN
AVCN provides you with complete control over your network environment. This includes assigning your own private IP address space, creating subnets, creating route tables, and configuring stateful firewalls. It closely resembles a traditional network, with firewall rules and specific types of communication gateways that you can choose to use.
To deploy the VM-Series firewall in OCI, your VCN must have at least three virtual network interfaces cards (VNICs) for the management interface and two data interfaces.- Ensure VCN CIDR block does not overlap with other VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (same or different regions) and with your organizations private IP network ranges.
- The VCN's CIDR blocks must not overlap with the CIDRs of another network you peer with.
- Ensure not all IP addresses are allocated at once within a VCN or Subnet, instead plan to reserve some IP addresses for future use.
- Hosts that have similar routing requirements can use same routing tables across multiple availability domains. For example, public hosts, private hosts, and NAT instances.
- Ensure security lists are used as Firewalls to manage connectivity North-South (incoming and outgoing VCN traffic) and East-West (internal VCN traffic between multiple subnets) and is applied at a subnet level. All instances within that subnet inherit all security rules in that SL.
- IP Addresses Reserved for Use by Oracle (169.254.0.0/16) must be excluded.
- VCN covers a single, contiguous IPv4
CIDR block of your choice. Inside the VCN, individual IPv4 subnets can be deployed for
cluster hosts. Access into each subnet is controlled by security lists. Additional
security is controlled at the host level by firewalls. Subnets are subdivisions
defined in a VCN. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of IP addresses that do
not overlap with other subnets in the VCN. You can designate a subnet to exist either
in a single availability domain or across an entire region. Subnets act as a unit of
configuration within the VCN: All VNICs in a given subnet use the same route table,
security lists, and DHCP options. You can designate a subnet as either public or
private when you create it. Private means VNICs in the subnet can't have public IP
addresses. Public means VNICs in the subnet can have public IP addresses at your
discretion. To control the network access, a tiered subnet strategy will be used for
the VCN. A common design pattern is to have the following subnet tiers:
- Public subnet for externally accessible hosts and Virtual Firewall appliances.
- Private subnet for internal hosts such as databases, application servers and private load balancers.
- DMZ subnet for public load balancers.
- OCI uses a series of route tables to send traffic out of your VCN and one route table is added to each subnet. A subnet is a division of your VCN. If you do not specify a route table, the subnet uses the VCN’s default route table. Each route table rule specifies a destination CIDR block and a next hop (target) for any traffic that matches the CIDR. OCI only uses a subnet’s route table if the destination IP address is outside the VCN’s specified CIDR block; route rules are not required to enable traffic within the VCN. And, if traffic has overlapping rules, OCI use the most specific rule in the route table to route traffic.
- Performance
- Selecting the proper instance size, which is determined by the Compute shape, determines the maximum available throughput, CPU, RAM, and number of interfaces
- Consider adding dedicated interfaces for FastConnect or VPN services.
- Consider using large Compute shapes for higher throughput and access to more network interfaces.
Depending on the amount of data, you can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect or IPSec VPN to manage costs. For faster access, you can store files that need frequent access in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage standard tier.
- Security
Deploying a Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall in OCI allows for centralized security policy configuration and monitoring of all physical and virtual Palo Alto Networks VM-Series instances.
- Availability
- Deploy your architecture to distinct geographic regions for greatest redundancy.
- Configure site-to-site VPNs with relevant organizational networks for redundant connectivity with on-premises networks.
- Consider Oracle high availability best practices.
- Cost
Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Firewall is available in bring-your-own-license (BYOL) and Pay As You Go license models for bundle 1 and bundle 2 in the Oracle Cloud Marketplace.
- Bundle 1 includes the VM-Series capacity license, threat prevention license, and a premium support entitlement.
- Bundle 2 includes the VM-Series capacity license with the complete suite of licenses that includes threat prevention, WildFire, URL filtering, DNS security, GlobalProtect, and a premium support entitlement.
Deploy
- Deploy using the stack in Oracle Cloud
Marketplace:
- Set up the required networking infrastructure as shown in the architecture diagram. See the example, Set up a hub-and-spoke network topology.
- Deploy applications, such as Oracle Siebel, on your environment.
- Oracle Cloud Marketplace has multiple listings for different configurations and licensing requirements. For example, the following listings feature bring your own licensing (BYOL) or paid. For each listing you choose, click Get App and follow the on-screen prompts:
- Deploy using the Terraform code in GitHub:
- Go to GitHub.
- Clone or download the repository to your local computer.
- Follow the instructions in the
READMEdocument.