Deploy TCS BaNCS on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with Exadata Cloud Service
The BaNCS applications are critical for the day-to-day operation of many financial institutions. They can be deployed at a scale that supports up to billions of accounts and hundreds of millions of transactions per day. These systems must be implemented in a way that provides the highest level of security, reliability and performance to satisfy each organizations own requirements and also meet the strict requirements of their local financial services regulators.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is the ideal platform to host BaNCS applications. The OCI services and underlying data center technology have been specifically designed and optimized to run business critical systems such as BaNCS. OCI has multiple regions available in many countries enabling organizations to configure geographically isolated disaster recovery (DR) architecture patterns while retaining the data within geographical boundaries for regulatory compliance. In addition OCI provides a number of database options including the highly optimized Exadata database service which is the most resilient and performant option available for a transactional system like BaNCS.
This Reference Architecture describes how to deploy BaNCS on OCI leveraging multi-region disaster recovery and Exadata database service.
Architecture
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture for a production and disaster recovery BaNCS environment. In order to simplify the diagram the non-production environments have not been depicted. Those environments will follow the same design pattern and will be contained in there own isolated network.
Detailed descriptions of the various solution component follow after the diagram..
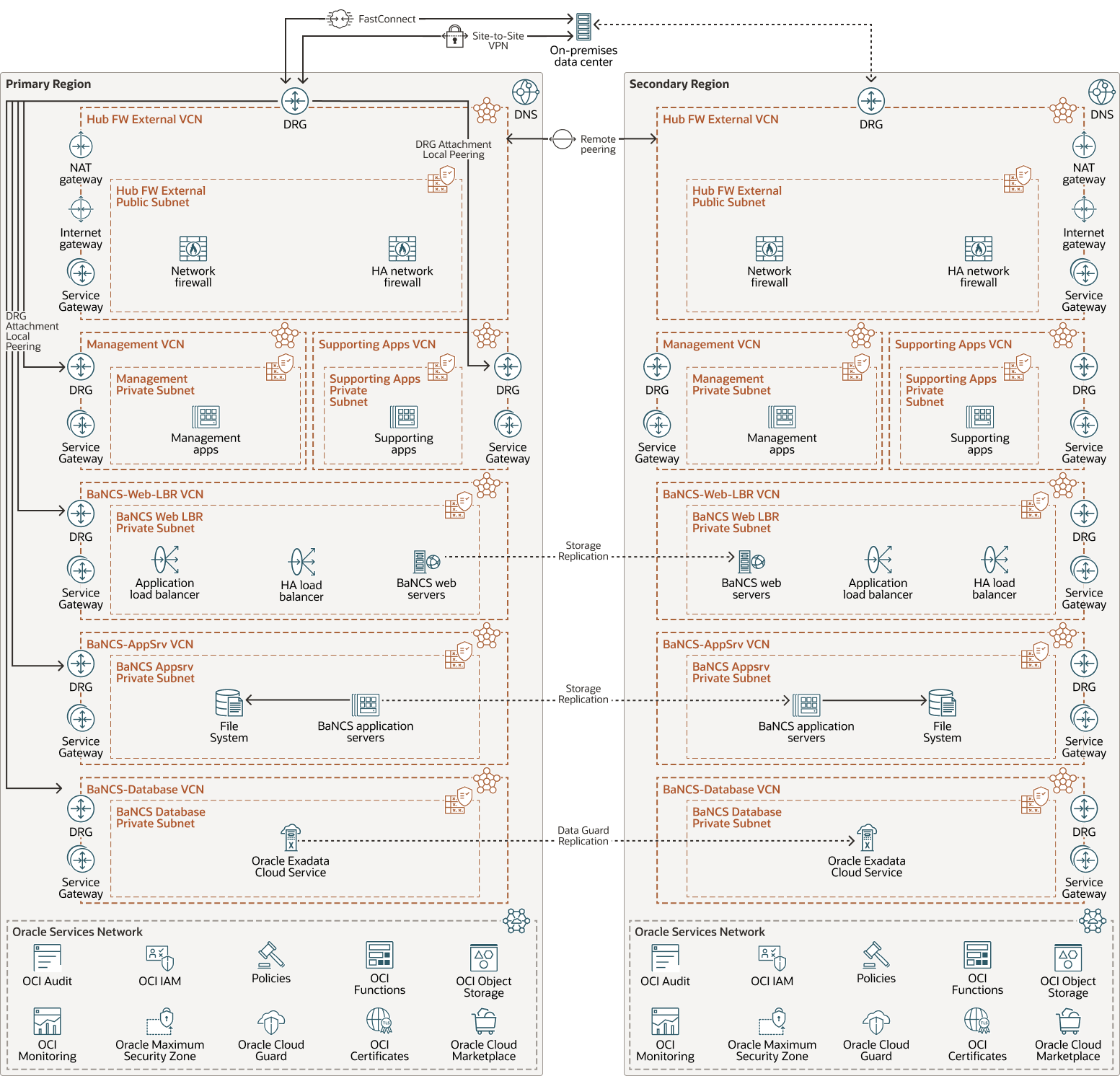
Description of the illustration bancs-ref-architecture-no-fd.png
bancs-ref-architecture-no-fd-oracle.zip
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for OCI. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy.
A tenancy is synonymous with a company or organization. Usually, a company will have a single tenancy and reflect its organizational structure within that tenancy. A single tenancy is usually associated with a single subscription, and a single subscription usually only has one tenancy. A company may chose to split their OCI resources, environments or applications across multiple tenancies if they wish. The tenancies can be linked and networks can be peered across tenancies if required. For the purpose of this BaNCS solution design a single tenancy has been used and the OCI concept of compartments (see below) has been used to provide fine grained isolation and access control to the various solution components.
- Region
An OCI region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents). In this solution two regions are used in order to provide a disaster recovery site that is geographically isolated from the primary site.
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an OCI tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain. For this deployment it is recommended that the BaNCS load balancers, network firewalls, web tier and application tier VMs are deployed in highly available clusters across multiple fault domains in order to ensure the maximum resilience to hardware failures.
- Identity and access management (IAM)
OCI Identity and Access Management(IAM) enables you to control who can access your resources in OCI and the operations that they can perform on those resources.
- Policy
An OCI IAM policy specifies who can access which resources, and how. Access is granted at the group and compartment level, which means you can write a policy that gives a group a specific type of access within a specific compartment, or to the tenancy.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an OCI region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private. This BaNCS reference architecture leverages multiple VCN's in a hub and spoke topology. This will be discussed in more detail in the section below.
- FastConnect
OCI FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and OCI. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in OCI. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another OCI region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Local peering gateway (LPG)
An LPG enables you to peer one VCN with another VCN in the same region. Peering means the VCNs communicate using private IP addresses, without the traffic traversing the internet or routing through your on-premises network. This solution has been created using a multi-attach DRG as the method of achieving local peering for the hub and spoke network. However it could equally be created using local peering gateways instead.
- Network address translation (NAT) gateway
The NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as OCI Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Network security group (NSG)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of OCI all traffic is denied, and you can control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of VNICs in a single VCN.
- Security zone
Security zones ensure Oracle's security best practices from the start by enforcing policies such as encrypting data and preventing public access to networks for an entire compartment. A security zone is associated with a compartment of the same name and includes security zone policies or a "recipe" that applies to the compartment and its sub-compartments. You can't add or move a standard compartment to a security zone compartment.
- Compute
OCI Compute enables you to provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it. OCI also provides the facility for capacity reservations for compute resources. This will reserve compute capacity in advance so that it will always be available for your workloads when you need it. It is often used to reserve capacity in the Disaster Recovery region to ensure that it is always possible to provision and start your DR resources in the event of a failover.
- Functions
Oracle Functions is a fully managed, multitenant, highly scalable, on-demand, Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) platform. It is powered by the Fn Project open source engine. Functions enable you to deploy your code, and either call it directly or trigger it in response to events. Oracle Functions uses Docker containers hosted in OCI Registry. In this solution the Functions can be leveraged to quickly build and run programs meet ad hoc requirements, such as disabling inactive users or verifying backup completion.
- Load balancer
The OCI Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- File storage
The OCI File Storage service provides a durable, scalable, secure, enterprise-grade network file system. You can connect to a File Storage service file system from any bare metal, virtual machine, or container instance in a VCN. You can also access a file system from outside the VCN by using OCI FastConnect and IPSec VPN.
- Exadata DB system
Exadata Cloud Service enables you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. You can provision flexible X8M systems that allow you to add database compute servers and storage servers to your system as your needs grow. X9M systems offer RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) networking for high bandwidth and low latency, persistent memory (PMEM) modules, and intelligent Exadata software. You can provision X9M systems by using a shape that's equivalent to a quarter-rack X9 system, and then add database and storage servers at any time after provisioning.
- Oracle services network
The Oracle services network (OSN) is a conceptual network in OCI that is reserved for Oracle services. These services have public IP addresses that you can reach over the internet. Hosts outside Oracle Cloud can access the OSN privately by using OCI FastConnect or VPN Connect. Hosts in your VCNs can access the OSN privately through a service gateway.
- Cloud Guard
You can use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in OCI. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
- Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
- Vault
OCI Vault enables you to centrally manage the encryption keys that protect your data and the secret credentials that you use to secure access to your resources in the cloud. In this solution the object, file, block storage services and the certificate service are all integrated with the vault service to manage their keys.
- Certificate Service
The OCI Certificates service is used to manage TLS certificates for load balancers and also storage encryption certificates.
- DNS Zones
The OCI DNS service is a distributed internet system that maps human-readable names (such as oracle.com) to IP addresses. Organizations can leverage OCI DNS to facilitate continuity of access to the BaNCS application in the event of a DR event.
Recommendations
- High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR)
The BaNCS application will generally require the highest level of availability and geographically isolated redundancy. In order to achieve the isolated redundancy in the event of a regional level disaster this solution has been distributed across two OCI regions. The primary region will host the production environment that actively replicates data to the second region, which is activated only when necessary. To minimize the RPO and RTO, the application tier file systems can be replicated from the primary site to the secondary site by using cross-region storage replication or a utility such as rsync. The database in this solution is the OCI Exadata database service, which uses Oracle Data Guard to provide cross-region replication to another Exadata service instance in the secondary region.
HA capability is provided through two main features. Core components such as network firewall, load balancers, and the BaNCS application and web servers will have multiple virtual machines (VMs) deployed in a cluster across OCI fault domains. This ensures business continuity since there will always be a secondary instance running in the case of an application or hardware fault within an availability domain. For the database tier, the Exadata database service provides multiple active compute and storage nodes in a real application cluster (RAC) to provide redundancy.
- Network
The network architecture used in this design is based on a hub and spoke topology to provide the highest level of security and segregation for management of the BaNCS applications. As per OCI best practices, the central hub VCN hosts an enterprise grade network firewall and public or customer (external) facing subnets. This sample solution uses a spoke VCN for a production BaNCS application stack and an additional spoke VCN has been provided for environment management related applications and utilities. Non-production environments would also be provisioned within their own spoke VCN.
- Database
This solution design is based on the Oracle database running on Exadata cloud service. This was chosen in order to deliver the highest level of performance and availability since the BaNCS application is a critical business system. The database configuration includes RAC and Data Guard in accordance with the Oracle best practice maximum availability architecture.
- Security
BaNCS applications are critical to business operations and the end-to-end security of the solution is very important It is essential that the entire solution is implemented with a least privileges security strategy and that the data is always encrypted in transit and at rest. This solution leverages many OCI security features.
Administrators of the OCI platform, the VCN, the BaNCS application and databases are managed using OCI IAM roles and policies. Oracle recommends provisioning and using multiple identity domains to separate the different administration and application users. In this design, one domain is used for the OCI administrator accounts and the other domain(s) are used for authenticating users of the various management and supporting applications. OCI Compartments are created and OCI resources allocated to them to allow fine grained segregation of the resources and associated IAM policies. Authentication of the administrators can be configured within OCI IAM or in a federated external Identity provider like Okta.An enterprise grade network firewall should be configured to prevent malicious and accidental network access to OCI and application resources. In addition the OCI security lists, network security groups, and route tables are used to control network access between OCI resources. Any external network traffic will be routed via OCI FastConnect or VPN.
All application and database storage is encryption by default. It is recommended that the customer self manages the encryption keys and wallets. In OCI the recommended way to manage keys and wallets is the OCI Vault service.
The OCI compartments associated with the various BaNCS application resources are associated with OCI security zones. These zones have custom recipes configured to enforce corporate security policies on any compute VM's, network, storage and database resources. If an administrator attempts to create or modify any resource that violates one of the policies then the operation will be denied.
Oracle recommends that other OCI services such as Cloud Guard, Data Safe, and vulnerability scanning be implemented in order to continuously monitor and manage the security posture of the entire BaNCS environment on OCI.
- Manageability
Within OCI the Observability and Management services provide a comprehensive suite of resources to assist with the management of the OCI platform and BaNCS application. This includes metric monitoring, event alerting, log management and analytics, application performance monitoring, database management, and operations insights. Given the size, complexity and criticality of the BaNCS deployment on OCI, Oracle highly recommends that these services are activated and configured or, alternately, have the OCI monitoring and log data streamed to a third party SEIM tool.
Considerations
- Availability
The architecture described here is based on a multi-region OCI deployment in order to provide a DR site that is a significant geographical distance from the primary site. Not all organizations and BaNCS deployments will have this requirement. Alternative options include using two OCI availability domains in a single region as the primary and secondary deployment sites. In this case, Oracle still recommends distributing the OCI resources across multiple fault domains in order to maximize the system availability.
- Database
The BaNCS application supports a number of database platforms for the persistence layer, including PostgreSQL and Oracle database. For organizations that have smaller BaNCS deployments, the OCI base database service is an excellent choice. It is a managed database service that is scalable, runs on performant x86 virtual machines and has the option to run in single node or multi-node RAC clusters for high availability. BaNCS also supports PostgreSQL so the OCI PostgreSQL service is another viable alternative. While neither option provides the same level of performance, resilience, or scalability of Exadata they might be more economical alternatives for smaller deployments. Both of those PaaS database options still provide significant manageability and total cost of ownership benefits over a manual database installation on IaaS.
- Security
In the example architecture provided above, an enterprise grade third party network firewall has been deployed on OCI Compute VMs. As an alternative, you can use the native OCI Network Firewall service, which you can deploy within a VCN and subnet of your choice and can configure to control north-south and east-west network traffic based on a set of security rules. You should compare the capability of the various network firewall options should before making this decision.
The OCI IAM services is used in this solution to store the OCI system administrator identities, roles and associated policies. It is federated externally for single signon and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for those users. Alternative deployments might take advantage of the IAM service native MFA capabilities or even create additional IAM Domains to manage the BaNCS application users in addition to OCI administrators.
With the Oracle database services on OCI the data encryption at rest is enabled using Oracle Transparent Database Encryption (TDE). The encryption wallet and keys are often stored and managed using the OCI Vault. A cheaper alternative to running a private vault is to host the encryption wallet locally on the database file system. These encryption files will be synchronized from the primary to secondary database instance by using Oracle Data Guard.
- Manageability
There are a number of solutions available with OCI to monitor, audit and manage an application deployment such as BaNCS. OCI itself provides a comprehensive suite of Observability and Management services that can be configured and enabled to meet most requirements. However there are many third party options that are commonly used such as Datadog, Splunk and Microsoft Sentinel. Fortunately OCI has a number of features such as the OCI Connector Hub which can easily facilitate the aggregation and transfer of OCI metrics and logs to third party systems.
- API Management
TCS BaNCS is an API-first application that unlocks the power of APIs to facilitate the effective use of data within an organizations broader finance ecosystem. You can use the OCI API Gateway service in combination with OCI IAM to provide centralized governance, acceleration and security to the BaNCS application APIs.
- Performance
Many factors contribute to the performance and ultimately the quality of the user experience for an application running on OCI. Many decisions have been made in this specific solution design for BaNCS that were aimed at providing the highest possible level of performance. From a networking perspective using a FastConnect interface into OCI instead of VPN will provide significant performance benefits. In terms of the database the benefits of Exadata cloud service versus the base database cloud service or PostgreSQL service was discussed earlier. Leveraging the OCI Compute VM flex shapes is also a great way to select the optimal level of physical resources like CPU, RAM and the number of network interfaces that are allocated to satisfy the workload at any point in time. Similarly the OCI storage tier components such as block volume have the flexibility to select performance characteristics such as IOPS and throughput to best suit the requirements. The BaNCS components such as the network firewall, web and application server VMs can use these OCI features to provide a cost effective solution that easily satisfies any organizations expectations for their BaNCS application performance.
Explore More
To learn more about running BaNCS on OCI, see the following resources:
-
TCS BANCS: A universal financial solution (TATA Consultancy Services product page)