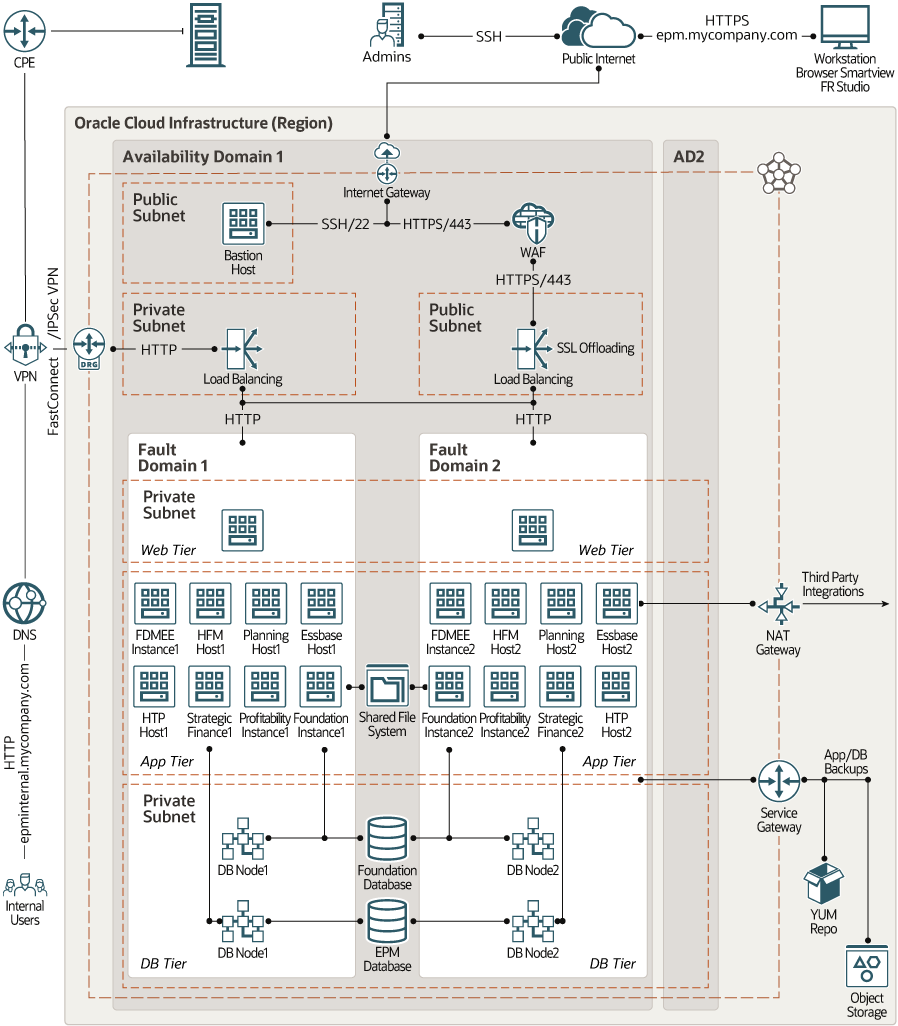
HA Architecture: Single Availability Domain
In this architecture, the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management applications and the databases are deployed across two fault domains in a single availability domain.
All the application instances in the topology are active. Redundant instances of the application are hosted in separate fault domains. So the instances aren't hosted on the same physical hardware. This architecture ensures high availability within the availability domain. A hardware failure or maintenance event that affects one fault domain doesn't affect the instances in the other fault domains. If an instance fails, then the traffic is diverted to the other instances in the availability domain, which continue to process the requests.
All the components in this multi-tier architecture are in a single region. The resources in each tier are isolated at the network level in separate subnets.
- Bastion Host
The bastion host is a compute instance that serves as a secure, controlled entry point to the topology from outside the cloud.
The bastion host is provisioned typically in a DMZ. It enables you to protect sensitive resources by placing them in private networks that can't be accessed directly from outside the cloud. The topology has a single, known entry point that you can monitor and audit regularly. So you avoid exposing the more sensitive components of the topology, without compromising access to them.
The bastion host in this architecture is attached to a public subnet and has a public IP address. Connections to the bastion host from administrators outside the cloud flow through the internet gateway attached to the VCN. You can configure an ingress security rule to allow SSH connections to the bastion host from the public internet. To provide an additional level of security, you can limit SSH access to the bastion host from only a specific block of IP addresses.
You can access compute instances in private subnets through the bastion host. Enable
ssh-agentforwarding, which allows you to connect to the bastion host, and then access the next server by forwarding the credentials from your local computer.You can also access the instances in the private subnet by using dynamic SSH tunneling. The dynamic tunnel provides a SOCKS proxy on the local port; but the connections originate from the remote host.
- Public Load BalancerHTTPS requests from external users, such as users of Hyperion Financial Reporting Web Studio, flow through the internet gateway attached to the VCN. The requests then pass through the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall (WAF) service, which protects the applications from malicious and unwanted internet traffic. Traffic that passes the WAF rules is forwarded to the public load balancer. The load balancer terminates SSL/TLS, and distributes HTTP requests to the private web tier.
Note:
To ensure domain resolution of your application endpoints, you should register the IP address of the public load balancer in your public DNS. - Private Load BalancerTraffic from your internal and on-premises users flows through IPSec VPN tunnels or FastConnect virtual circuits to the dynamic routing gateway (DRG) that's attached to the VCN. A private load balancer intercepts the requests and distributes them to the private web tier.
Note:
To ensure domain resolution of your application endpoints, you should register the IP address of the private load balancer in your on-premises DNS. - Web Tier
The web tier is hosted on two compute instances, both attached to the same private subnet. The instances are in separate fault domains, ensuring high availability of the web tier.
- Application Tier
The application tier includes compute instances for the following Hyperion components. (The abbreviations in parentheses are the labels used for these components in the architecture diagram.)
- Oracle Hyperion Financial Data Quality Management, Enterprise Edition (FDMEE)
A packaged solution that helps finance users develop standardized financial data management processes by using a web-based guided workflow.
- Oracle Hyperion Financial Management (HFM)
A multidimensional online analytical processing server on RDBMS that provides an environment for web-based consolidation, tax provision, QMR, JSK applications.
The application delivers global financial consolidation, reporting, and analysis in a single, highly scalable software solution.
- Oracle Hyperion Planning
A centralized, Excel and web-based planning, budgeting, and forecasting solution that integrates financial and operational planning processes and improves business predictability.
- Oracle Essbase
An online analytical processing (OLAP) server that provides an environment for deploying prepackaged applications or developing custom applications.
- Oracle Hyperion Tax Provision (HTP)
A comprehensive global tax provision solution for multinational companies reporting under US GAAP or IFRS.
The application encompasses all the stages of the corporate tax provision process, including tax automation, data collection, tax provision calculation, return-to-accrual automation, and tax reporting and analysis. The application is built using Oracle Hyperion Financial Management, and it leverages all the functionality provided by Financial Management.
- Oracle Hyperion Strategic Finance
A financial forecasting and modeling solution with on-the-fly scenario analysis and modeling capabilities, which helps you quickly model and evaluate financial scenarios, and offers out of the box treasury capabilities for sophisticated debt and capital structure management.
- Oracle Hyperion Profitability and Cost Management
An application that provides actionable insights, by discovering drivers of cost and profitability, empowering users with visibility and flexibility, and improving resource alignment.
- Oracle Hyperion Foundation Services
Common infrastructure components that enable you to install and configure all the modules of the Enterprise Performance Management system; and to manage users, security, metadata, and the life cycle of the applications.
Foundation Services are necessary regardless of whether you want to deploy Hyperion Financial Management, or Hyperion Planning, or both.
Each of the application-tier components is deployed on two compute instances, which are provisioned in a separate fault domain. So every component in the application tier is tolerant to failures at the fault-domain level.
All the compute instances in the application tier are attached to a private subnet. So, the applications are isolated at the network level from all the other resources in the topology, and they are shielded from unauthorized network access.- The NAT gateway enables the private compute instances in the application tier to access hosts outside the cloud (for example, to download application patches or for any external integrations). Through the NAT gateway, the compute instances in the private subnet can initiate connections to the internet and receive responses, but won’t receive any inbound connections initiated from hosts on the internet.
- The service gateway enables the private Oracle Linux compute instances in the application tier to access a Yum server within the region to get operating-system updates and additional packages.
- The service gateway also enables you to backup the applications to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage within the region, without traversing the public internet.
The components in the application tier have access to shared Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage, for storing shared binaries and data generated by Hyperion applications.
- Oracle Hyperion Financial Data Quality Management, Enterprise Edition (FDMEE)
- Database Tier
The database tier contains Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Database instances. For high availability, use 2-node virtual machine (VM) DB systems or Exadata DB systems.
This architecture contains two dual-node database systems: one for Hyperion Foundation Services, and the other for the applications.
- The two nodes in each RAC database are placed in separate fault domains, ensuring that each database cluster is tolerant to failures at the fault-domain level.
- All the database nodes are attached to a private subnet. So, the databases are isolated at the network level from all the other resources in the topology, and they are shielded from unauthorized network access.
- The service gateway enables you to backup the databases to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage within the region, without traversing the public internet.