Deploy Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Database@AWS
For large enterprises, particularly those with complex Oracle E-Business Suite deployments and associated applications, a strategic multi-cloud architecture partner is essential.
Leveraging both Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure through Oracle Database@AWS enables optimal performance and resilience. This architecture provides a blueprint for deploying Oracle E-Business Suite applications on AWS while harnessing the unparalleled database capabilities of Oracle Database@AWS. This reference architecture is one that Apps Associates helped design for a large customer.
Before You Begin
- Ensure that you have adequate Oracle Exadata Database Service limits and OCI service limits prior to provisioning. See OCI Service limits for more information. See Requesting a Service Limit Increase for how to increase service resources.
- Planning your network topology:
- You need at least one AWS Account with a purchase offer for Oracle Database@AWS. In this case, we have used 2 subscriptions as we deployed multiple Oracle Database Appliance instances in different regions/accounts.
- You need at least one Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) that you can leverage for provisioning Oracle Database@AWS. However, you can architect with multiple VPCs. In our case, as we were deploying multiple Oracle Database@AWS in different regions or accounts, we used different VPCs.
- The classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) blocks for any AWS VPC and OCI VCNs must not overlap.
- You need to allow NFS, SMB, and iSCSI ports for Amazon FSx for NetApp Open Network Technology for Appliance Products (ONTAP).
- The CIDR blocks for any Amazon VPCs must not overlap with on-premises networks.
- The application VMs are deployed on AWS EC2 instances while databases are deployed on Oracle Cloud with Exadata infrastructure sitting inside the AWS data centers.
- You need separate VPCs for application and database.
- For multiregion deployment, the exact same architecture is deployed on both the regions.
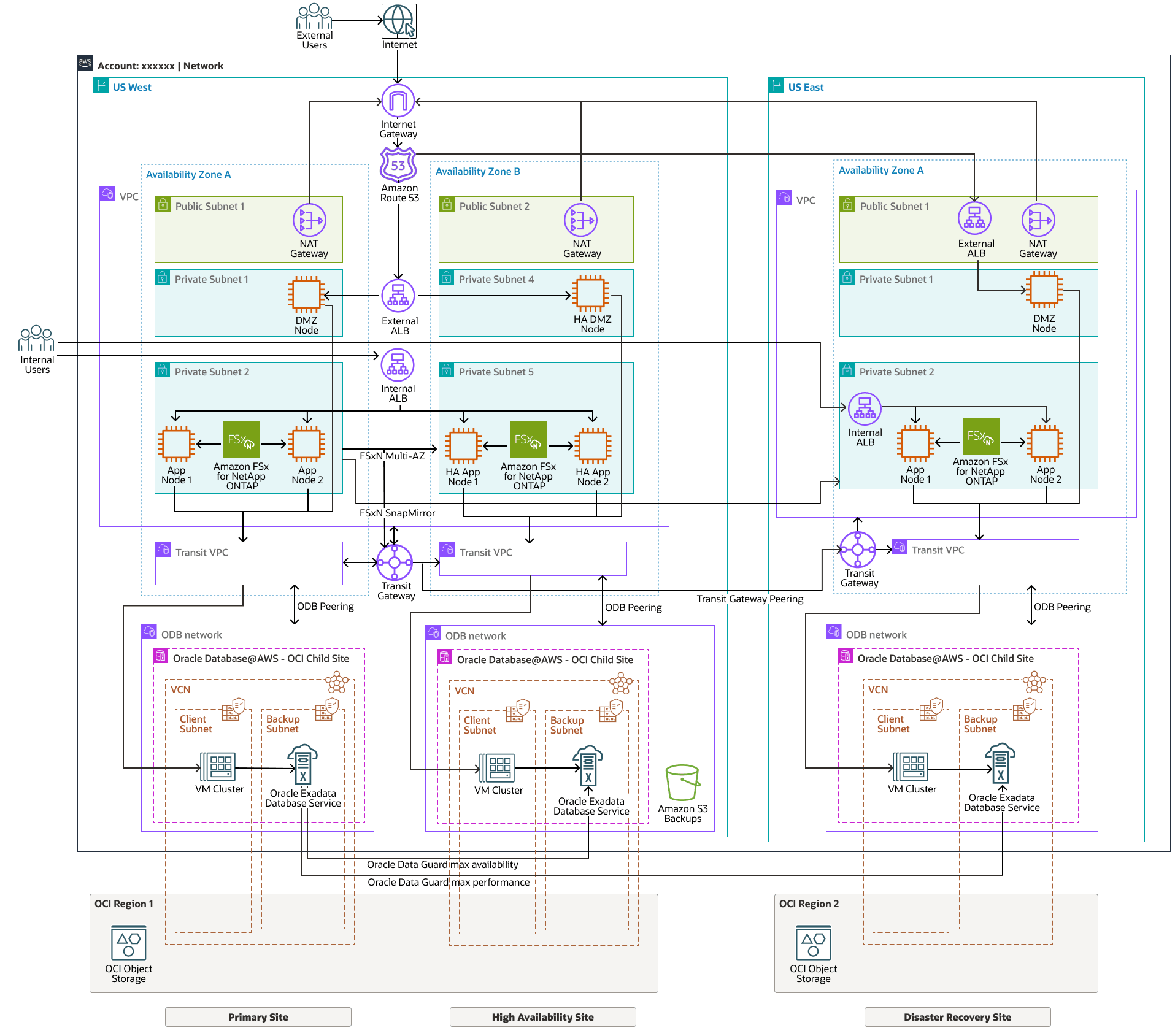
Architecture
This architecture adheres to AWS landing zone best practices, employing multiple VPCs to logically separate shared and workload resources.
It establishes a highly scalable network topology by using AWS transit gateways, simplifying the deployment of complex hub-and-spoke networks. This robust network infrastructure facilitates seamless routing across AWS regions, between virtual networks, and to on-premises locations by using Direct Connect, Point-to-Site, and Site-to-Site VPN, all secured by AWS.
The following diagram shows the architecture for deploying Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Database@AWS.
ebs-db-aws-architecture-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following Oracle components:
- OCI region
An OCI region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, hosting availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain shouldn't affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A virtual cloud network (VCN) is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an OCI region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
In AWS, a VPC is the functional equivalent of a VCN.
- Network security group
(NSG)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of OCI you control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of virtual network interface cards (VNICs) in a single VCN.
- Oracle Database@AWS
Oracle Database@AWS is an Oracle Database cloud service on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) that runs Oracle Database workloads in your Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment.
Oracle Database@AWS brings OCI technologies, such as Oracle Exadata Database Service, Oracle Autonomous Database, Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) and Oracle Data Guard to AWS customers.
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated
Infrastructure
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure enables you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. Oracle Exadata Database Service delivers proven Oracle Database capabilities on purpose-built, optimized Oracle Exadata infrastructure in the public cloud. Built-in cloud automation, elastic resource scaling, security, and fast performance for all Oracle Database workloads helps you simplify management and reduce costs.
- OCI Object Storage
OCI Object Storage provides access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store data directly from applications or from within the cloud platform. You can scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability.
Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
This architecture has the following AWS components:
- AWS availability zone
An availability zone is a physically separate data center within a region designed to be available and fault-tolerant. Availability zones are close enough to have low-latency connections to other availability zones.
- AWS Virtual Private Cloud
An AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources, like EC2 instances, in a virtual network that you define. It provides a way to create your own private network within the AWS cloud, giving you control over your network configuration, including IP address range, subnets, route tables, and security groups.
- Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP is a fully managed service that provides highly reliable, scalable, high-performing, and feature-rich file storage built on NetApp's popular ONTAP file system. FSx for ONTAP combines the familiar features, performance, capabilities, and API operations of NetApp file systems with the agility, scalability, and simplicity of a fully managed AWS service.
It offers scalability, efficiency, and security for enterprise workloads, including databases, virtualization, and AI applications. NetApp integrates with major cloud providers like AWS, and Google Cloud to enable seamless hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. With features like snapshots, deduplication, and disaster recovery, NetApp helps businesses optimize storage and data protection strategies. For this design we are using it for the Oracle EBS applications’ servers and for better security between production and non-production for cloning using Snap Mirror.
AWS FSx for NetApp ONTAP is used for Oracle E-Business Suiteshared application tier file system (shared APPL_TOP) and as backup storage for Oracle databases using RMAN.
- AWS Transit GatewayAWS Transit Gateway is a network transit hub used to interconnect virtual private clouds (VPCs) and on-premises/other networks. In the case of Oracle DB@AWS that is the ODB Network. As your cloud infrastructure expands globally, inter-region peering connects transit gateways together using the AWS Global Infrastructure. All network traffic between AWS data centers is automatically encrypted at the physical layer
- AWS Direct Connect
AWS Direct Connect provides a dedicated network connection between an on-premises network and the AWS Cloud, bypassing the public internet. This private connection offers increased bandwidth, reduced network costs, and a more consistent network experience compared to internet-based connections
- Secure File Transfer Protocol
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a network protocol that enables secure file transfer over SSH (Secure Shell), ensuring encryption and data integrity. Unlike traditional FTP, SFTP protects data during transmission by encrypting both commands and files, preventing unauthorized access. It supports authentication methods such as passwords, SSH keys, and multifactor authentication for enhanced security. SFTP is widely used for secure file sharing in enterprises, cloud environments, and automated data transfers.
- Account
An AWS account is a fundamental resource container within Amazon Web Services (AWS) that holds your AWS resources and configurations. It's the primary way you interact with AWS services, providing a secure boundary for your cloud environment. Essentially, it's where you create, manage, and pay for your cloud-based resources.
Recommendations
- Ensure that you complete the onboarding process for Oracle Database@AWS before provisioning the Oracle Database@AWS.
- Higher latencies or performance degradation may be observed when AWS NetApp files are NFS Mounted over AWS a transit gateway topology where the network traffic is routed through a firewall.
- Primary and standby database subnets should be in distinct VPCs configured with non-overlapping IP classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) ranges.
- Ensure that you have access to an AWS Account where Oracle Database@AWS is provisioned
- Ensure that you have access to an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy.
- Ensure that you have non-overlapping CIDR blocks between any AWS VPCs and OCI VCNs.
- Ensure that you have adequate Oracle Exadata Database Service limits prior to provisioning.
- Ensure the physical locations of the AWS EC2 Instances and Oracle VM Clusters are the same. Logical locations are different than the physical locations.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Client Connectivity
This network setup allows client connectivity from AWS resources.
- AWS Direct Connect
The AWS Direct Connect cost varies from one region to another. The cost is influenced by factors like port fees, data transfer rates, and the specific location of the Direct Connect location. Data transfer costs, in particular, can differ significantly between regions.
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated
InfrastructureCost
- Deployed infrastructure has consistent cost and can be shut down at any time (Minimum 48 hours is charged).
- Run time costs are determined by the number of ECPUs assigned to the VM which is scalable.
- Licensing options include both Bring Your Own License (BYOL) and License Included.
- Oracle Support Rewards are available for BYOL.
Performance- Customers experience the same performance that they would experience with any other Exadata deployment (Oracle Exadata Database Service, Oracle Exadata Database Service on Cloud@Customer, or on-premises).
- Oracle does not charge any data egress fees for Oracle Database@AWS, but depending on AWS architecture AWS may charge data movement fees.
- Availability
Exadata deployments have a 99.95% service level agreement (SLA). Higher numbers can be reached by using a maximum availability architecture (MAA) which can include setting up a disaster recovery site and using backup and restore capabilities such as Oracle Database Zero Data Loss Autonomous Recovery Service.
Explore More
Learn more about the features of this architecture and about related architectures.
-
Implement disaster recovery with local and regional standbys on Oracle Database@AWS
-
Implement disaster recovery with cross-zonal Data Guard on Oracle Database@AWS
-
Implement disaster recovery with cross-regional Data Guard on Oracle Database@AWS
-
Deploy Active Data Guard Far Sync to protect data across Oracle Database@AWS regions