Move On-Premises Data to SaaS Using Integration Services on Oracle Cloud
To make health care simpler and more affordable for the members, patients, and communities it serves, Minnesota-based HealthPartners is modernizing its entire technology stack by moving its on-premises and back-office applications to a PaaS for SaaS deployment on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
For more than 80 years, the nonprofit organization has worked to create a health system that combines patient care, personalized insurance plans, and innovative research. Today, HealthPartners’ team of 28,000 colleagues serves more than 1.8 million medical and dental health plan members nationwide and more than 1 million patients across Minnesota and western Wisconsin.
In addition to refactoring its on-premises apps to Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Resource Planning, Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Performance Management, and Oracle Fusion Cloud Supply Chain & Manufacturing SaaS applications, HealthPartners uses Oracle Integration Cloud Service to bring the SaaS data into its OCI tenancy. In OCI, the SaaS data is stored in an Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) database, which is backed up using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. HealthPartners uses Oracle Data Guard to connect the ATP database at its primary site in the US-Ashburn region to its disaster recovery site in the US-Phoenix region.
This deployment enables:
- Mobile connectivity for hospice nurses and other remote workers to log time and to simplify payroll activities
- Real-time replenishment of medicines, surgical equipment, and other fast-moving medical supplies
Goals of a future-state deployment are to:
- Improve the network configuration
- Tighten the security posture
- Centralize analytics and reporting
Architecture
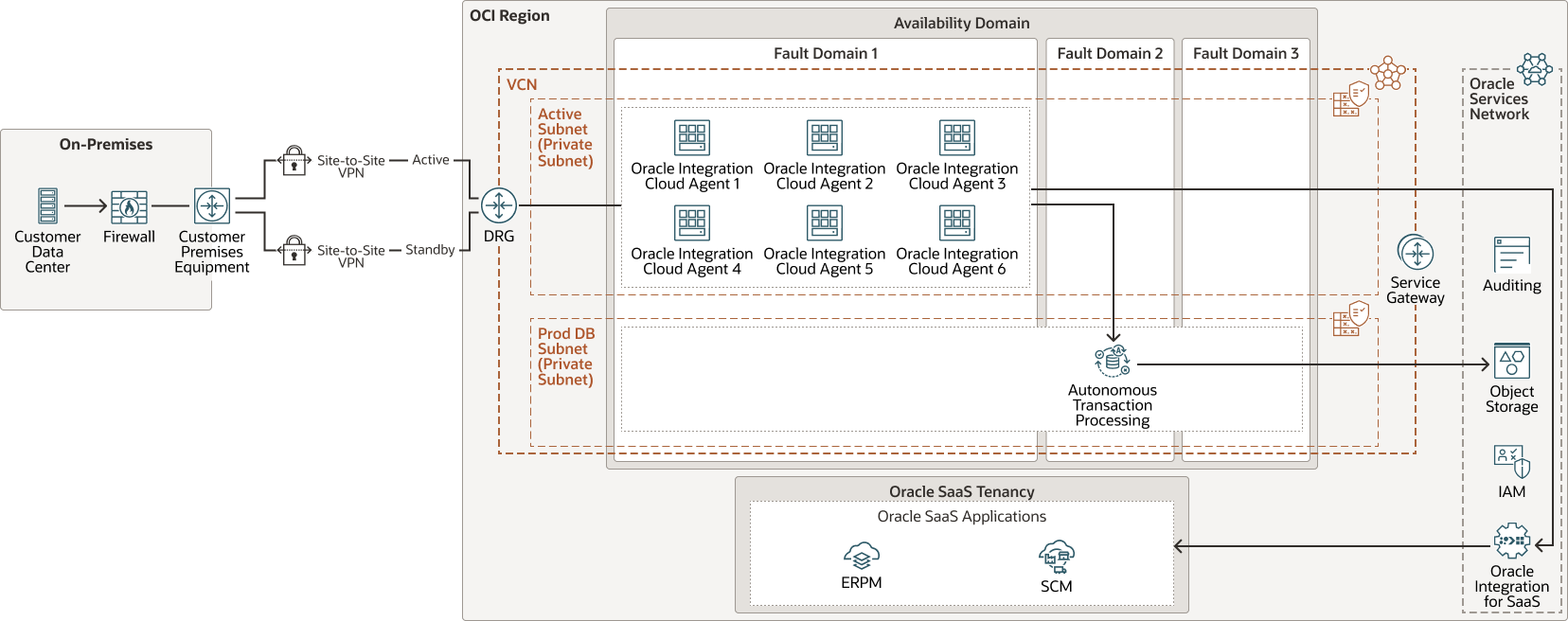
Although there are multiple ways to deploy hybrid integrations, HealthPartners chose to deploy the connectivity agents on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) in a virtual cloud network (VCN). Health Partners' on-premises environment is connected through a site-to-site virtual private network (VPN) to the VCN by using a dynamic routing gateway (DRG).
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
The connectivity agents are installed on virtual machine instances. Agents are deployed on separate instances for each integration for a total of six integrations. The connectivity agents only communicate with private IP addresses. This adds a layer of security by controlling what data the agents receive and where the agents send the data. In this case, the agents allow data to be first received from on premises and then sent from the Oracle Integration Cloud Service for SaaS instance to Oracle SaaS applications.
To create a boundary between the on-premises environment and the VCN, an on-premises firewall is configured with policies to inspect traffic and to ensure that the agents are allowed as traffic destinations. The agents also send data to an Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) database, which acts as a data store.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage is used for backups. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management is used to authenticate user access to the OCI tenancy. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit is used to review audit information from the OCI tenancy.
On the roadmap for HealthPartners are the following:
-
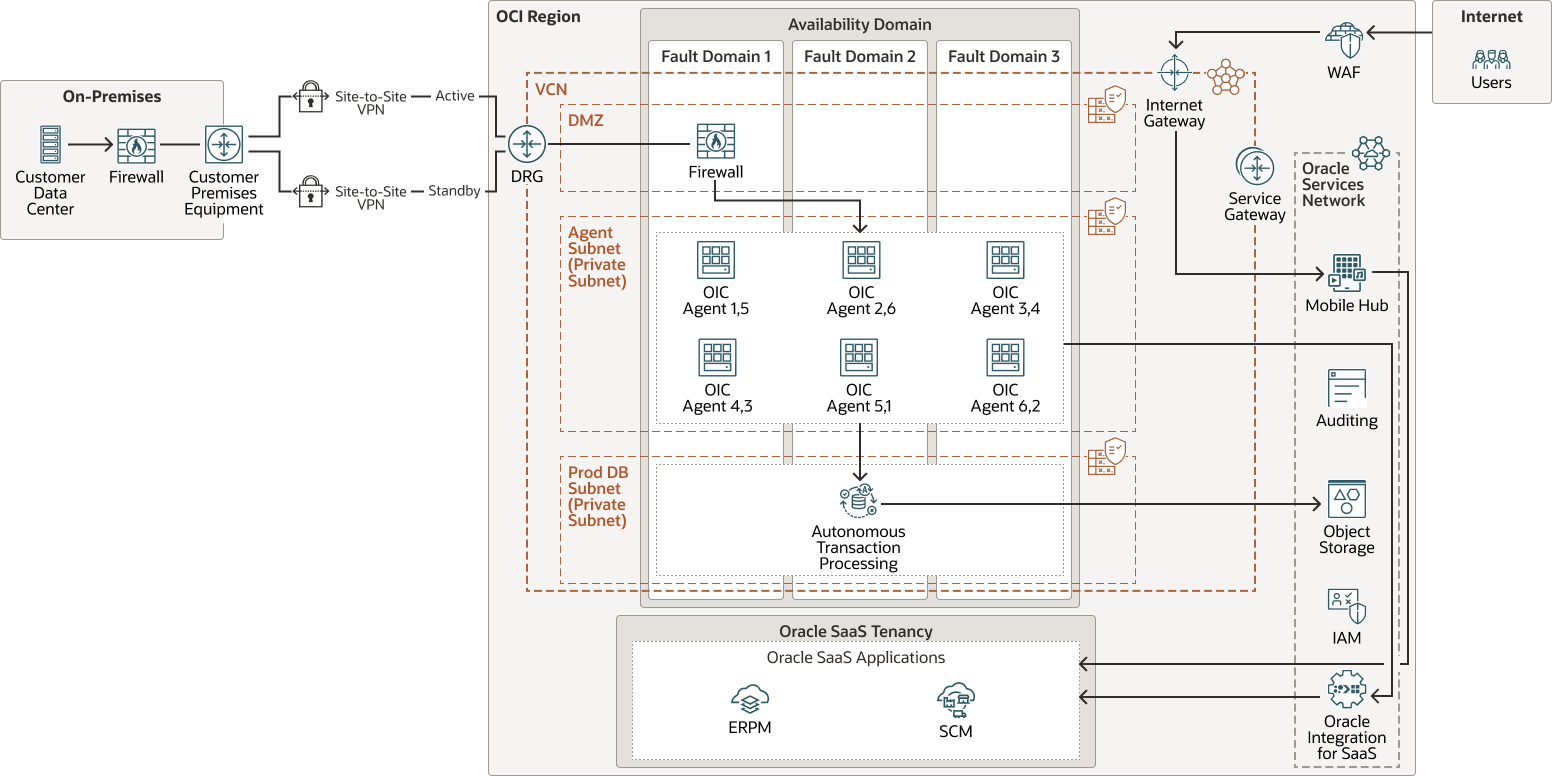
Implement high-availability OIC connectivity agents by creating agent groups, installing multiple agents on instances, and by placing the agent instances in different fault domains. This allows for high availability as well as for the horizontal scaling of agents.
-
Leverage the ATP data store with Oracle Analytics Cloud to provide insight into real-time data for business decision making.
-
Create a disaster recovery plan that allows operations to continue if an outage occurs in the region by deploying the agents in another region.
-
Investigate the integration of Oracle Mobile Hub to build applications to connect to the ERP, EPM, and HCM systems.
-
Deploy a DMZ subnet with a firewall for an additional layer of security and deploy Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall for mobile access.
-
Allow mobile user access after they are deployed as an entry point into the VCN.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
healthpartners-oci-future-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the access control plane for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Cloud Applications. The IAM API and the user interface enable you to manage identity domains and the resources within the identity domain. Each OCI IAM identity domain represents a standalone identity and access management solution or a different user population.
- Audit
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit service automatically records calls to all supported Oracle Cloud Infrastructure public application programming interface (API) endpoints as log events. Currently, all services support logging by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Integration for SaaS
Oracle Integration is a fully managed service that allows you to integrate your applications, automate processes, gain insight into your business processes, and create visual applications.
Oracle Integration for SaaS, a streamlined version of Oracle Integration, gives you the features and benefits of Oracle Integration with a focus on SaaS.
- Autonomous Transaction
Processing
Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing is a self-driving, self-securing, self-repairing database service that is optimized for transaction processing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating the database, as well as backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
Get Featured in Built and Deployed
Want to show off what you built on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure? Care to share your lessons learned, best practices, and reference architectures with our global community of cloud architects? Let us help you get started.
- Download the template (PPTX)
Illustrate your own reference architecture by dragging and dropping the icons into the sample wireframe.
- Watch the architecture tutorial
Get step by step instructions on how to create a reference architecture.
- Submit your diagram
Send us an email with your diagram. Our cloud architects will review your diagram and contact you to discuss your architecture.