Deploy High-Performance GPU computing for Government AI Workloads
DGX Cloud’s shared resource environment may be less suitable for customers in US Government regions who need the added security of keeping all data and resources under the control of their own tenancies. We have another solution for you.
Oracle now makes it easy to deploy a private cluster of bare metal NVIDIA GPU systems in our regions for Oracle US Government Cloud (FedRAMP High). All cloud resources and data remain under your cloud tenancy, giving you full control over software versions, administrative access, encryption keys, and resource sharing.
Oracle GPU Cluster with NVIDIA A100 GPUs or NVIDIA H100 GPUs is deployed by launching the HPC Cluster stack from the Marketplace. With just a few click and settings, Terraform and Ansible scripts automatically deploy hardware and software for a cluster environment with ultra-low latency RoCEv2 cluster network based on NVIDIA networking, cluster networking drivers, SLURM for job scheduling, NVIDIA Pyxis and Enroot for distributed container runtime. Bring your own large language models and machine learning workloads or pull NVIDIA PyTorch and NeMo containers to run NVIDIA AI Enterprise compatible workloads entirely within your secure tenancy.
- Large Language Models
- Artificial Vision
- Machine Learning
- Simulation
Architecture
This architecture deploys a bastion or head node, which runs the scheduler and can be used as a bastion server for access to the cluster.
You can create a compute processing node, using a variety of NVIDIA GPU instance types, with your processing requirements. We recommend placing the compute processing node in the secure private subnet. You can deploy NVIDIA GPU compute cluster instance from Oracle Cloud Marketplace.
This architecture is deployed using public and private virtual cloud networks (VCNs). The customer network can access the head node and compute node only through IPSec VPN, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect, or public internet.
The architecture uses a region with one availability domain and regional subnets. You can use the same architecture in a region with multiple availability domains. We recommend that you use regional subnets for your deployment, regardless of the number of availability domains. You can access these cluster networks from Oracle Cloud Marketplace or deploy them manually. In either case, we recommend using the baseline reference architecture and then adjusting it to meet your specific requirements.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
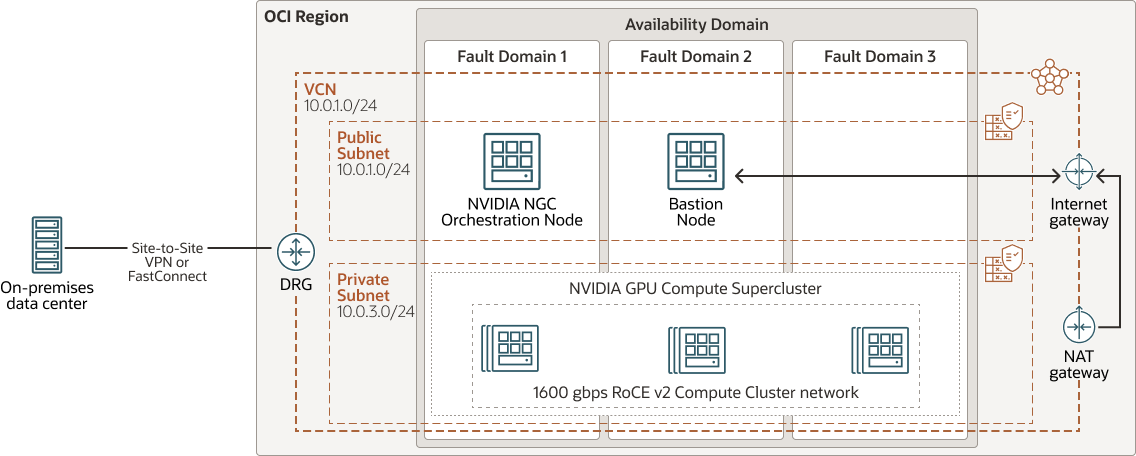
Description of the illustration nvidia-ai-gvt-hpc-oci.png
nvidia-ngc-ai-gvt-hpc-oci-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain shouldn't affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Bastion host
The bastion host is a compute instance that serves as a secure, controlled entry point to the topology from outside the cloud. The bastion host is provisioned typically in a demilitarized zone (DMZ). It enables you to protect sensitive resources by placing them in private networks that can't be accessed directly from outside the cloud. The topology has a single, known entry point that you can monitor and audit regularly. So, you can avoid exposing the more sensitive components of the topology without compromising access to them.
- Compute node
Select the bare metal GPU shape you are using in this cluster. For example, select BM.GPU4.8 powered by 4 x NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs, as shown in the example above, or select BM.GPU.H100.8 powered by 8 x NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs for FP8 performance benefits using the NVIDIA Transformer Engine.
- Orchestration node
The orchestration node performs cluster node management, provisioning, deprovisioning, and deployment of software configurations as well as managing compute workflows and jobs orchestration.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
Use regional subnets.
- Security lists
Use security lists to define ingress and egress rules that apply to the entire subnet.
- Bastion node
Use the VM.Standard.E5.Flex Compute shape. Since the node is used as a bastion host and to schedule HPC jobs, it doesn’t require locally attached storage or GPU processing.
- GPU Compute Cluster node
Use the BM.GPU.A100.-v2.8 Compute shape because this node is used for GPU compute workflows and highly compute intensive jobs.
Considerations
When deploying high-performance computing (HPC) on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, consider these implementation options.
- Performance
To get the best performance, choose the correct compute shape with appropriate bandwidth.
- Availability
Consider using a high-availability option based on your deployment requirements and region. Options include using multiple availability domains in a region and fault domains.
- Cost
A bare metal GPU instance provides necessary CPU power for a higher cost. Evaluate your requirements to choose the appropriate compute shape.
- Monitoring and alerts
Set up monitoring and alerts on CPU and memory usage for your nodes, so that you can scale the shape up or down as needed.
Deploy
-
Deploy using the stack in Oracle Cloud Marketplace:
- Go to Oracle Cloud Marketplace.
- Click Get App.
- Follow the on-screen prompts. For government requirements and operating environments, see Configure an HPC cluster stack to deploy NVIDIA AI on an OCI Government Region.
- Accept the End User License Agreement.
- Deploy using the code in GitHub:
- Go to GitHub.
- Clone or download the repository.
- Follow the instructions in the
READMEdocument.
Explore More
Learn more about the features of this architecture.
- NVIDIA NeMo
- Best practices framework for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Running Applications on Oracle Cloud Using Cluster Networking (blog)
- Running PyTorch distributed data parallel jobs on OCI GPU cluster (blog)
- Announcing general availability for OCI Compute bare metal instances powered by NVIDIA H100 GPUs (blog)