Learn About Connecting Oracle Cloud with Other Cloud Providers
You might run your cloud workloads on Oracle Cloud and one or more other cloud providers for various business and technical reasons. Cross-cloud workloads need a secure, low-latency interconnection between Oracle Cloud and the other cloud providers.
About Multicloud Deployments
A multicloud deployment uses public cloud services from more than one cloud provider.
- Oracle E-Business Suite running on Oracle Cloud, with datasets replicated to Microsoft Azure Data Lake, for analytics.
- .NET applications deployed on Microsoft Azure using a database running on Oracle Cloud.
Note that the term multicloud in this solution refers to multiple public clouds. An environment that spans private and public clouds is considered a hybrid cloud deployment.
Architecture
This architecture shows an application running in a third-party cloud connected to a database in Oracle Cloud.
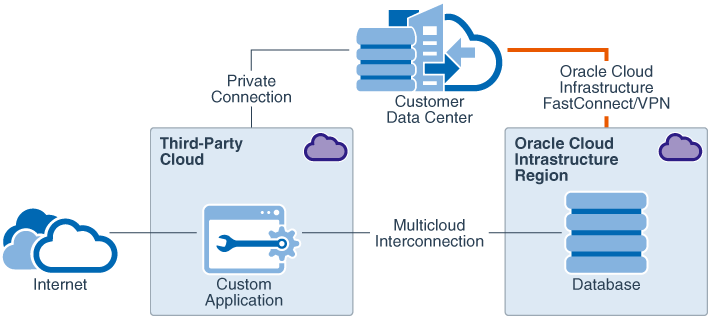
- To administer and maintain the resources in the cloud, you need private access to both the clouds.
- You can set up a private connection from your data center to Oracle Cloud by using either Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect virtual circuits or IPSec VPN connections. FastConnect provides a dedicated connection that bypasses the public internet. IPSec VPN connections are secure tunnels through the public internet.
- To administer the resources in the other cloud providers, you need similar private access.
- As shown in the architecture, a key requirement for a multicloud topology is a secure, low-latency connection between the cloud providers.
The method that you use to interconnect the third-party cloud with Oracle Cloud depends on your security constraints, latency requirements, and budget.