Architectures That Meet Workload Requirements
In customer deployments, there are many variations of architecture that will work. In some cases, these variations are designed to achieve a particular outcome, and in other cases they are to support a particular hardware capability or limitation. And in still others, they reflect preferences of the architect.
In every case, we recommend leveraging the baseline reference architecture and adjusting as needed so that your specific requirements are met. Starting from scratch can be time-consuming and comes with the risk that some important consideration has been overlooked. The reference architectures can help reduce the time and effort required to successfully deploy your PeopleSoft environment in the cloud
Networking and Connectivity
The primary objectives for the networking and connectivity architecture is to provide secure, high-speed connectivity between your cloud resources and any users and/or systems that would need to access those resources.
Effective networking and connectivity architecture also illustrates mechanisms by which you can design a network topology that best meets your needs, with the ability to isolate resources between bastion host, application tiers, database tiers and load balancing for security and management purposes.
Objectives of the Architecture
- Isolation from other customers and your other workloads.
- Network-level isolation between web/application tiers and database tiers.
- Monitoring and management access to all application and database tiers.
- Private/dedicated access from corporate campus(es) to the application.
- Ensuring low latency between cloud environment and your data center.
- Secure network access to the application via encrypted links over the public internet.
- Private network connectivity to other systems or services hosted on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- Load balancing across multiple application nodes for performance and availability.
Understand the Reference Architecture
The following figure illustrates the networking and connectivity reference architecture:
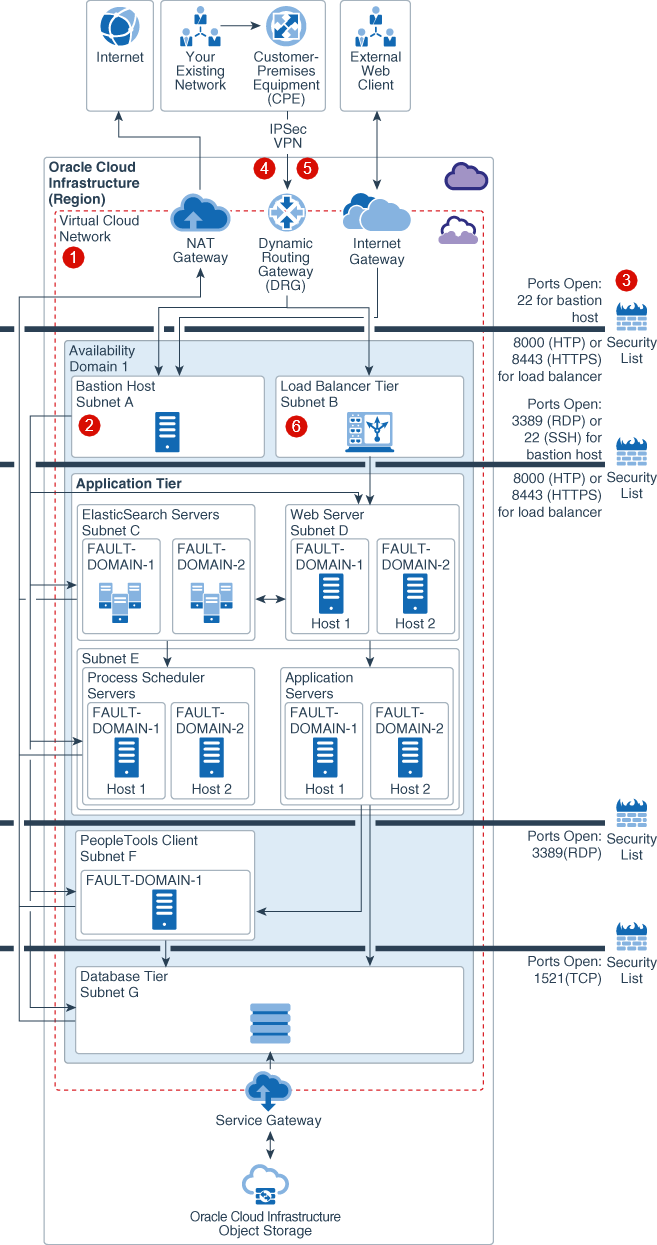
Description of the illustration psft_single_ad_withcallouts-networking.png
Virtual Cloud Network ![]() : A Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) is basically your own private network within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It provides isolation for your PeopleSoft workload from any other workload on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, including your other workloads in a different VCN. You can subdivide your VCN using subnets to ensure resource isolation and apply security rules to enforce secure access. You can also add route tables and rules to send traffic out of your VCN, similar to traditional network route rules.
: A Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) is basically your own private network within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It provides isolation for your PeopleSoft workload from any other workload on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, including your other workloads in a different VCN. You can subdivide your VCN using subnets to ensure resource isolation and apply security rules to enforce secure access. You can also add route tables and rules to send traffic out of your VCN, similar to traditional network route rules.
You can create instances in a private or a public subnet based on whether you want to permit access to the instances from the internet. Instances that you create in a public subnet are assigned a public IP address and you can access these instances from the public internet. Conversely, you cannot assign a public IP address to instances created in a private subnet therefore you can’t access these instances over the internet. You can, however, add a NAT gateway to your VCN to give instances in a private subnet the ability to initiate connections to the internet and receive responses for the purposes of applying OS and application updates. NAT gateways won’t receive inbound connections initiated by the internet.
We recommend creating separate subnets for each tier, such as bastion host, database, application, and load balancing, to ensure that appropriate security requirements can be implemented across the different tiers.
Bastion Host ![]() : The bastion host is an optional component that can be used as a jump server to access and manage Oracle Cloud Infrastructure instances in the private subnet. You can also access instances in a private subnet by using dynamic SSH tunneling.
: The bastion host is an optional component that can be used as a jump server to access and manage Oracle Cloud Infrastructure instances in the private subnet. You can also access instances in a private subnet by using dynamic SSH tunneling.
Internet Gateway (IGW): You can connect to instances that are placed in public subnets using the IGW. To access your instances from the internet, you also need to create your bastion host in a public subnet and access the bastion host from the IGW.
- Deploy all instances in a private subnet: Recommended for all production environments with no internet-facing endpoints. This type of deployment is useful when you want to have a hybrid deployment with the cloud as an extension to your existing data centers.
- Deploy instances in public and private subnets: You can deploy a few instances in a public subnet and a few instances in a private subnet. This type of deployment is useful when the deployment includes internet-facing and non-internet facing endpoints. In this configuration, some application instances are placed in a public subnet, and others are placed in a private subnet. For example, you may have application instances serving internal users and another set of application instances serving external users.
- Deploy all instances in a public subnet: Best for quick demos or for production-grade deployments with no internal endpoints. This deployment is suitable only if you don’t have your own data center or you can’t access instances over VPN, and you want to access the infrastructure over the internet. Although instances with public IP addresses can be accessed over the internet, you can restrict access by using security lists and security rules
Internal Firewalls ![]() : A security list provides a virtual firewall for each tier, with ingress and egress rules that specify the types of traffic allowed in and out.
: A security list provides a virtual firewall for each tier, with ingress and egress rules that specify the types of traffic allowed in and out.
FastConnect ![]() : If you require fast and predictable data transfer speeds, we offer FastConnect which guarantees a certain level of accessible bandwidth. Multiple partners across the world offer dedicated network connections between customer premises and Oracle data centers. This allows you to access your PeopleSoft implementation as if it is running in your own data center.
: If you require fast and predictable data transfer speeds, we offer FastConnect which guarantees a certain level of accessible bandwidth. Multiple partners across the world offer dedicated network connections between customer premises and Oracle data centers. This allows you to access your PeopleSoft implementation as if it is running in your own data center.
IPSec VPN Connect ![]() : For lower cost, but still secure access over the internet, you can use an encrypted Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) virtual private network (VPN) tunnel to connect from your HQ or on-premises data center to your PeopleSoft resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. From your on-premises environment, you can access your cloud instances in a private subnet by connecting through a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG). The DRG is the gateway that connects your on-premises network to your cloud network.
: For lower cost, but still secure access over the internet, you can use an encrypted Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) virtual private network (VPN) tunnel to connect from your HQ or on-premises data center to your PeopleSoft resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. From your on-premises environment, you can access your cloud instances in a private subnet by connecting through a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG). The DRG is the gateway that connects your on-premises network to your cloud network.
Load Balancing ![]() : Pre-configured, redundant load balancers are available on private and public subnets to balance traffic within the implementation and from external connections, respectively.
: Pre-configured, redundant load balancers are available on private and public subnets to balance traffic within the implementation and from external connections, respectively.
- For internal endpoints that aren’t accessible from the internet, use a private load balancer. Both the primary and the standby instances of a load balancer reside in the same private subnet. You can access private load balancers in the VCN or in your data center over the IPSec VPN through a DRG. The private load balancer accepts traffic from your data center and distributes the traffic to underlying application instances.
- For internet-facing endpoints, use a public load balancer. A public load balancer has a public IP address and it’s accessible from the internet. You can access the public load balancers from the internet through the IGW.
- For accessing both internal and internet-facing endpoints, you can set up private load balancers to serve internal traffic and set up public load balancers to serve the traffic from the internet.
Resiliency and High Availability
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's resiliency and high availability architecture builds resiliency, redundancy and high availability (HA) into the cloud infrastructure that is supporting PeopleSoft and its backend datasets.
Objectives of the Architecture
- Ensures system resiliency and anti-affinity, meaning that PeopleSoft is available even if an application instance goes down
- Provides server redundancy via multiple active-active nodes at each application tier.
- Provides redundancy strategy for database tiers.
- Provides a backup strategy for non-database tiers.
- Provides backup requirements for database tiers.
Understand the Reference Architecture for Deploying PeopleSoft in a Single Availability Domain
At a basic level, you can achieve resiliency and high availability for your PeopleSoft deployment even within a single availability domain (AD). This diagram illustrates the networking and connectivity reference architecture for deploying PeopleSoft in a single availability domain:
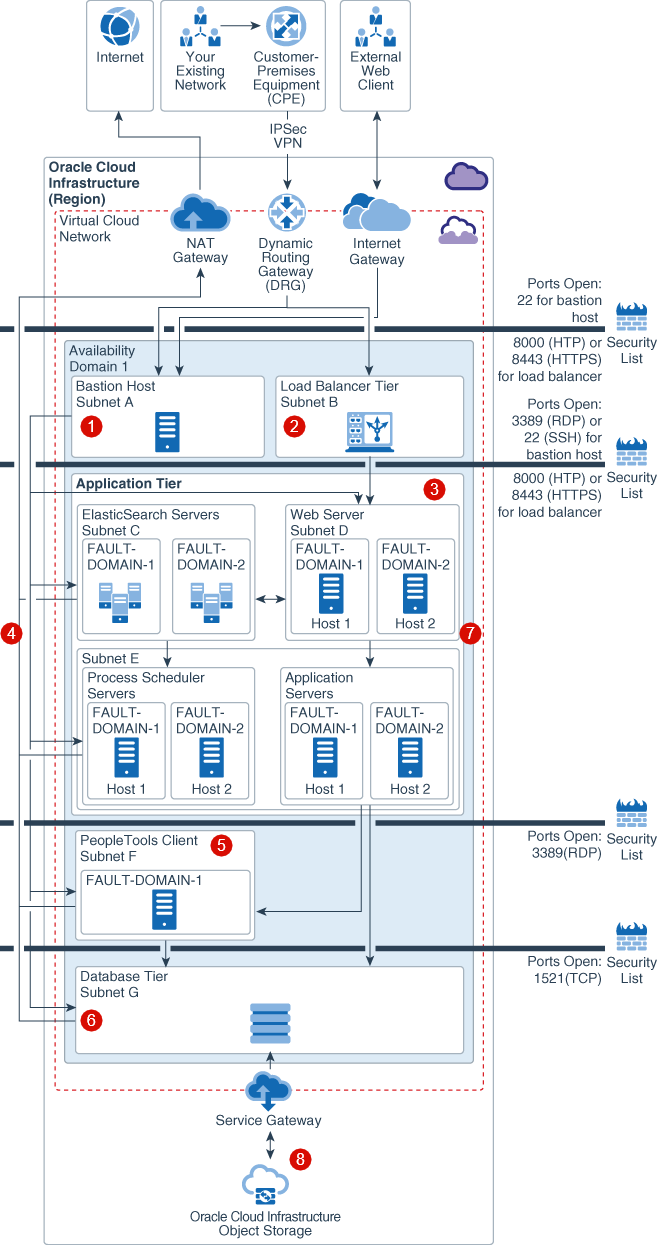
Description of the illustration psft_single_ad_withcallouts-components.png
Bastion Host ![]() : The bastion host is an optional component that you can use as a jump server to access the instances in the private subnet.
: The bastion host is an optional component that you can use as a jump server to access the instances in the private subnet.
Load Balancer Tier ![]() : We recommend having load balancers in their own tier or subnet to load balance traffic to PeopleSoft web servers. The load balancer receives requests from users, and then routes these requests to the application tier.
: We recommend having load balancers in their own tier or subnet to load balance traffic to PeopleSoft web servers. The load balancer receives requests from users, and then routes these requests to the application tier.
System Resilience ![]() : A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure that is distinct from other fault domains in the same AD, and each AD has three fault domains. Fault domains let you distribute your application instances so that they are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. As a result, a hardware failure or hardware maintenance event that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. By using fault domains, you can protect your instances against unexpected hardware failures and planned outages.
: A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure that is distinct from other fault domains in the same AD, and each AD has three fault domains. Fault domains let you distribute your application instances so that they are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. As a result, a hardware failure or hardware maintenance event that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. By using fault domains, you can protect your instances against unexpected hardware failures and planned outages.
Active-Active Server Redundancy in the Application Tier ![]() : This tier contains redundant instances of the PeopleSoft application servers, PeopleSoft web servers, ElasticSearch servers, and PeopleSoft Process Scheduler to provide high availability. Redundancy is enabled for all servers in the application tier through the usage of fault domains. This helps ensure that you can continue accessing the application even if an instance goes down. All instances are active and receive traffic from the load balancer and middle tier.
: This tier contains redundant instances of the PeopleSoft application servers, PeopleSoft web servers, ElasticSearch servers, and PeopleSoft Process Scheduler to provide high availability. Redundancy is enabled for all servers in the application tier through the usage of fault domains. This helps ensure that you can continue accessing the application even if an instance goes down. All instances are active and receive traffic from the load balancer and middle tier.
PeopleTools Client ![]() : Use the PeopleTools client to perform administration activities, such as development, migration, and upgrade.
: Use the PeopleTools client to perform administration activities, such as development, migration, and upgrade.
Redundancy in the Database Tier ![]() : This tier contains database system instances. For performance and HA requirements, Oracle recommends that you use two-node Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) database systems or Oracle Database Exadata Cloud Service in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
: This tier contains database system instances. For performance and HA requirements, Oracle recommends that you use two-node Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) database systems or Oracle Database Exadata Cloud Service in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Backup Strategy - Application Tier ![]() : Backup of the application tiers can be configured by using the policy-based backup feature of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volumes. Block Volumes provide you with the capability to perform volume backups automatically based on a schedule and retain them based on the selected backup policy.
: Backup of the application tiers can be configured by using the policy-based backup feature of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Block Volumes. Block Volumes provide you with the capability to perform volume backups automatically based on a schedule and retain them based on the selected backup policy.
Backup Strategy - Database Tier ![]() : Use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage to perform a backup using Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN). To back up or patch the database to Object Storage, the database system's VCN must be configured with either a service gateway or an IGW. It is recommended that you use a service gateway rather than an IGW for backup and patching because service gateway does not traverse the internet.
: Use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage to perform a backup using Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN). To back up or patch the database to Object Storage, the database system's VCN must be configured with either a service gateway or an IGW. It is recommended that you use a service gateway rather than an IGW for backup and patching because service gateway does not traverse the internet.
Disaster Recovery
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides PeopleSoft implementations that ensure you can build disaster recovery (DR) into your deployment in case of unforeseen events that would require you to failover and still keep PeopleSoft up and running
Objectives of the Architecture
- Disaster recovery within a single region:
- Active-Active components across availability domains
- Active-Passive components across availability domains
- Regional subnets across availability domains
- Load-balancing across availability domains
- Storage synchronization across availability domains
- Database disaster recovery across availability domains
- Disaster recovery across multiple regions:
- Application replication between regions
- Storage replication between regions
- Cross-region copy lets you asynchronously copy object storage datasets
- Cross-region backup copy for block volumes
- Database protection between regions
Understand the Reference Architecture for Deploying PeopleSoft in a Single Region
To ensure that PeopleSoft is available if one availability domain goes down, we recommend that you deploy across multiple availability domains. This diagram illustrates the reference architecture for deploying PeopleSoft in multiple availability domains in a single region.
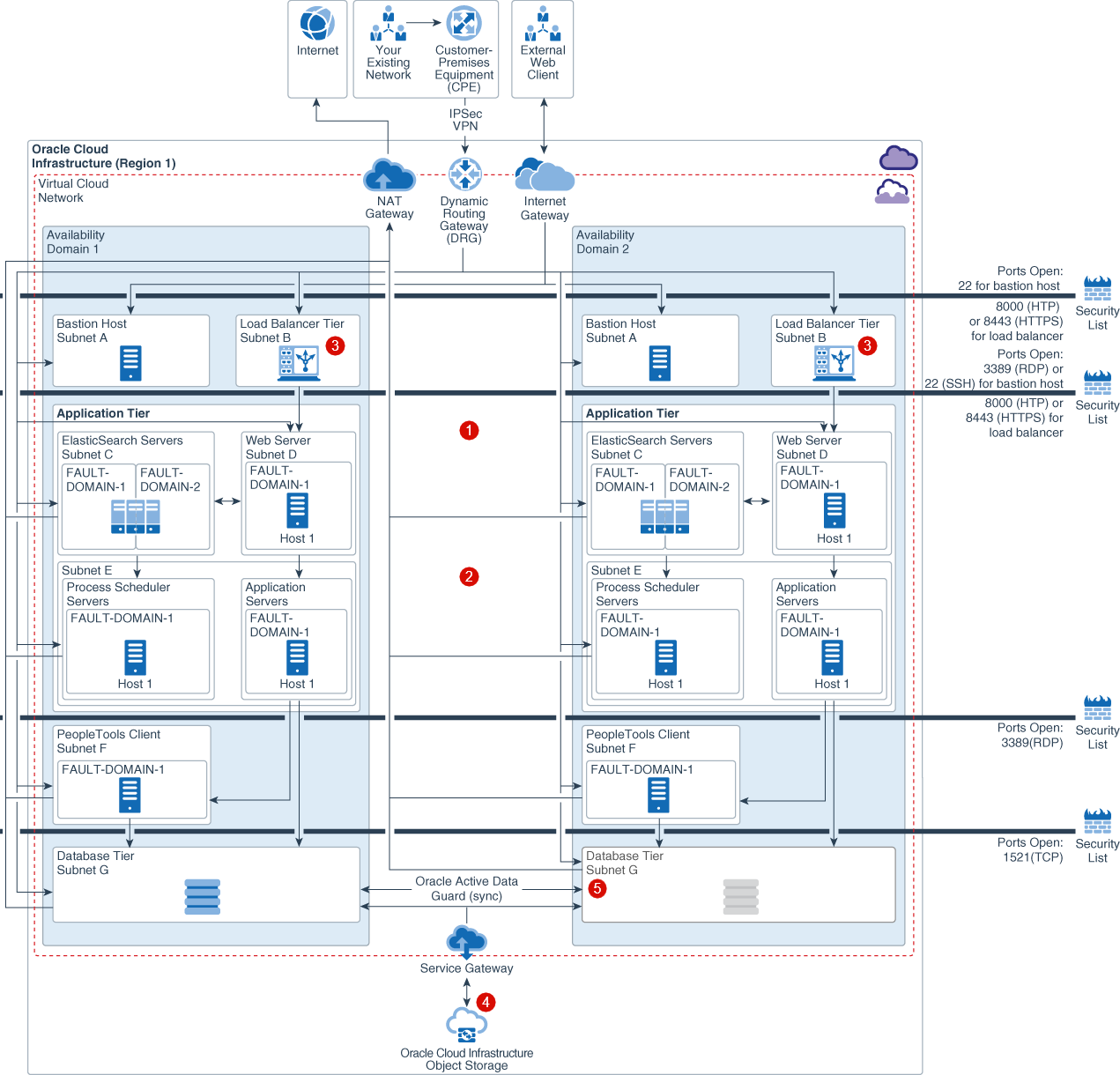
Description of the illustration psft_multi_ad_withcallouts.png
Active-Active Components across availability domains ![]() : Clustering of supported services across availability domains provides protection from an availability domain failure. In this architecture bastion hosts, load balancers, and application tier servers in both availability domains are in active state.
: Clustering of supported services across availability domains provides protection from an availability domain failure. In this architecture bastion hosts, load balancers, and application tier servers in both availability domains are in active state.
Active-Passive Components across availability domains ( ): If you are using Active-Passive architecture, use rsync to synchronize application servers across availability domains.
Regional Subnets across availability domains ![]() : Regional subnets span the entire region providing benefits like protection from availability domain network failure, simplified PeopleSoft service deployment and management.
: Regional subnets span the entire region providing benefits like protection from availability domain network failure, simplified PeopleSoft service deployment and management.
Load Balancing across availability domains ![]() : Public load balancing distributes traffic across the PeopleSoft servers across all configured availability domains, providing protection from an availability domain failure.
: Public load balancing distributes traffic across the PeopleSoft servers across all configured availability domains, providing protection from an availability domain failure.
Storage Synchronization across availability domain ![]() : Block Volume backups (boot and block) are replicated across all availability domains within a region and can be restored to any availability domain within the same region. Object Storage is a regional service. Data is stored redundantly across multiple storage servers and across multiple availability domains automatically.
: Block Volume backups (boot and block) are replicated across all availability domains within a region and can be restored to any availability domain within the same region. Object Storage is a regional service. Data is stored redundantly across multiple storage servers and across multiple availability domains automatically.
Database DR across Availability Domains ![]() : We recommend setting up database instances in both availability domains. Availability domain 1 hosts the primary database instances while availability domain 2 hosts the standby database instances. In each availability domain, at least two database instances are set up to ensure high availability. If a database instance is not available in availability domain 1, then the second database instance in availability domain 1 continues processing requests. Data Guard or Active Data Guard may be selected depending on your use case and database edition for replication across availability domains. Active Data Guard requires Enterprise Edition – Extreme Performance.
: We recommend setting up database instances in both availability domains. Availability domain 1 hosts the primary database instances while availability domain 2 hosts the standby database instances. In each availability domain, at least two database instances are set up to ensure high availability. If a database instance is not available in availability domain 1, then the second database instance in availability domain 1 continues processing requests. Data Guard or Active Data Guard may be selected depending on your use case and database edition for replication across availability domains. Active Data Guard requires Enterprise Edition – Extreme Performance.
Understand the Reference Architecture for Deploying PeopleSoft Across Multiple Regions
For true data recovery capabilities, you should set up a data recovery site for PeopleSoft in a different geographical region. This diagram illustrates the reference architecture for deploying PeopleSoft across multiple regions.
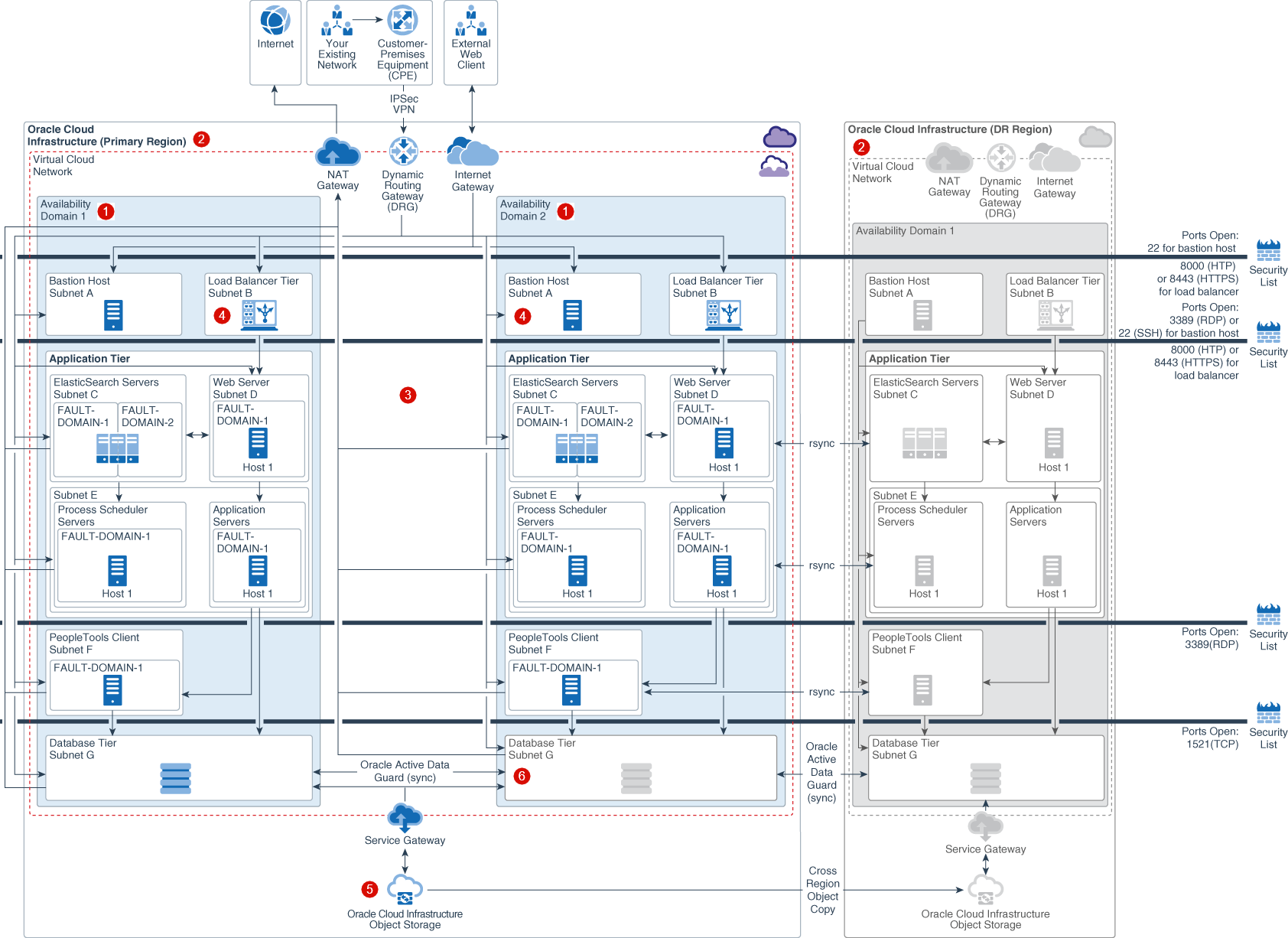
Description of the illustration psft_multi_region_withcallouts.png
Active-Active Components across availability domains ![]() : Clustering of supported services across availability domains provides protection from an availability domain failure. Again, bastion hosts, load balancers, and application tier servers in both availability domains are in active state.
: Clustering of supported services across availability domains provides protection from an availability domain failure. Again, bastion hosts, load balancers, and application tier servers in both availability domains are in active state.
Active-Passive Components across Regions ![]() : If you are using Active-Passive architecture, use rsync to synchronize application servers across availability domains.
: If you are using Active-Passive architecture, use rsync to synchronize application servers across availability domains.
Regional Subnets across availability domains ![]() : Regional subnets span the entire region providing benefits like protection from availability domain network failure, simplified PeopleSoft service deployment and management.
: Regional subnets span the entire region providing benefits like protection from availability domain network failure, simplified PeopleSoft service deployment and management.
Load Balancing across availability domains ![]() : Load Balancing distributes traffic across the PeopleSoft servers across all configured availability domains, providing protection from availability domain failure.
: Load Balancing distributes traffic across the PeopleSoft servers across all configured availability domains, providing protection from availability domain failure.
Storage Synchronization across availability domains ![]() : Block Volume backups (boot and block) are replicated across all the availability domains within a region and can be restored to any availability domain within the same region. Object Storage is a regional service. Data is stored redundantly across multiple storage servers and across multiple availability domains automatically.
: Block Volume backups (boot and block) are replicated across all the availability domains within a region and can be restored to any availability domain within the same region. Object Storage is a regional service. Data is stored redundantly across multiple storage servers and across multiple availability domains automatically.
Database DR across Availability Domains ![]() : The use of either Data Guard or Active Data Guard is dependent on your use case and database edition. Active Data Guard requires Enterprise Edition – Extreme Performance.
: The use of either Data Guard or Active Data Guard is dependent on your use case and database edition. Active Data Guard requires Enterprise Edition – Extreme Performance.
Security
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides a security architecture that enables you to maintain your security posture when running your business-critical PeopleSoft application and associated applications in the Oracle Cloud
As a cloud provider, Oracle provides and operates a secure infrastructure. Security has been designed into every aspect of our infrastructure to help our customers achieve better protection, isolation and control. We started with taking a unique design approach, separating the network and server environments. This way, if an attack occurs on a VM, we can contain that threat and prevent it from moving to other servers, resulting in better protection and lower risk for customers. We also hyper-segment our physical network and backend infrastructure for secure isolation between customer instances and backend hosts. Additionally, we’ve implemented hardware-based root of trust, making sure each server is pristine each and every time it is provisioned.
However, security is a shared responsibility between Oracle and our customers. Therefore, we provide security tools and also support your existing tools, so you can maintain granular control over identity and access management (IAM), networking, compute, and data management for your PeopleSoft deployment in the cloud without having to rebuild your security posture.
Objectives of the Architecture
- Ensure PeopleSoft and associated data assets are completely isolated from other tenants’ workloads and Oracle’s staff so to limit the effect of noisy neighbors and prevent lateral movement of attacks.
- Protect your internet-facing PeopleSoft applications from cyberattacks.
- Encrypt your data in a way that allows you to meet your security and compliance requirements.
- Segregate operational responsibilities and restrict access to cloud services in order to reduce risk associated with malicious and accidental user actions.
- Be able to leverage existing security assets such as identity providers and other third-party security solutions to secure access to your PeopleSoft application and data.
- Audit and monitor actions taken on your cloud resources so that you can meet audit requirements.
- Demonstrate compliance readiness to internal security and compliance teams, end-customers, auditors and regulators.
Understand the Security Reference Architecture
This diagram illustrates the security reference architecture provided for PeopleSoft running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
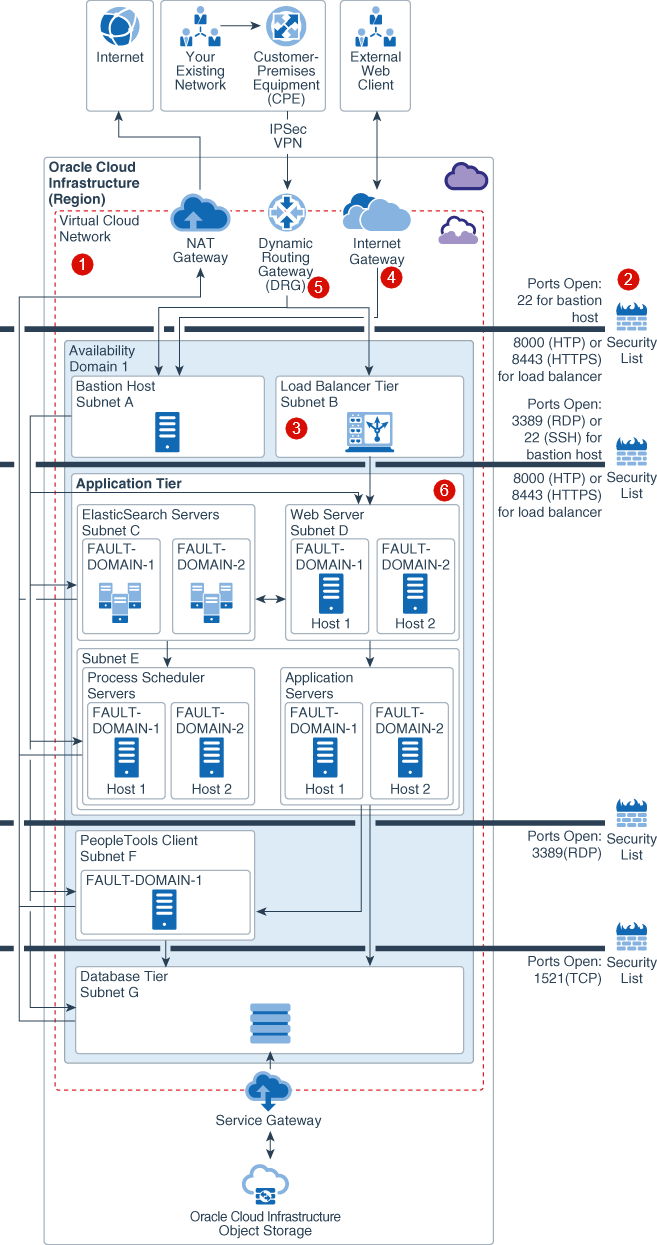
Description of the illustration psft_single_ad_withcallouts-security.png
- VCN
 : A VCN provides isolation for your PeopleSoft workload from any other workload on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, including your other workloads in a different VCN.
: A VCN provides isolation for your PeopleSoft workload from any other workload on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, including your other workloads in a different VCN.
- Internal Firewalls
 : Implement virtual firewalls at the subnet level using VCN security lists.
: Implement virtual firewalls at the subnet level using VCN security lists.
- Load Balancing Traffic Securely
 : TLS 1.2 is supported by default to securely balance traffic within the implementation and from external connections
: TLS 1.2 is supported by default to securely balance traffic within the implementation and from external connections
- Secure Traffic between Availability Domains and Regions: Communications between availability domains are encrypted with Media Access Control security (MACsec) to prevent layer 2 security threats such as wiretapping, DDoS, intrusion, man-in-the-middle and playback attacks. VCN traffic that travel between regions are either sent over private links or are encrypted.
- Secure Connectivity to Public Internet
 : For security, a VCN has no internet connectivity by default. Therefore, internet-bound traffic to/from a VCN must pass through an IGW. Virtual routing tables can be implemented with private IP addresses for use with NAT and 3rd party firewall devices for additional security.
: For security, a VCN has no internet connectivity by default. Therefore, internet-bound traffic to/from a VCN must pass through an IGW. Virtual routing tables can be implemented with private IP addresses for use with NAT and 3rd party firewall devices for additional security.
- Secure Connectivity between your VCN and Data Center
 : Traffic can be routed through a DRG for private traffic. It is used with an IPSec VPN or FastConnect connection to establish private connectivity between a VCN and an on-premises or other cloud network.
: Traffic can be routed through a DRG for private traffic. It is used with an IPSec VPN or FastConnect connection to establish private connectivity between a VCN and an on-premises or other cloud network.
- Protect Internet-facing Applications
 : Oracle provides a Web Application Firewall (WAF) service with 250 pre-defined OWASP and compliance rules. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure WAF acts as a reverse proxy that inspects all traffic flows or requests before they arrive at the origin web application. It also inspects any request going from the web application server to the end user. Additionally, Oracle’s optional global anycast DNS service also takes advantage of DNS-based DDoS protections providing resiliency at the DNS layers.
: Oracle provides a Web Application Firewall (WAF) service with 250 pre-defined OWASP and compliance rules. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure WAF acts as a reverse proxy that inspects all traffic flows or requests before they arrive at the origin web application. It also inspects any request going from the web application server to the end user. Additionally, Oracle’s optional global anycast DNS service also takes advantage of DNS-based DDoS protections providing resiliency at the DNS layers.
Server Isolation: If you require complete workload and data isolation at the server level for security and/or performance requirements, you can leverage bare metal compute shapes. These shapes are single tenant, so they offer consistently high performance and are immune to noisy-neighbor issues. There is also no Oracle managed hypervisor and Oracle staff have no access to memory nor local NVMe storage while the instance is running.
If you have more flexible requirements for PeopleSoft, our multi-tenant VM shapes leverage a security-hardened hypervisor that provides strong isolation between customers. And regardless of shape type, bare metal or VM, all servers are wiped clean and installed with gold state firmware when newly provisioned.
Data Encryption: By default, all data that customers store with any of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure’s storage or data management services, including Block Volumes, boot volumes, Object Storage, File Storage, and Database, is encrypted at rest using strong AES keys or TDE in the case of database encryption.
Key Management: For customers that require the ability to control their own cryptographic keys for security or compliance purposes, we offer Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Key Management. With Key Management, you can centralize key lifecycle management in FIPS 140-2 Level 3 hardware security modules (HSMs).
Identity and Access Management: Identity management including authentication, authorization, tools to help you organize and control access to resources according to organizational hierarchy, and the ability to leverage existing identity providers is such a rich topic that we devoted a separate section to IAM below.
Audit and Logging: Oracle automatically records calls to all supported Oracle Cloud Infrastructure public application programming interface (API) endpoints as log events. Currently, all services support logging by our Audit service. You can leverage this data to perform diagnostics, track resource usage, monitor compliance, and collect security-related events.
Compliance: Depending on where you do business and industry-specific practices, you may need to demonstrate compliance readiness to internal teams and to external auditors. Oracle continually engages with external assessment entities and independent auditors to meet a broad set of international and industry-specific compliance standards for service deployments on our cloud.
Identity and Access Management
With Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's Identity and Access Management (IAM) architecture, you can group and isolate resources according to your organizational structure and hierarchy, control who has access to cloud resources, what type of access a group of users has, and to which specific resources.
Objectives of the Architecture
- Securely isolate cloud resources based on organizational structure.
- Authenticate users to access cloud services via browser interface, REST API, SDK or CLI.
- Authorize groups of users to perform actions on appropriate cloud resources.
- Enable managed service provider (MSP) or systems integrator (SI) to manage infrastructure assets while still allowing your operators the ability to access resources.
- Authorize application instances to make API calls against cloud services.
- Federate identities using your existing identity provider (IDP).
IAM Supporting Services
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers a single model for authentication and authorization, and it also integrates with your existing identity provider.
- Compartments: Compartments are a fundamental component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for organizing and isolating your cloud resources. A common approach is to create a compartment for each major part of your organization. For example, you can place all database resources in a database compartment and only grant database administrators access. You can also use them to ensure isolation between business units and to logically group resources for the purposes of measuring usage and billing.
- Authentication and Credential Management: By default, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure enforces a strong password policy for access to the console user interface and to the Swift client for database backups to Object Storage. Administrators can also modify password policies for all local or non-federated users using Oracle IAM service. Each user can automatically reset their own console passwords and manage their own API keys. However, you must have administrator permissions to manage credentials for users other than yourself. Learn more about managing user credentials.separation of duties.
- Policies: Leverage policies to authorize a group of users to take action on cloud resources in a specified compartment or across the tenancy. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure policies are written in human-readable language, so they are simple to define and easy to understand.
- IAM for MSP/SIs: A common use case is to have an MSP or SI manage your cloud infrastructure assets while still retaining the entitlement to operate your cloud resources. Compartments and policies can be used in conjunction to ensure clear.
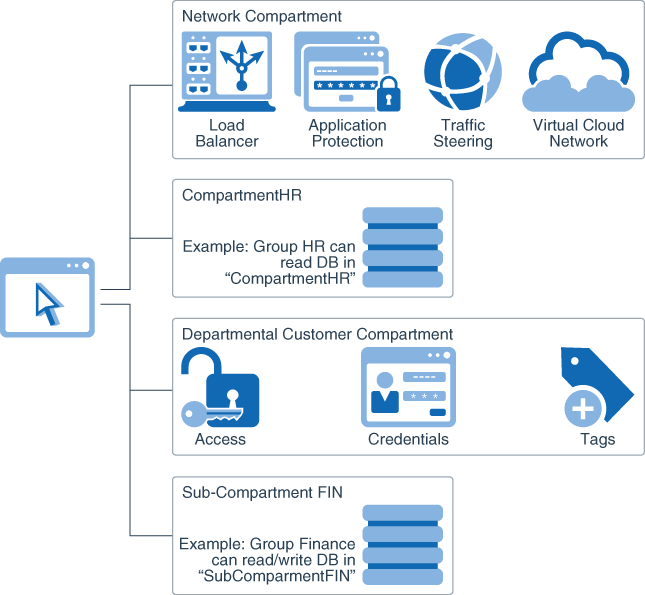
Description of the illustration iam_for_msp-sis.png - Instance Principals: Allow users to call IAM-protected APIs from an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compute instance without the need to create users or manage credentials for that instance. You may have a PeopleSoft application or an integrated application running on a compute instance that requires access to object storage. By grouping the appropriate compute instances as “principal” actors, you can simply attach policies to enable them to make API calls against other cloud services such as object storage.
- Federation: Oracle IAM supports federation with Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) and any other SAML 2.0 compliant identity provider.
- When you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your tenant administrator account is automatically federated with Oracle Identity Cloud Service. Federating with Oracle Identity Cloud Service automatically allows you to have a seamless connection between services without having to create a separate username and password for each one.
- As a PeopleSoft customer, you may be leveraging the application’s own security mechanisms to provide authentication with integrated applications on-premises that leverage Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), Oracle Access Manager (OAM) or other 3rd party solutions. Therefore, we recommend federating your favorite IDP with IDCS which will automatically provide federation for all Oracle cloud offerings.
Cost Management and Governance
When transitioning from from a capital expenditure model, where many costs are fixed at project implementation, to an operating expenditure model, where costs scale up and down with system usage, customers often require cost management tools to understand and control these cloud costs within their organization.
- Set and manage cloud budgets.
- Prevent overspending.
- Ensure accurate cost tracking across departments and project.
- Analyze which departments, services and projects are contributing to cloud usage over time.
- Get granular usage details for invoice reconciliation.
- Identify areas to optimize cost.
Cost Management and Governance Supporting Services
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's cost management and governance architecture is supported by the services outlined here.
Compartments: Compartments can be used to ensure isolation of cloud resources between business units. In addition, they are also used to logically group resources for the purposes of measuring usage and billing. We typically recommend creating a compartment for each major part of your organization, i.e. business unit or department. Compartments can also be nested to support sub-departments as well.
Tagging: Leverage tags to track cost and usage of resources that are associated with a particular project that span multiple departments. In addition, you can streamline resource management by tagging and then scripting bulk actions on exactly the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources you want. Tags leverage policies and controls to ensure tagging integrity and to prevent users from creating excessive tags, duplicate tags, and manipulating existing tags.
Budgets: Once resources are assigned to compartments that match your specific use-cases, departments or regions of operation, you can set budgets, view how spend is tracking against budgets, and configure alerts so that unexpected usage is flagged before a budget is actually exceeded.
Cost Analysis: The billing cost analysis dashboard can help visualize the big buckets that are contributing to cloud usage and cost. You can analyze costs by cloud service, compartments and tags. For example, an analyst or administrator can use this tool to identify the difference between increased production or dev/test usage, as well as the difference between increased usage of storage versus networking.
Detailed Usage Reports: CSV files containing detailed resource-level and hour-by-hour data, including all associated metadata, i.e. tags and compartments. Export detailed usage reports as CSV files and import into existing business intelligence tools for invoice reconciliation use cases, to get more granularity into your bill and to identify areas for cost optimization. For example, you can leverage the detailed usage data and combine with CPU utilization data from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring service to identify instances with low CPU utilization to shut down.
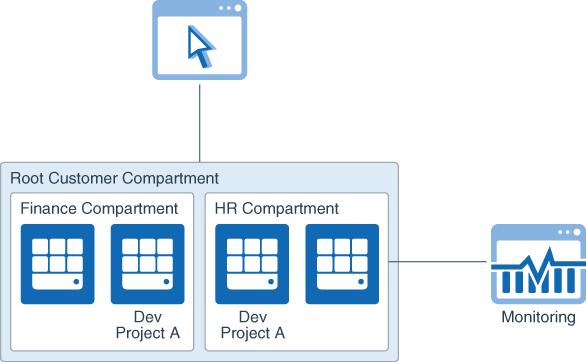
Description of the illustration cost_management_compartments.png
Monitoring
You need to be able to monitor the health and capacity of cloud infrastructure resources in order to optimize PeopleSoft performance at all times and in real time. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides an architecture to meet those needs.
Objectives of the Architecture
Objectives include ensuring availability and performance of PeopleSoft on the cloud and detecting and fixing anomalies before they can impact your business. Additionally, you might require the visibility to identify bottlenecks and under-utilized resources to optimize accordingly.
Monitoring Supporting Services
You might already be leveraging monitoring tools like Oracle Enterprise Manager and Oracle Management Cloud for your existing PeopleSoft deployment. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers infrastructure monitoring natively within the console, but it can also support your existing monitoring tools.
- Multi-Tier Monitoring of Hybrid/Multi-Cloud Environments: For most multi-tier migration scenarios, we recommend leveraging Oracle Management Cloud. Oracle Management Cloud provides integrated monitoring across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. It performs monitoring through use of agents across various tiers from infrastructure to application performance, security, and even end-user activity. And it integrates with Oracle Enterprise Manager for Oracle Database performance and capacity analytics.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring: Cost-effective and out-of-the-box metrics and dashboards are provided for IT to monitor cloud resources such as compute instances, block volumes, virtual NICs, load balancers, and object storage buckets natively within the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console. For example, you can leverage Monitoring to track CPU utilization, memory utilization and integrate with compute autoscaling. You can also integrate with open-source visualization tools, run your own metrics queries, and have your applications emit their own custom metrics, enabling you to visualize, monitor and alarm on all critical time-series data from one place in the console.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure performs agentless monitoring. Currently this native infrastructure monitoring service does not monitor database services. For that, we recommend either Oracle Management Cloud or Oracle Enterprise Manager, depending on if Oracle Database is deployed on-premises or as a cloud service.
Migration and Deployment
When it comes to migrating a complex, highly customized and deeply integrated application like PeopleSoft, it’s important to do it with as little re-architecture as possible so that there’s limited downtime and the transition is completely seamless for end-users.
Objectives of the Architecture
- Provide application-aware tooling that allow you to keep existing customizations and integrations.
- Enable post-migration application configuration.
- Enable data migration.
Understand the Migration and Deployment Reference Architecture
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure provides a migration and deployment architecture that ensures minimal re-architecture and limits downtime, ensuring a seamless transition for end-users.
Application Migration: PeopleSoft Cloud Manager is an application-aware migration and administration tool that can help you migrate, deploy and manage your PeopleSoft environment on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure along with the different services that are needed by the application to run seamlessly. It can also help you configure the application after the migration is complete.
- Lift and shift an on-premises environment to Oracle Cloud.
- Provision PeopleSoft environments on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute and Oracle Database Cloud Services.
- Create reusable deployment templates.
- Self-service provisioning of PeopleSoft environments, if desired.
- Manage multiple environments from a single page.
- Perform on-demand health checks on environments.
- Enable application lifecycle management in Oracle Cloud.
- Automatically download PeopleSoft Update Manager (PUM) images, PeopleSoft Release Patchsets (PRPs) and PeopleTools patches.
- Clone environments by creating templates from running instances.
- Lift: Using the lift utility provided in PeopleSoft Cloud Manager, PeopleSoft application environment data and the supporting Oracle Database is packed into DPK format and uploaded to Oracle Object Storage. The lift utility “lifts” the application tier (middle tier) and database tier independently and packages them into separate DPKs. PeopleSoft Cloud Manager supports two types of database lift — hot backup and cold backup. Hot backup is performed with RMAN using Oracle Database Cloud Backup Module (ODCBM). Cold backup is performed by taking a cold backup of the pluggable database.
- Shift: PeopleSoft Cloud Manager downloads the lifted DPKs and creates a new environment on Oracle Cloud. Once shifted, customers can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to further manage, scale up or scale down or clone these environments.
Application Configuration & Deployment: In addition to lift & shift, you can also use PeopleSoft Cloud Manager to define a multi-node topology including the number, type and size of VMs (CPU, memory, storage) needed for Linux and Windows together. Once your topology is defined, you can combine with your PeopleSoft DPK to create an environment template that can be deployed at a click.
If you are on a prior version of PeopleSoft or if you want to customize your deployment per specific needs, Oracle still supports manual lift & shift.
You can also leverage Terraform scripts to automate orchestration for your PeopleSoft deployments on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Data Migration: During an application-aware migration, VMs and physical machines will never be captured or migrated. Only data and specific configuration files are captured and prepared for migration. PeopleSoft Cloud Manager will deploy a new instance of the application in the Oracle Cloud environment or use an existing instance of the application in the target environment.
- FastConnect: Oracle FastConnect is another option for securely connecting on-premises data centers and networks to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It's the optimal choice for organizations that need to transport large datasets. Port speeds are available in 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps increments when working with a third-party connectivity provider, and 10 Gbps increments when co- locating with Oracle.
- IPSec VPN Connect: Relatively small datasets—up to approximately 2 terabytes (TBs)—can typically be transported over the public internet without problems. We recommend using IPsec VPN Connect, which provides encrypted and secure connectivity between your source environment and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to securely write data into Object Storage and then restore from there. The first step to setting up an IPsec VPN Connect between the source environment and Oracle is establishing a DRG. The DRG should be set up to connect Oracle's cloud with any on-premises routers. Use multiple IPsec tunnels to ensure redundancy.
- Storage Gateway: Once a secure connection has been established, organizations can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Storage Gateway to securely create copies of on-premises files and place them into Oracle Object Storage without the need to modify applications.
- Data Transfer Appliance: Each Data Transfer Appliance enables organizations to migrate up to 150 TBs of data. Appliances can be requested via the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console after creating a transfer job. The appliance should be configured and connected to the on-premises network. Migration teams also need to mount NFS volumes off the appliance and copy the data onto the appliance. After the data is copied, ship the appliance back to Oracle and monitor the status of the data transfer.
- Data Transfer Disk: Oracle's Data Transfer Disk is another offline data transfer solution. You can send data as files on encrypted disks to an Oracle transfer site. Then site operators upload the files into your designated object storage bucket. Users are free to move the uploaded data into other Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services as needed. For details on the supported disk types.
Migration Expertise from Oracle and Partners: Oracle Managed Cloud Services (OMCS) and established SI partners also provide extensive PeopleSoft migration expertise and experience.
3rd-Party Integrations: If you are running PeopleSoft on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure you can integrate with other ISV applications. We have a broad ecosystem of ISV partners that we are working with in our Marketplace already and have a process for onboarding additional ISVs into our cloud.