Migrate a Microsoft SQL Server to Oracle Cloud
This is tested against a Microsoft SQL Server 2016 database, but the steps are generic and you should be able to adapt them to later versions of Microsoft SQL Server.
Architecture
After migrating the data to OCI, you can use the built-in machine learning, analytics, and AI tools to run complex queries across multiple data types, and build sophisticated analytical models.
- Data scientists can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Catalog to explore, discover, and analyze data.
- Business analysts can access and visualize information.
- Developers can build data-driven applications.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
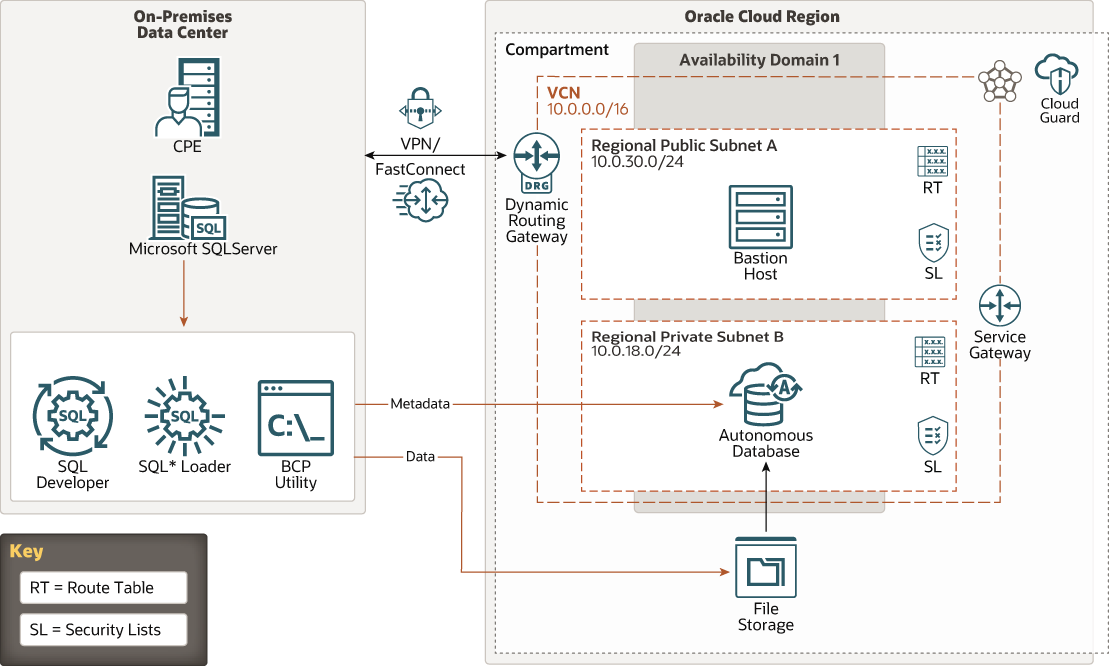
Description of the illustration mssql-adb.png
The on-premises data center shown in this architecture has the following components:
- Customer-premises equipment (CPE)
CPE is the on-premises endpoint for the VPN Connect or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect interconnection between the on-premises data center and the virtual cloud network (VCN) in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a third-party RDBMS used to build large-scale data warehousing applications.
- Oracle SQL Developer
Oracle SQL Developer is a development environment that simplifies the development and management of Oracle Database. It offers a complete end-to-end development of your PL/SQL applications, a worksheet for running queries and scripts, a DBA console for managing the database, a reports interface, a complete data modeling solution, integrated Oracle REST Data Services, and a migration platform for moving your 3rd party databases to Oracle, such as MS SQL Server to Oracle.
Oracle SQL Developer is certified to run on all supported Oracle Databases.
- SQL Loader
SQL*Loader loads data from external files into tables of an Oracle Database. SQL*Loader uses the field specifications in the control file to interpret the format of the datafile, parse the input data, and populate the bind arrays that correspond to a SQL INSERT statement using that data. The Oracle Database accepts the data and executes the INSERT statement to store the data in the database.
- Bulk Copy Program (bcp)
The bulk copy program utility (bcp) bulk copies data between an instance of Microsoft SQL Server and a data file in a user-specified format. The bcp utility can be used to import large numbers of new rows into SQL Server tables or to export data out of tables into data files.
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure side of the architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Cloud Guard
You can use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
Every Compute instance is deployed in a VCN that can be segmented into subnets.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
-
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service provides a durable, scalable, secure, enterprise-grade network file system. You can connect to a File Storage service file system from any bare metal, virtual machine, or container instance in a VCN. You can also access a file system from outside the VCN by using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect and IPSec VPN.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Bastion host
The bastion host is a compute instance that serves as a secure, controlled entry point to the topology from outside the cloud. The bastion host is provisioned typically in a demilitarized zone (DMZ). It enables you to protect sensitive resources by placing them in private networks that can't be accessed directly from outside the cloud. The topology has a single, known entry point that you can monitor and audit regularly. So, you can avoid exposing the more sensitive components of the topology without compromising access to them.
- Autonomous database
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure autonomous databases are fully managed, preconfigured database environments that you can use for transaction processing and data warehousing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating the database, as well as backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
- File storage
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service provides a durable, scalable, secure, enterprise-grade network file system. You can connect to a File Storage service file system from any bare metal, virtual machine, or container instance in a VCN. You can also access a file system from outside the VCN by using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect and IPSec VPN.
About Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage Service
If you’re looking for shared storage for services in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, then consider using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service is a managed file storage service that can be accessed concurrently by thousands of compute instances.
Using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service
The service is a persistent, shared file system in Oracle Cloud. It provides a durable, scalable, distributed, enterprise-grade network file system that supports Network File System version 3.0 (NFSv3) and Network Lock Manager (NLM) for file locking functionality.
Large compute clusters of thousands of instances can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service for high-performance shared storage. Storage provisioning is fully managed and automatic. Storage scales seamlessly from kilobytes to exabytes without upfront provisioning. You have redundant storage for resilient data protection.
By default, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service uses AES-256 encryption to encrypt all file systems. Encryption happens at the file level. Data and metadata are encrypted at rest rather than while in transit. You can’t turn off encryption.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service is fully managed and is offered across all availability domains in each Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. You can connect to an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service file system from any bare metal instance, virtual machine instance, or container instance in your virtual cloud network (VCN). You can also access a file system from outside the VCN by using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect and an Internet Protocol security (IPSec) virtual private network (VPN).
Use cases for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage service
The service is designed to meet the needs of applications and users that require an enterprise file system across a wide range of use cases. You’d use it when your application or workload includes big data and analytics, media processing, or content management, and you require Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX)-compliant file system access semantics and concurrently-accessible storage. For example, you’d use File Storage service in any of these use cases:
-
Enterprise applications that need shared files, such as Oracle E-Business Suite
-
Oracle Applications that need shared file storage to optimize capacity consumption and to ease deployments
-
Analytic applications and Apache Hadoop environments that use a repository to store analysis source data and value-added data
-
Microservices-based architectures, where you need persistent storage for container environments
-
Transactional file workloads, databases, scale-out file workloads, and high-performance computing (HPC) (for example, web application servers that need access to file data and need the ability to scale access across many instances)
-
Graphics, where you process video data and use a file system to store transcoded data or stream data
-
General purpose file systems, for storing unstructured and structured data
-
Container-based applications, where you store persistent application state for each container for Docker environments and Kubernetes environments
About Required Services and Roles
This solution requires the following services and roles:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Oracle SQL Developer
- Microsoft SQL Server Administrator
- JDBC Java Database drivers
- (Optional) Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage
These are the roles needed for each service.
| Service Name: Role | Required to... |
|---|---|
Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure: Admin |
Provision and setup resources. |
Oracle SQL Developer: db_datareader user on source
Microsoft SQL Server Database system,
mwrep user on target Oracle Database
system
|
Export the data from Microsoft SQL Server and save it to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File Storage, load and migrate objects and data to the Oracle autonomous database. |
Microsoft SQL Server:
db_owner user
|
Switch SQL Server Database to
ReadOnly mode.
|
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure File
Storage: Admin |
Create a file system and store the exported data from the Microsoft SQL Server database. |
See Learn how to get Oracle Cloud services for Oracle Solutions to get the cloud services you need.