Move Infor LN and Infor OS to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Infor LN is a discrete manufacturing ERP used by many organizations in the world. Typically, an Infor LN deployment will be accompanied with Infor OS which plays the role as a digital transformation tool that can apply automation, prediction, and business insights.
You can use Infor LN and Infor OS with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) to create a sustainable competitive advantage for deployments that form different perspectives and provide cost structure optimization, on demand capacity planing, deployment agility, security and faster time to market. This reference architecture is a baseline for deploying Infor LN and Infor OS on OCI.
Architecture
The following architectural diagram illustrates the required landing zone configuration and resources to deploy Infor LN and Infor OS on OCI . This architecture assumes that Infor LN and Infor OS will share the same database and will use Microsoft Active Directory (AD) with Domain Controller (DC), also hosted in OCI, as the identity provider. Oracle Identity Cloud Service will manage the identify federation between AD and Infor LN/Infor OS and single sign-on enablement.
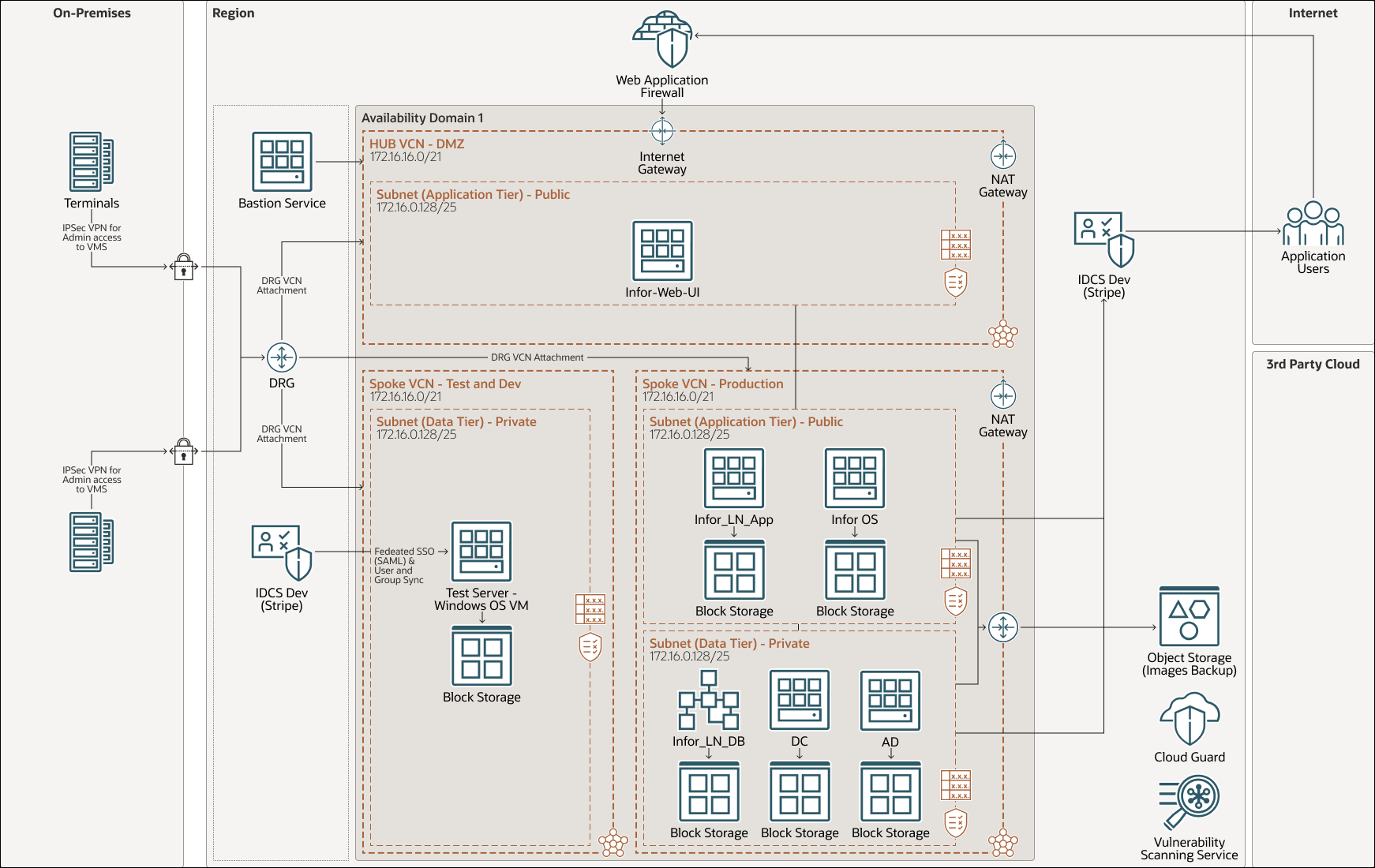
Description of the illustration infor-oci-arch.png
- Tenancy
When you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Oracle creates a tenancy for your company. A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure wherein you can create, organize, and administer your cloud resources.
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Compartment
Compartments are cross-region logical partitions within an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure tenancy. Use compartments to organize your resources in Oracle Cloud, control access to the resources, and set usage quotas. To control access to the resources in a given compartment, you define policies that specify who can access the resources and what actions they can perform.
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end. The load balancer provides access to different applications.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- NAT gateway
The NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Web application firewall
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall (Oracle WAF) is a cloud-based, global security service that protects applications from malicious and unwanted internet traffic. The WAF , which is fully integrated with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure management console can protect any internet-facing web application and provides consistent rule enforcement across an organization's web applications.
- Cloud Guard
You can use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
- Security zone
Security zones ensure Oracle's security best practices from the start by enforcing policies such as encrypting data and preventing public access to networks for an entire compartment. A security zone is associated with a compartment of the same name and includes security zone policies or a "recipe" that applies to the compartment and its sub-compartments. You can't add or move a standard compartment to a security zone compartment.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Oracle Database Cloud Service
Oracle Database Cloud Service lets you easily build, scale, and secure Oracle databases in the cloud. You create databases on DB Systems, as a virtual machines with block volumes, both of which provide high performance and cost-efficient pricing. The service also enables support for 'cloud-first' Oracle RAC implementation on virtual machine servers at the virtual cloud network layer.
- Internet Gateway
An internet gateway as an optional virtual router that connects the edge of the VCN with the internet. To use the gateway, the hosts on both ends of the connection must have public IP addresses for routing. Connections that originate in your VCN and are destined for a public IP address (either inside or outside the VCN) go through the internet gateway. Connections that originate outside the VCN and are destined for a public IP address inside the VCN go through the internet gateway.
- Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG)
A DRG acts as a virtual router, providing a path for traffic between your on-premises networks and VCNs, and can also be used to route traffic between VCNs. Using different types of attachments, custom network topologies can be constructed using components in different regions and tenancies. Each DRG attachment has an associated route table which is used to route packets entering the DRG to their next hop. In addition to static routes, routes from the attached networks are dynamically imported into DRG route tables using optional import route distributions.
- Bastion Service
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Bastion provides restricted and time-limited access to target resources that don't have public endpoints. Bastions let authorized users connect from specific IP addresses to target resources using Secure Shell (SSH) sessions. When connected, users can interact with the target resource by using any software or protocol supported by SSH. For example, you can use the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to connect to a Windows host, or use Oracle Net Services to connect to a database.
- Identity cloud service
Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) is an Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) solution available in Oracle Public Cloud (OPC). It is designed to extend enterprise controls by automating PaaS and SaaS account provisioning and deprovisioning, simplifying the user experience for accessing cloud applications by providing seamless integration with enterprise identity stores and authentication services, and facilitating compliance activities by clearly reporting on cloud application usage.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
Use regional subnets.
- Security
Use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure proactively. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
- Security zones
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
- Load balancer bandwidth
While creating the load balancer, you can either select a predefined shape that provides a fixed bandwidth, or specify a custom (flexible) shape where you set a bandwidth range and let the service scale the bandwidth automatically based on traffic patterns. With either approach, you can change the shape at any time after creating the load balancer.
Considerations
Consider the following factors when deploying this reference architecture.
- Environments
This Architecture considre on environment for Test and Development for Infor-LN and Infor-OS in one machine. In production environment, a singleton model is applied , without redundancy
- Security
VPN access is maintained to facilitate the access from any on premise terminals to the OCI resources. Internet access in protected by Web application firewall. Application level access is maintained by IDCS
- Availability
This Architecture assumes single nodes for both Infor-LN and Infor-OS. This deployment can be extended to implement high availability setup for both applications
- Cost
This architecture considered a cost effective way for deployment from resources point of view . One environment for Inofr-LN and Infor-OS for non-production , and single server for each application in production with a consolidated database .