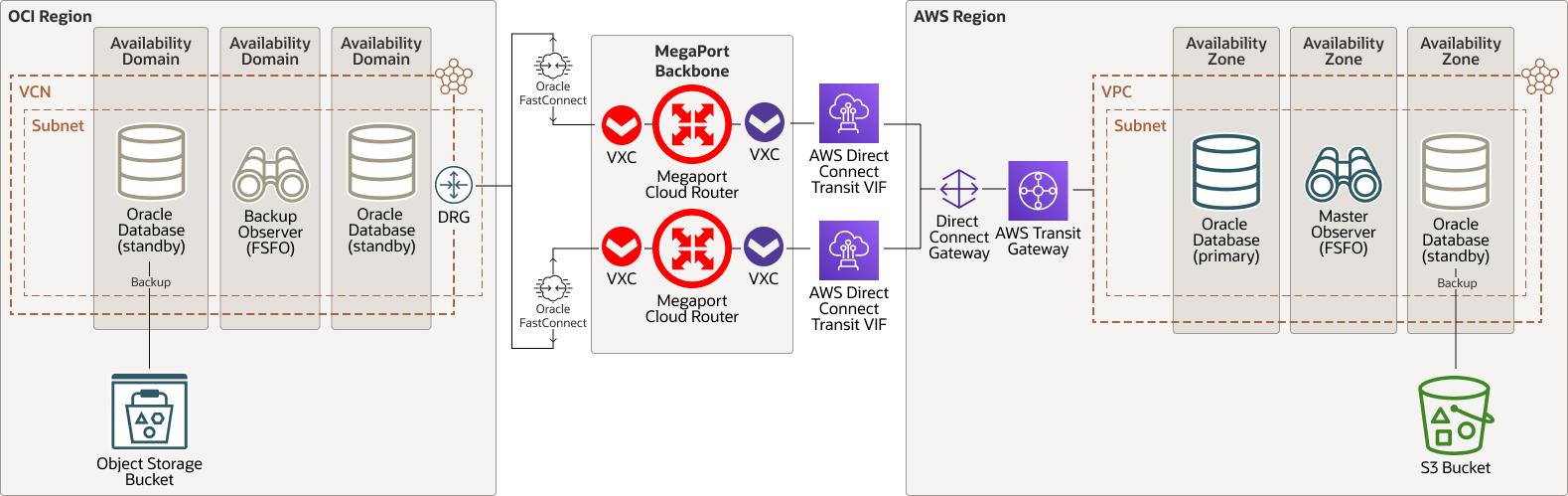
Enable multicloud high availability and data protection across OCI and AWS with Megaport
This architecture uses Oracle Data Guard and Megaport to provide reliable failover for key databases in a multicloud environment that spans Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Maintaining business continuity and ensuring IT resiliency is a top priority for IT leaders today. Enterprises from every sector and industry are increasingly implementing multicloud solutions to benefit from best-in-class services, competitive pricing, agility, flexibility, and higher availability while enhancing risk management and avoiding vendor lock-in.
Megaport is a global network-as-a-service provider that offers private interconnection to major cloud providers. You can use Megaport's multicloud services to set up private, cross-cloud connectivity between a primary Oracle Database in AWS and a standby Oracle Database in OCI.
Oracle Data Guard ensures high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery for mission-critical application data. With Data Guard, you can initiate failover of the primary database to the standby database either manually, by using the Data Guard Broker command-line interface (DGMGRL) or Oracle Enterprise Manager, or automatically, by configuring Fast-Start Failover (FSFO).
Architecture
This architecture shows a Data Guard configuration across OCI and AWS. Deploying a local standby database ensures high availability in the event of local failure and during planned maintenance. Standby databases across cloud providers ensure disaster recovery, higher resiliency, and simplify data migration.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
multicloud-failover-oci-aws-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
Oracle Cloud components
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- VM DB System
Oracle VM Database System is an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) database service that enables you to build, scale, and manage full-featured Oracle databases on virtual machines. A VM database system uses OCI Block Volumes storage instead of local storage and can run Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) to improve availability.
- Data Guard
Oracle Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to remain available without interruption. Oracle Data Guard maintains these standby databases as copies of the production database. Then, if the production database becomes unavailable because of a planned or an unplanned outage, Oracle Data Guard can switch any standby database to the production role, minimizing the downtime associated with the outage.
- Observers
Observers are Compute nodes that have the necessary Oracle Database software installed and configured to initiate FSFO of the Oracle Database in a Data Guard configuration. Having FSFO observers in the deployment removes the need for manual intervention when database failover is necessary and reduces the overall downtime.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
Amazon Web Services components
- Region
An Amazon Web Services region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability zones. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability zones
An availability zone is one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity in an AWS Region. Availability zones give customers the ability to operate production applications and databases that are more highly available, fault tolerant, and scalable than would be possible from a single data center.
- Virtual private cloud (VPC)
A virtual private cloud is a virtual network that you create in an Amazon Web Services region.
- Direct Connect
Direct Connect is a private network circuit between a VPC and a network outside AWS. It offers stable throughput and low latency, bypassing the public Internet. It is the AWS equivalent of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect.
- Transit virtual interface (VIF)
A transit virtual interface allows you to access one or more Amazon VPC Transit Gateways associated with Direct Connect gateways. You can use transit virtual interfaces with 1/2/5/10 Gbps AWS Direct Connect connections.
- Direct connect gateway (DGW)
A direct connect gateway builds upon virtual private gateway capabilities, adding the ability to connect to up to 10 VPCs across regions.
- Transit Gateway (TGW)
Transit Gateway connects virtual private clouds and on-premises networks through a central hub. This simplifies your network and puts an end to complex peering relationships. It acts as a cloud router, and each new connection is only made once.
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
Amazon Simple Storage Service is the AWS equivalent of Oracle Cloud Object Storage Service. You can use it to store data such as Oracle Database backups.
Megaport components
- Software-defined network (SDN)
Megaport’s on-demand global Software Defined Network enables fast, flexible, and secure connectivity to the world’s top cloud providers, including Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, across 750+ locations in North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe.
- Megaport Cloud Router (MCR)
Megaport Cloud Router is a virtual routing service designed for cloud-to-cloud connectivity that provides private connectivity at Layer 3. From any of Megaport's Routing Zones, you can connect to the critical cloud and managed services, without hardware. MCR allows you to route data between cloud providers without hairpinning traffic back to a data center or your on-premises environment.
- Megaport Virtual Cross Connect (VXC)
With an MCR configured, you can create Virtual Cross Connects to connect to services on the Megaport network without the need for any physical infrastructure. A VXC is a private point-to-point Ethernet connection between an A-end, such as your MCR, and a B-end, such as OCI FastConnect, AWS Direct Connect, or Azure ExpressRoute.
Recommendations
Use the following recommendations as a starting point to set up Oracle Data Guard for your multicloud environment. Your requirements might differ from the architecture described here.
- VCN
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
- Choice of interconnection location
This architecture requires one or more geographic locations for its components: the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) region and associated Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect edge node, the Amazon Web Services (AWS) region and associated AWS Direct Connect edge node, and the Megaport Cloud Router (MCR) location. To achieve the optimal end-to-end latency, Oracle recommends that you select a metro which has each of these architecture elements in close proximity. The MCR is available in 33 metros across 13 countries.
- High availability
This architecture shows a redundant and resilient design that uses dual FastConnect connections and dual AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute connections, which are routed via dual Megaport MCRs. For application that are not production or that are not business critical, a single node architecture may suffice. To achieve the highest availability, Oracle recommends that you deploy redundant network resources for each component of the architecture.
- Observer Location
An FSFO best practice is to run the observer process on a host that is located in a different data center than both the primary and standby database. To achieve this, this reference architecture deploys a master and a backup observer in different data centers than those hosting the databases.
- Active Data Guard
Enable Active Data Guard to benefit from advanced capabilities such as offloading production read-only workload to a synchronized standby, unique block corruption detection and automatic repair, rolling upgrade, fast incremental backups, and application continuity.
- Standby Backups
Create database backups from the standby database to offload the backup overhead from the primary host.
- Fault domains
In OCI regions with a single availability domain or AWS regions with a single availability zone, use different fault domains to host the primary database, the standby database, and the FSFO observer. A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain. Fault domains aren't shown in the architecture diagram.
Considerations
When implementing connectivity for a cross-cloud topology, consider the following factors:
- Performance
The Megaport Cloud Router (MCR) can scale from 1 Gb/sec to 10 Gb/sec, which means it scales to support the highest data rates supported by the cloud service providers. The rate limit is an aggregate capacity that determines the speed for all connections through the MCR. MCR bandwidth is shared between the Cloud Service Provider (CSP) connections that are added to it.
- Security
The cross-cloud interconnection shown in this architecture is based on a private connection, which is more secure than the public internet. You can choose to encrypt this traffic, but it is not encrypted in this architecture.
- Availability
The MCR is available in 33 metropolitan areas across 13 countries, including: Canada, the United States, France, the United Kingdom, Germany, Netherlands, Ireland, Sweden, Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Australia, and New Zealand.
- Cost
The total cost of the cross-cloud interconnection depends on:
- Megaport
The cost of the Megaport Cloud Router and the Virtual Cross Connects from MCR to the CSPs.
- Amazon Web Services
The AWS Direct Connect Port fee, the egress data transfer fee, and the cost of Amazon S3.
- Oracle
The cost of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect and Oracle Object Storage. There are no egress fees from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- Megaport
Deploy
MCR deployment is self-service through the Megaport Portal. To deploy this reference architecture, you need access to the Megaport Portal, Oracle Cloud Portal, and AWS or Azure Portal. Megaport sets up the interconnection points with OCI and AWS.
Explore More
Learn more about implementing connectivity for multicloud topologies with Oracle Cloud and other providers using the Megaport Cloud Router.
Review these additional resources:
- How to connect OCI FastConnect to AWS Direct Connect via the Megaport MCR
- Megaport documentation
- Megaport MCR locations
- How to build multicloud disaster recovery environments with Oracle and Megaport
- Common Megaport multicloud scenarios
- Learn about protecting your cloud topology against disasters
- Using Oracle Data Guard
- Role Transition Best Practices Data Guard and Active Data Guard