Use Oracle Analytics Cloud service with MySQL HeatWave
HeatWave supports the same business intelligence (BI) and data visualization tools as Oracle MySQL Database Service. With Oracle Analytics Cloud, data analysts can analyze data and build reports in real-time.
Architecture
This architecture uses a two-node Heatwave cluster attached to Oracle MySQL Database Service to run an eCommerce application (OLTP processing) and Oracle Analytics Cloud (OLAP processing).
A HeatWave cluster includes a MySQL System node and two or more HeatWave nodes. Both eCommerce application and OAC connect to the MySQL node in the HeatWave cluster. OLTP transactions from the eCommerce application run in the MySQL node while OLAP queries from Oracle Analytics Cloud (OAC) run in HeatWave nodes for accelerated performance.
On-premises users access the application and the analytics service by using a private access channel and a site-to-site VPN or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect connection, while internet users access them by using a public endpoint.
The following diagram illustrates this reference architecture.
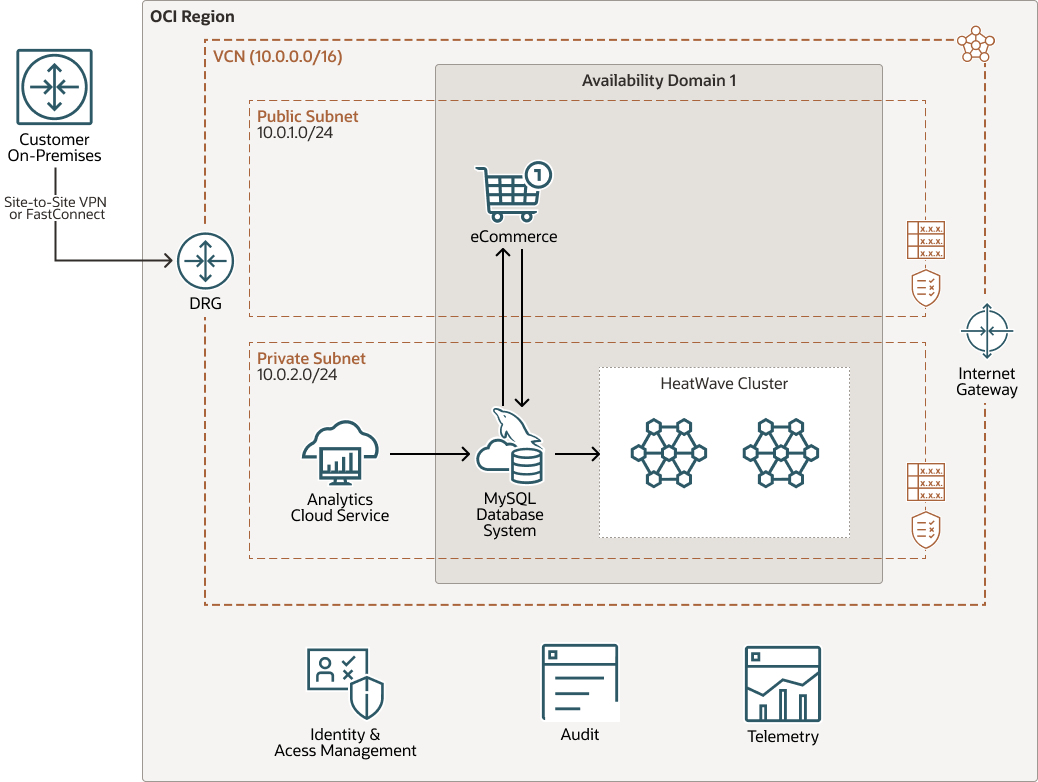
Description of the illustration architecture-oac-heatwave.png
architecture-oac-heatwave-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect provides an easy way to create a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the access control plane for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Cloud Applications. The IAM API and the user interface enable you to manage identity domains and the resources within the identity domain. Each OCI IAM identity domain represents a standalone identity and access management solution or a different user population.
- Oracle MySQL Database Service
Oracle MySQL Database Service is a fully managed Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) database service that lets developers quickly develop and deploy secure, cloud native applications. Optimized for and exclusively available in OCI, Oracle MySQL Database Service is 100% built, managed, and supported by the OCI and MySQL engineering teams.
Oracle MySQL Database Service has an integrated, high-performance analytics engine (HeatWave) to run sophisticated real-time analytics directly against an operational MySQL database.
- Compute
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service enables you to provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it.
- Analytics
Oracle Analytics Cloud is a scalable and secure public cloud service that empowers business analysts with modern, AI-powered, self-service analytics capabilities for data preparation, visualization, enterprise reporting, augmented analysis, and natural language processing and generation. With Oracle Analytics Cloud, you also get flexible service management capabilities, including fast setup, easy scaling and patching, and automated lifecycle management.
Recommendations
Your requirements might differ from the architecture described here. Use the following recommendations as a starting point.
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
- HeatWave cluster
In this reference architecture, we have used a 2-node deployment of the HeatWave cluster. Use the "Estimate Node Count" feature available during the provisioning of the HeatWave cluster if you are unsure of the number of nodes needed for your HeatWave cluster.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Resource limits
Consider the best practices, limits by service, and compartment quotas for your tenancy.
- MySQL Database Service
You need to specify a hostname for your MySQL Database instance during provisioning (use the advanced option) to enable the connectivity from Oracle Analytics Cloud to the database.
Create the MySQL service using a MySQL.HeatWave.VM.Standard.E3 or MySQL.HeatWave.BM.Standard.E3 shape.
- Connectivity
Consider using FastConnect if you want a dedicated, private connection between your premises and OCI, otherwise use VCN Connect.
Deploy
The Terraform code for this reference architecture is available as a sample stack in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resource Manager. You can also download the code from GitHub, and customize it to suit your specific requirements.
- Deploy using the sample stack in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resource
Manager:
- Click

If you aren't already signed in, enter the tenancy and user credentials.
- Select the region where you want to deploy the stack.
- Follow the on-screen prompts and instructions to create the stack.
- After creating the stack, click Terraform Actions, and select Plan.
- Wait for the job to be completed, and review the plan.
To make any changes, return to the Stack Details page, click Edit Stack, and make the required changes. Then, run the Plan action again.
- If no further changes are necessary, return to the Stack Details page, click Terraform Actions, and select Apply.
- Click
- Deploy using the Terraform code in GitHub:
- Go to GitHub.
- Clone or download the repository to your local computer.
- Follow the instructions in the
READMEdocument.