Deploy Oracle Retail Xstore Office on Oracle Autonomous Database
Oracle Retail Xstore Office and POS are the industry leading retail omnichannel and stores solution. This reference architecture allow retailers to adopt Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) to host Oracle Retail Xstore Office and provides the following benefits:
- Reliable infrastructure
- High performance
- High availability
- Auto scaling
- Disaster recovery
- Managed services
Architecture
This cloud solution deploys Oracle Retail Xstore Office in a load balanced application architecture with Oracle Autonomous Database at the backend. Oracle Autonomous Database provides high performance, autoscaling and tuning capabilities with additional benefits of maximum database uptime, security and productivity.
The Xcenter web and application servers are deployed in separate Fault Domains to provide fault tolerance. Oracle managed Autonomous Transaction Processing - Dedicated database (ATP-D) is deployed in the database private subnet. You have the option to use the Autonomous Transaction Processing - Shared (ATP-S) database, Oracle Database Cloud Services, or manage your own database on VM or bare metal in OCI. Shared OCI File Storage is mounted by all the web and application servers.
Retail store POS access the Xcenter in OCI via site-to-site VPN for central data lookup and sales data replication. Internet users access the application through Internet Gateway. Retail business IT supports the cloud environment via the Bastion Service. The application is placed in a private subnet behind the public load balancer and Oracle Web Application Firewall (WAF).
Store POS systems replicate sales data to Xcenter database through the application server. The OCI managed API Gateway allows Xstore Office to integrate with 3rd party retail applications. The OCI network address translation (NAT) gateway allows outbound internet access for resources in the private subnets.
The following diagram illustrates the high performance reference
architecture.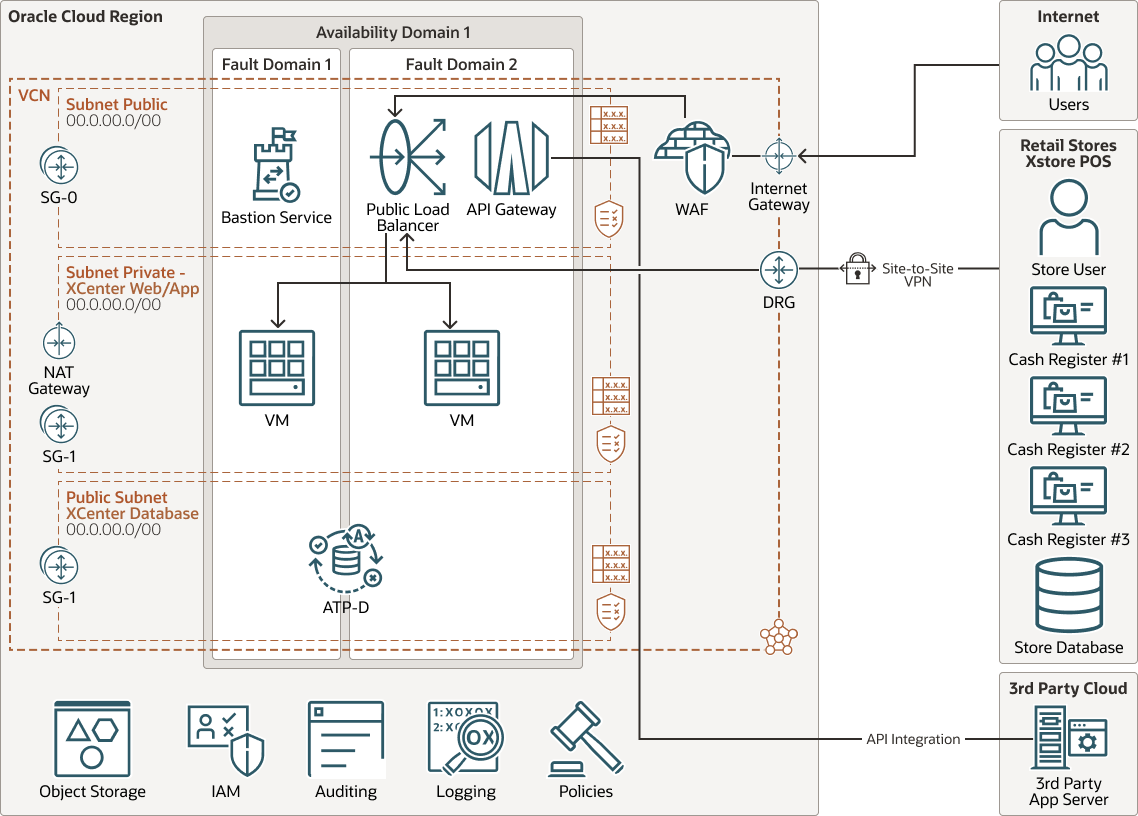
Description of the illustration oci_adb_xstore_office_arch.png
oci-adb-xstore-office-arch-oracle.zip
Retail business requires high availability (HA). You can deploy the Xcenter web and application in separate Availability Domains of the same region and load balance across the servers in two or more Availability Domains. The standby load balancer is deployed in a separate Availability Domain. Autonomous Data Guard is set up to sync the data from active ATP to the local standby ATP database.
The Xstore Office Disaster Recovery (DR) can be set up in a remote OCI region. The DR will have the same architecture as production with reduced compute footprint to save the cost. In the event of disaster or DR testing, the environment can be scaled up quickly in cloud. Autonomous Data Guard is used to sync the active ATP database to the remote standby ATP database.
The following diagram illustrates the HA and DR architecture.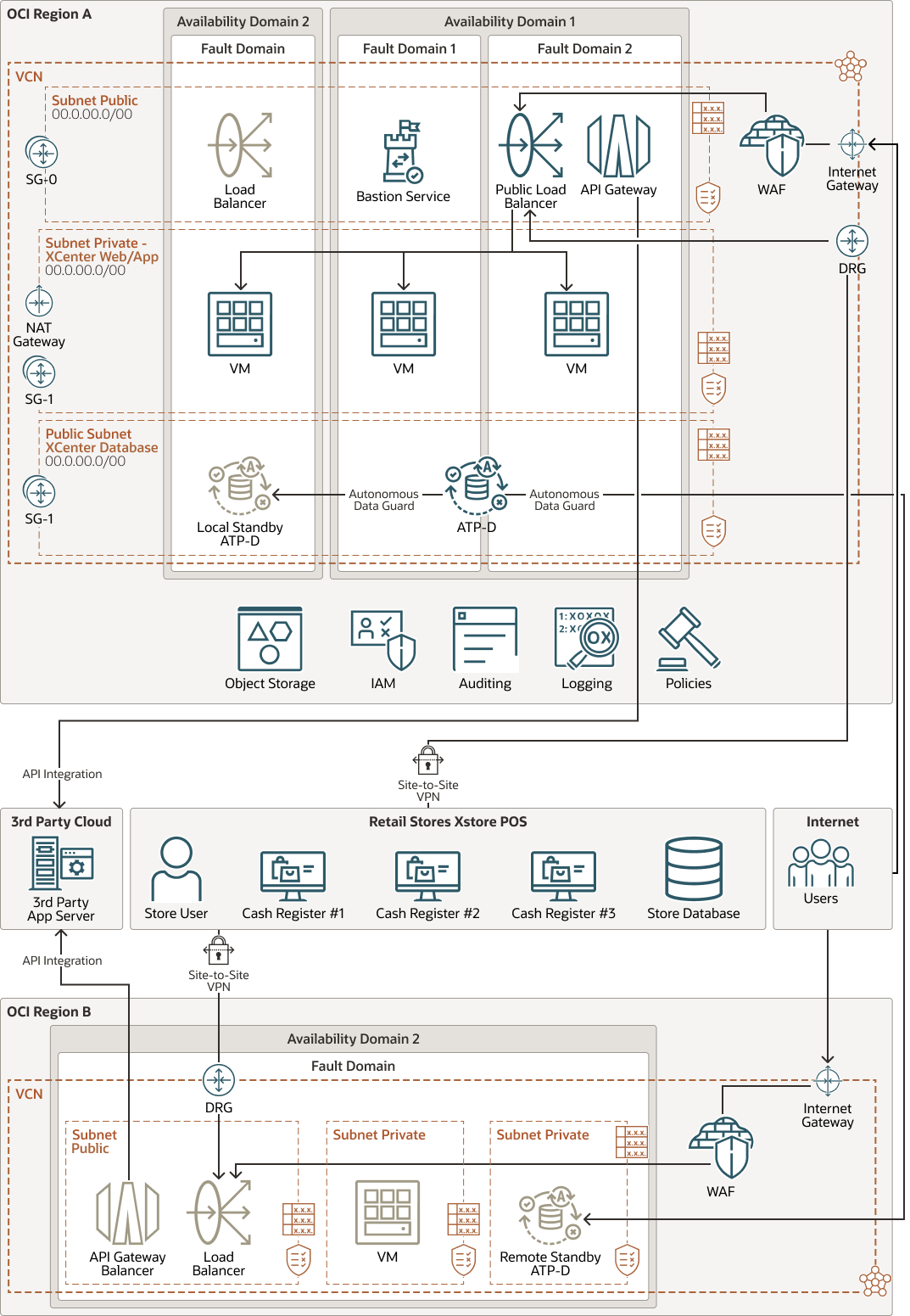
Description of the illustration oci_adb_xstore_office_ha_arch.png
oci-adb-xstore-office-ha-arch-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domains
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain is unlikely to affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domains
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you complete control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Load balancer
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancing service provides automated traffic distribution from a single entry point to multiple servers in the back end.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Network address translation (NAT) gateway
A NAT gateway enables private resources in a VCN to access hosts on the internet, without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and never traverses the internet.
- Security zone
Security zones ensure Oracle's security best practices from the start by enforcing policies such as encrypting data and preventing public access to networks for an entire compartment. A security zone is associated with a compartment of the same name and includes security zone policies or a "recipe" that applies to the compartment and its sub-compartments. You can't add or move a standard compartment to a security zone compartment.
- Object storage
Object storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can seamlessly scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Autonomous Database
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Autonomous Database is a fully managed, preconfigured database environments that you can use for transaction processing and data warehousing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating the database, as well as backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
- Autonomous Transaction Processing
Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing is a self-driving, self-securing, self-repairing database service that is optimized for transaction processing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating the database, as well as backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
Recommendations
- VCN
When you create a VCN, determine the number of CIDR blocks required and the size of each block based on the number of resources that you plan to attach to subnets in the VCN. Use CIDR blocks that are within the standard private IP address space.
Select CIDR blocks that don't overlap with any other network (in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, your on-premises data center, or another cloud provider) to which you intend to set up private connections.
After you create a VCN, you can change, add, and remove its CIDR blocks.
When you design the subnets, consider your traffic flow and security requirements. Attach all the resources within a specific tier or role to the same subnet, which can serve as a security boundary.
- Security
Use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure proactively. Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
- Security zone
Security zones ensure Oracle's security best practices from the start by enforcing policies such as encrypting data and preventing public access to networks for an entire compartment. A security zone is associated with a compartment of the same name and includes security zone policies or a "recipe" that applies to the compartment and its sub-compartments. You can't add or move a standard compartment to a security zone compartment.
- Network security group (NSG)
Network security group (NSG) acts as a virtual firewall for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, all traffic is denied, and you can control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of VNICs in a single VCN.
- Load balancer bandwidth
While creating the load balancer, you can either select a predefined shape that provides a fixed bandwidth, or specify a custom (flexible) shape where you set a bandwidth range and let the service scale the bandwidth automatically based on traffic patterns. With either approach, you can change the shape at any time after creating the load balancer.
- Managed Service
Managed Service provides specific functionality without requiring you to perform maintenance tasks related to optimizing performance, availability, scaling, security, or upgrading. With a managed service, you can focus on delivering features for your customers instead of worrying about the complexity of operations. OCI managed services such as Autonomous Database are recommended to lower the total ownership cost.
- Database
As Xstore is a mission critical enterprise application, consistently high performance is critical. The ability to control upgrade, patches, and auditability of cloud operations are critical to the business. ADB-D is recommended for the isolation, consistent performance, security, and auditability. Autonomous Database has a 99.95% availability SLA. It’s HA by default. The SLA increases to 99.995% availability with a standby. This includes both planned and unplanned outages.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture.
- Implementation
There are some mandatory components that need to be deployed along with Xcenter, for example, Apache server for data files and deployments exchange, RTLog generator utility. These are separate workloads and logging and monitoring.
A separate component can be deployed in OCI to provide the curbside pickup capability. Xstore provides web service integration that can be used for this, but is limited by the store VPN.
- Compliance
Depending upon implementation, Xcenter may store customer related data. Storing this data may have legal requirements. OCI Data Safe is recommended to understand data sensitivity, evaluate data risks, mask sensitive data, implement and monitor security controls, assess user security, and monitor user activity – all in a unified console.
- Migration and upgrade
If migration to OCI is combined with version upgrade, on-premises Xcenter and OCI Xcenter need to co-exist during the rollout period. This process is called ‘hybridization’ in regular Xstore upgrades and typically takes 2-5 months depending on the number of stores.