Identify VCN Topology and Specifications
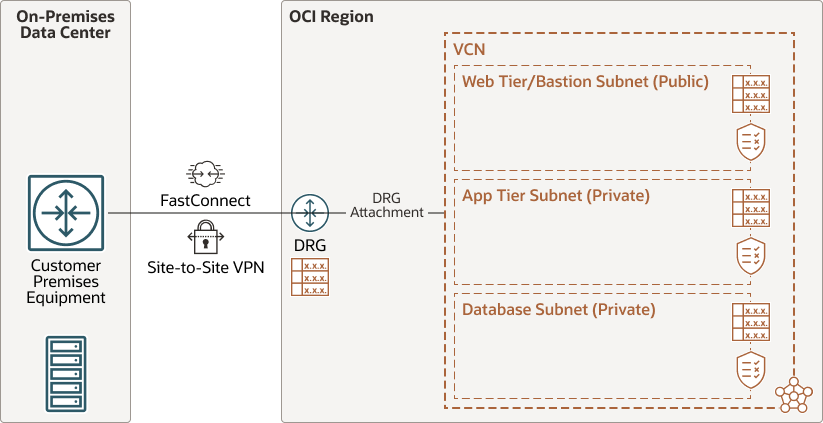
Single Network Architecture
The following diagram shows an example of a single-network architecture:
Note:
Oracle recommends using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall (OCI WAF) or OCI Network Firewall for security reasons if you have internet-facing applications (public IPs).Hub-and-Spoke Network Architecture
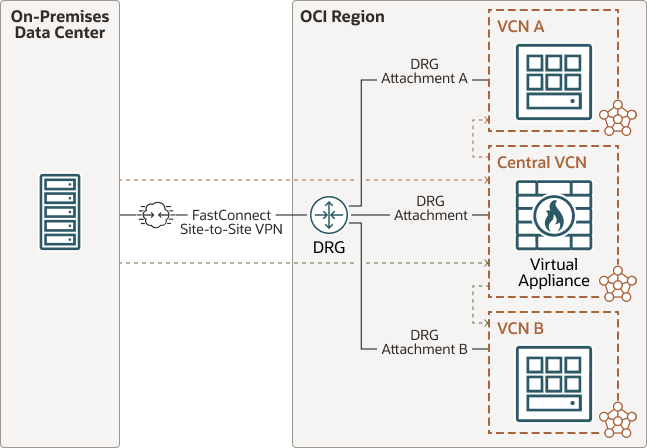
The following diagram shows an example of using a hub-and-spoke network architecture:
Hub-and-spoke network architecture is the Oracle-recommended architecture for most deployments. Use hub-and-spoke network architecture if your business requires one or more of the following (not an exclusive list):
- Use (or plan to use) multiple VCNs to separate workloads.
- Centralize internet-facing traffic in a hub VCN, where network firewall, internet-facing load balancers, WAF and internet gateway resources are managed.
- Maintain network separation for production, test, and development environments.
Virtual Cloud Network Specifications
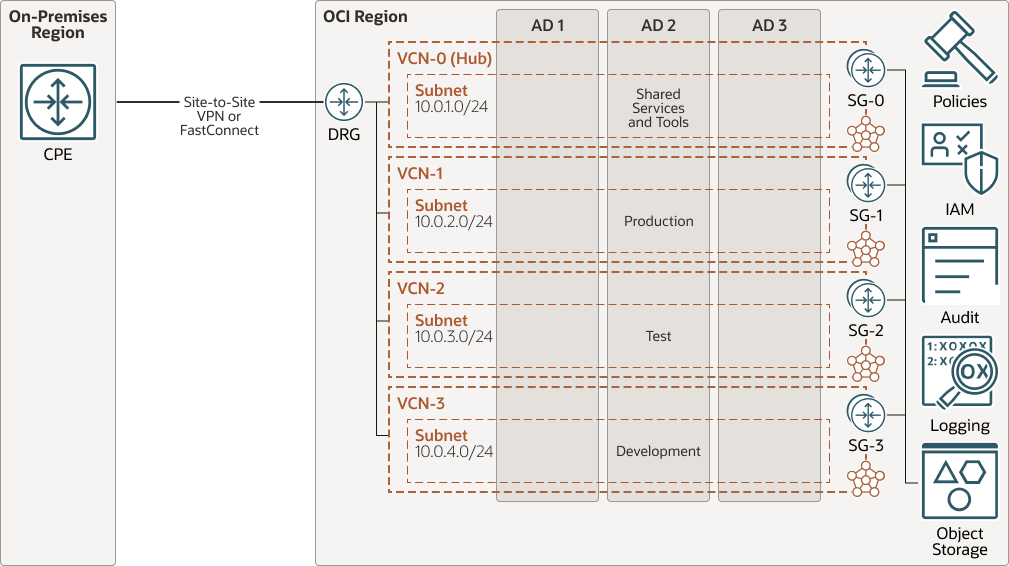
The following image shows how you can maximize the use of availability domains for high availability designs.
Oracle recommends:
- Using regional subnets that span all availability domains for high availability.
- Creating separate VCNs for different workloads.
Note:
For regions with a single availability domain, use fault domains to enhance resiliency.
Size Your VCN or Subnets
Plan your VCNs for future expansion, and select an IP address range that avoids overlap with your on-premises or other networks.
The following table provides guidance on how to size your VCNs based on your need.
| VCN Size | Netmask | Subnet Size | Number of Subnets in VCN | Usable IPs per Subnet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | /24 | /27 | 8 | 29 |
| Medium | /20 | /24 | 16 | 253 |
| Large | /18 | /22 | 16 | 1021 |
| Extra Large | /16 | /20 | 8 | 4093 |
Different subnets within a VCN can use different CIDR block sizes to optimize for specific workload needs.
Note:
OCI reserve three IP addresses in each subnet.Security Lists and Network Security Groups
Security lists let you define a set of security rules that apply to all resources in a subnet.
Use NSGs for more granular, application-level security. NSGs enable you to define rules for specific VNICs, load balancers, database systems, and so on.
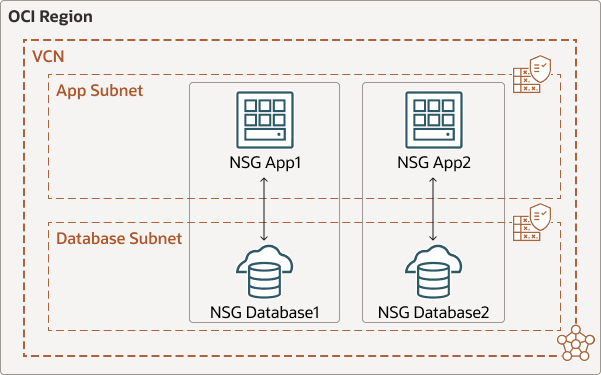
The following graphic shows an example of how you can separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements using NSGs and allow only resources using NSG_DB1 connect to the resource using NSG_App1.
You can use both security lists and NSGs to control access to your resources in both private and public subnets. If you use both NSGs and security lists, then the outcome will be the combined summary rules from the NSG and the security list.
Oracle recommends using NSGs to:
- Separate VCN subnet architecture from application security requirements.
- Define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs.
Tip:
If you use security lists, Oracle recommends that you use an individual security list per subnet instead of a combined one for all subnets.Route Tables
Tip:
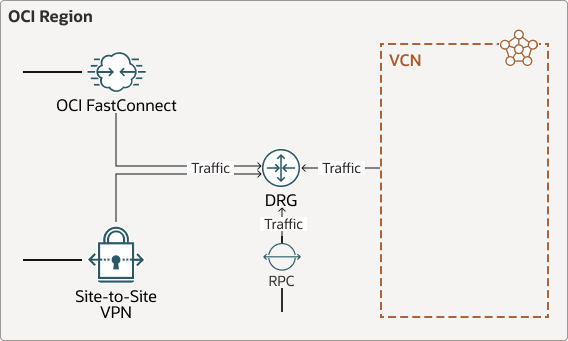
Oracle recommends importing routes using import route distributions.The following diagram shows route tables associated at the DRG level:
DRG-level route tables manage:
- VCN attachments
- FastConnect/Virtual Circuit attachments
- IPSec/VPN attachments
- Remote peering connection (RPC) attachments
Note:
A static route in a route table can't point to FastConnect or IPsec attachments; use import route distribution instead.Within a VCN/subnet, use static routes to direct traffic to gateways. Assign individual route tables to each subnet to control outbound traffic. Resources within the same VCN can communicate without explicit routes (implicit routing), but appropriate security rules must be in place.
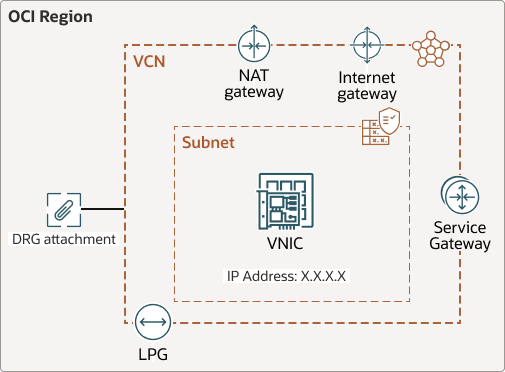
The following diagram shows gateways where route tables can be associated as well as other resources:
Route tables are normally associated per subnet to control traffic from each specific subnet. You can configure advanced routing from resources within subnet or towards resources within a subnet.
Route tables can be associated with:
- Subnet
- VCN (ingress), attached to the DRG attachment. Typically used when forcing traffic to a firewall.
- Internet gateway
- NAT gateway
- Service gateway
- LPG
- VNIC
- IP address