Learn About Key Design Decisions for OCI Workload Networking
Architecture
This architecture shows a complete architecture after you set up your networking and connectivity. Use this architecture to make key design decisions specific to your organizational needs.
The following diagram illustrates the finished reference architecture for a resilient OCI network.
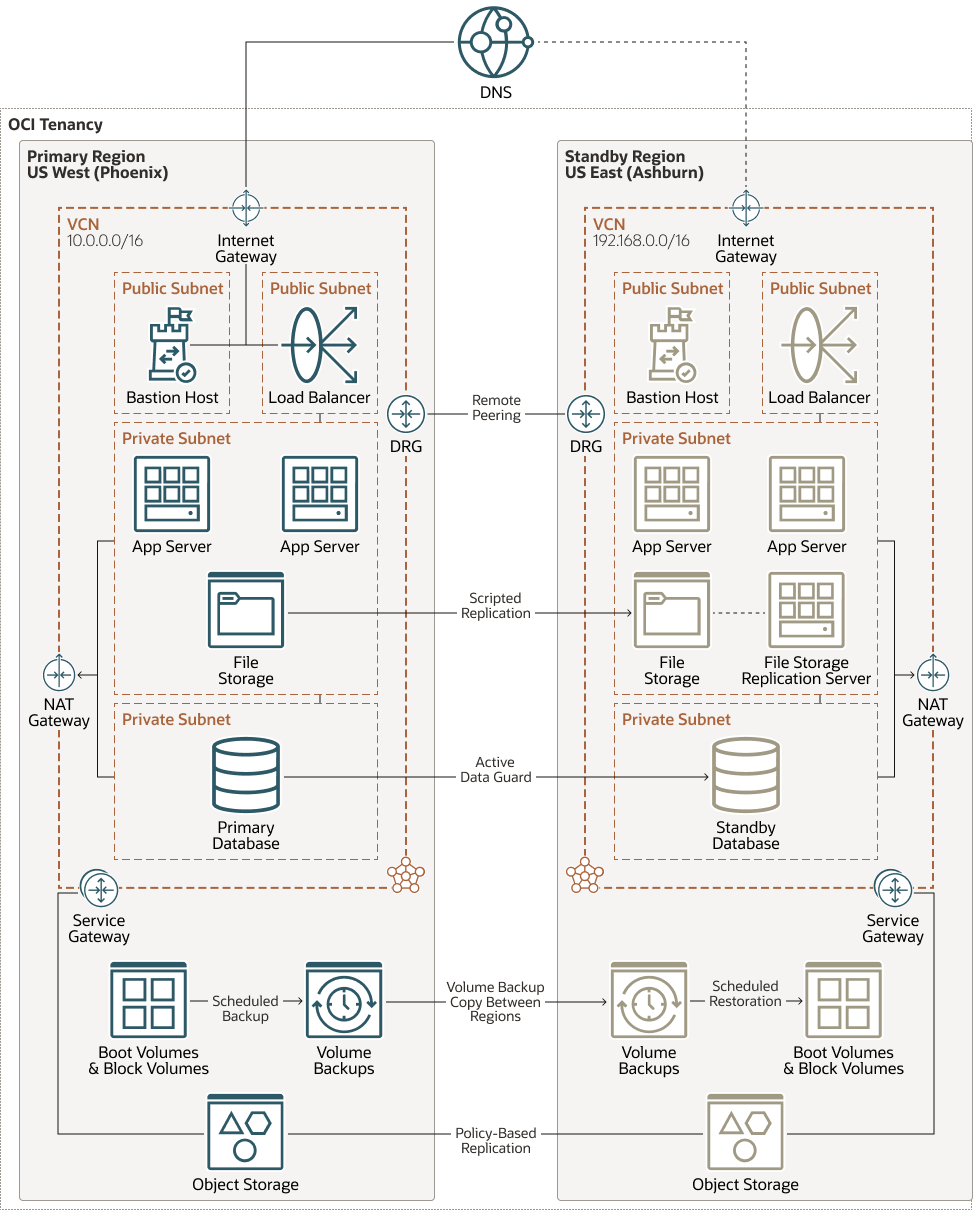
Description of the illustration multi-region-deployment-full-arch.png
multi-region-deployment-full-arch-oracle.zip
This architecture supports the following components:
- OCI virtual cloud
network and subnet
A virtual cloud network (VCN) is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an OCI region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Network security group
(NSG)
NSGs act as virtual firewalls for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of OCI you control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of virtual network interface cards (VNICs) in a single VCN.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that is allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Dynamic routing gateway
(DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another OCI region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Local
peering
Local peering allows two VCNs within the same OCI region to communicate directly using private IP addresses. This communication does not traverse the internet or your on-premises network. Local peering is enabled by a Local Peering Gateway (LPG), which serves as the connection point between VCNs. Configure an LPG in each VCN and establish a peering relationship to allow instances, load balancers, and other resources in one VCN to securely access resources in another VCN within the same region.
- OCI FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect creates a dedicated, private connection between your data center and OCI. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- OCI Site-to-Site VPN
OCI Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs on OCI. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.