Design an OCI Generative AI powered SQL agent for databases and applications
This reference architecture outlines a SQL Agent designed to facilitate Natural Language (NL) interactions with an Oracle Database.
Built on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI (OCI Generative AI) models, the agent allows users to perform Text-to-SQL queries, data analysis, and reporting through a robust, scalable system, designed to handle schemas with hundreds of tables.
The SQL agent can be also integrated in a more general architecture, with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), enabling users to combine analysis on structured and unstructured data.
Architecture
The core of the solution consists of a set of Python components, based on the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure SDK for Python and the open-source library LangChain:
- Router: Identifies the request type (SQL generation and data retrieval or data analysis) and directs it to the appropriate processing pipeline. The component is based on LLM with a specialized prompt.
- Schema Manager: Manages all metadata related to the database schema. It plays a crucial role in providing, for each NL request, the list of tables (“restricted schema”) to be used for SQL generation and all associated metadata. It leverages a 23ai database and Semantic Search within the database, to find the tables relevant for the user NL request.
- SQL Generator: Translates the NL request into an executable SQL statement on the connected "Data" database. It uses an ensemble of LLM models to enhance accuracy and increase the success rate of correctly generated SQL statements. The LLM models are provided by the OCI Generative AI service.
- SQL Cache: Stores NL instructions (and their SQL equivalents) for the most frequent requests.
- SQL Executor: Enables syntax validation of the generated SQL statement and executes the instruction.
- AI Data Analyzer: Analyzes stored conversational data to generate responses for analysis requests or report generation.
The following diagram illustrates the logical architecture.

Description of the illustration oci-genai-sql-agent-logical.png
oci-genai-sql-agent-logical-oracle.zip
A distinctive feature of this solution is its flexible management of database schemas, powered by Vector Search and Generative AI.
During the set up, a comprehensive summary is generated for each database table using a Large Language Model (LLM). This summary includes the table schema, relevant business queries, and sample data. The summaries are stored in the 23ai database along with embedding vectors created by the OCI Generative AI Embedding model.
When a user submits a query, semantic search identifies candidate tables for query composition, and a reranking mechanism refines this list to ensure optimal results.
The SQL Agent manages the conversation history with the user. The exchanged messages, linked via a conversation_id, are stored using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Cache with Redis (OCI Cache with Redis).
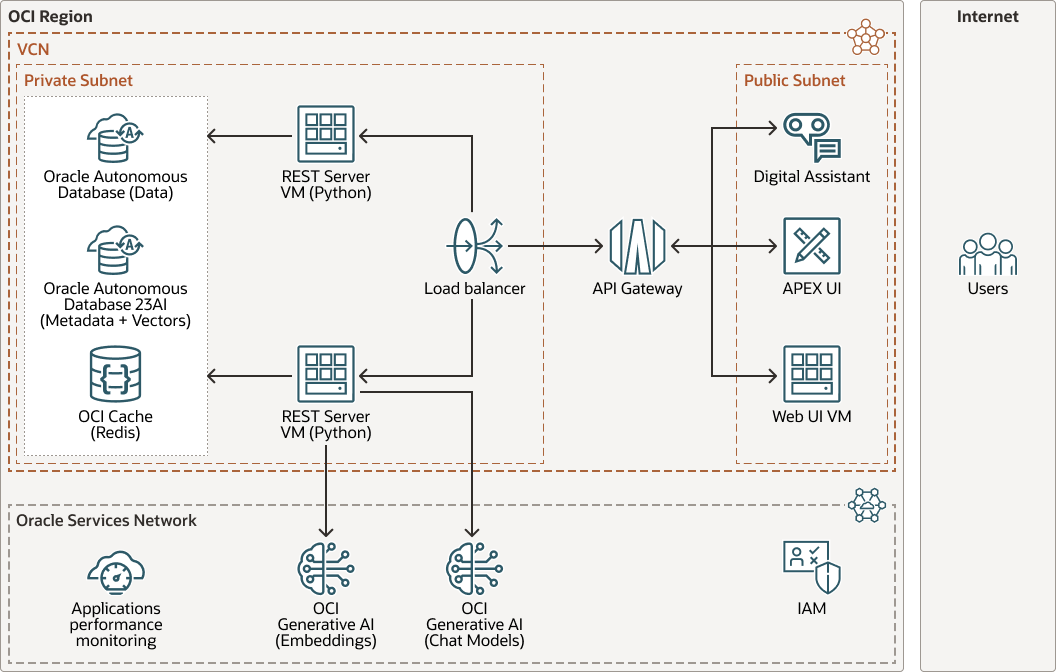
The SQL Agent is exposed through a REST API, is Open-API compliant, and implemented with the FastAPI library. This REST API can connect to any user interface (the diagram suggests Oracle Digital Assistant, a UI built with Oracle APEX, or a generic Web UI).
Integration with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Application Performance Monitoring Cloud Service for gathering usage statistics and response times for various OCI components is based on the approach documented in the Enhancing Observability in RAG Solutions with Oracle Cloud (blog) link in the Explore More section.
The following diagram describes the physical architecture, with all the OCI services involved.
oci-genai-sql-agent-arch-oracle.zip
The architecture has the following components:
- OCI Generative AI
Embedding Model
Convert text to vector embeddings to use in applications for semantic searches, text classification, or text clustering. The OCI Generative AI embedding models transforms each phrase, sentence, or paragraph that you input, into an array with 384 (light models) or 1024 numbers, depending on the embedding model that you select.
You can use these embeddings for finding similarity in phrases that are similar in context or category. Embeddings are typically stored in a vector database. Embeddings are mostly used for semantic searches where the search function focuses on the meaning of the text that it's searching through rather than finding results based on keywords.
- OCI Generative AI
Chat Model
Ask questions and get conversational responses through an AI chat interface. Prompt the OCI Generative AI chat models to generate text. You can ask questions in natural language and optionally submit text such as documents, emails, and product reviews to the chat models and each model reasons over the text and provides intelligent answers. For some models, you can submit images and ask questions about the image. The chat models keep the context of your previous prompts and you can continue the chat with follow-up questions.
- Application Performance Monitoring
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Application Performance Monitoring provides deep visibility into the performance of applications and provides the ability to diagnose issues quickly in order to deliver a consistent level of service. This includes the monitoring of the multiple components and application logic spread across clients, third-party services, and back-end computing tiers, on premises or in the cloud.
- APEX Service
Oracle APEX is a low-code development platform that enables you to build scalable, feature-rich, secure, enterprise apps that can be deployed anywhere that Oracle Database is installed. You don't need to be an expert in a vast array of technologies to deliver sophisticated solutions. Oracle APEX includes built-in features such as user interface themes, navigational controls, form handlers, and flexible reports that accelerate the application development process.
- API Gateway
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure API Gateway enables you to publish APIs with private endpoints that are accessible from within your network, and which you can expose to the public internet if required. The endpoints support API validation, request and response transformation, CORS, authentication and authorization, and request limiting.
- Autonomous Data Warehouse
Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse is a self-driving, self-securing, self-repairing database service that is optimized for data warehousing workloads. You do not need to configure or manage any hardware, or install any software. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating the database, as well as backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
- Cache with Redis
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Cache with Redis is a comprehensive, managed-in-memory caching solution built on the foundation of open source Redis. This fully managed service accelerates data reads and writes, significantly enhancing application response times and database performance to provide an improved customer experience.
- Compute
With Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute, you can provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it.
Recommendations
- Database access
This solution should be implemented to enable only “read-only” access to the data in the database. Even if it is possible, with instructions in the prompt, to forbid DDL and DML instructions, for additional security the connection to the “Data" database should be done using a READ ONLY database user.
- Security
Use Oracle Cloud Guard to monitor and maintain the security of your resources in OCI proactively. Oracle Cloud Guard uses detector recipes that you can define to examine your resources for security weaknesses and to monitor operators and users for risky activities. When any misconfiguration or insecure activity is detected, Oracle Cloud Guard recommends corrective actions and assists with taking those actions, based on responder recipes that you can define.
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, OCI validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Cloud Guard
Clone and customize the default recipes provided by Oracle to create custom detector and responder recipes. These recipes enable you to specify what type of security violations generate a warning and what actions are allowed to be performed on them. For example, you might want to detect Object Storage buckets that have visibility set to public.
Apply Cloud Guard at the tenancy level to cover the broadest scope and to reduce the administrative burden of maintaining multiple configurations.
You can also use the Managed List feature to apply certain configurations to detectors.
- Security Zones
For resources that require maximum security, Oracle recommends that you use security zones. A security zone is a compartment associated with an Oracle-defined recipe of security policies that are based on best practices. For example, the resources in a security zone must not be accessible from the public internet and they must be encrypted using customer-managed keys. When you create and update resources in a security zone, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure validates the operations against the policies in the security-zone recipe, and denies operations that violate any of the policies.
- Network security groups (NSGs)
You can use NSGs to define a set of ingress and egress rules that apply to specific VNICs. We recommend using NSGs rather than security lists, because NSGs enable you to separate the VCN's subnet architecture from the security requirements of your application.
Considerations
When planning to run this solution on OCI consider the following security details.
- Security
In a production setting, all the components for the SQL Agents should be deployed in a private network.
Access to the REST API should be provided only through the OCI API Gateway. The Load Balancer is designed to enable the deployment of all Python components on multiple VMs, to achieve higher reliability and scalability.
Access to OCI Generative AI services requires the proper setup of the OCI Generative AI policies.