Network Security
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Networking service supports provisioning virtual cloud networks (VCNs) and subnets, which you can use to isolate your resources in the cloud at the network level.
The VCNs can be configured for internet connectivity or connected to your on-premises data centers by using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect circuits or IPSec VPN connections. You can use bidirectional stateful and stateless firewall rules, communication gateways, and route tables to control the flow of traffic to and from the networks that you create. Firewalls and access control lists (ACLs) specified for a VCN are propagated throughout the network topology and control plane, ensuring a multitiered and defense-in-depth implementation. For more information about networking in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, see Overview of Networking.
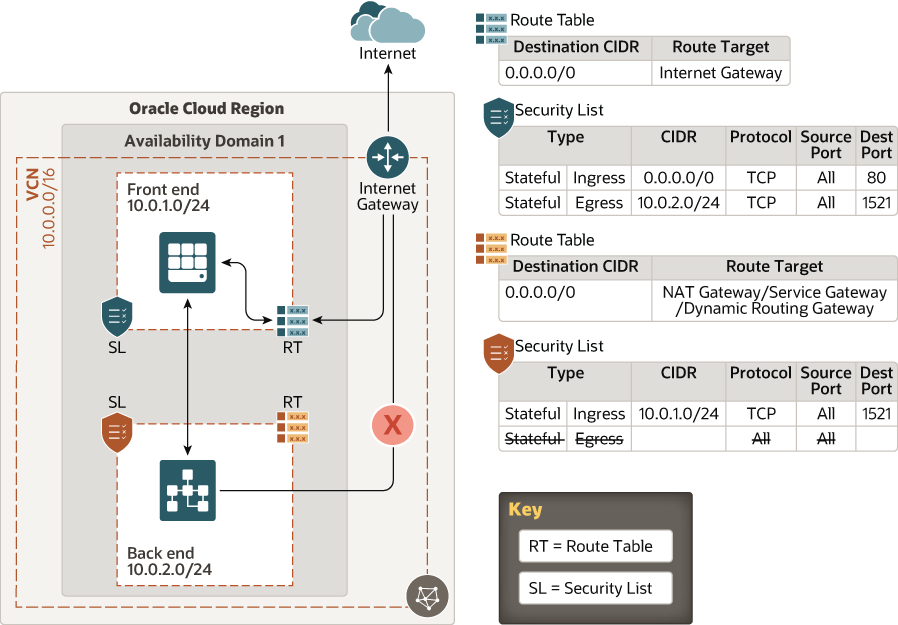
The following architecture illustrates how you can use subnets, route tables, and security lists to secure your network boundaries.
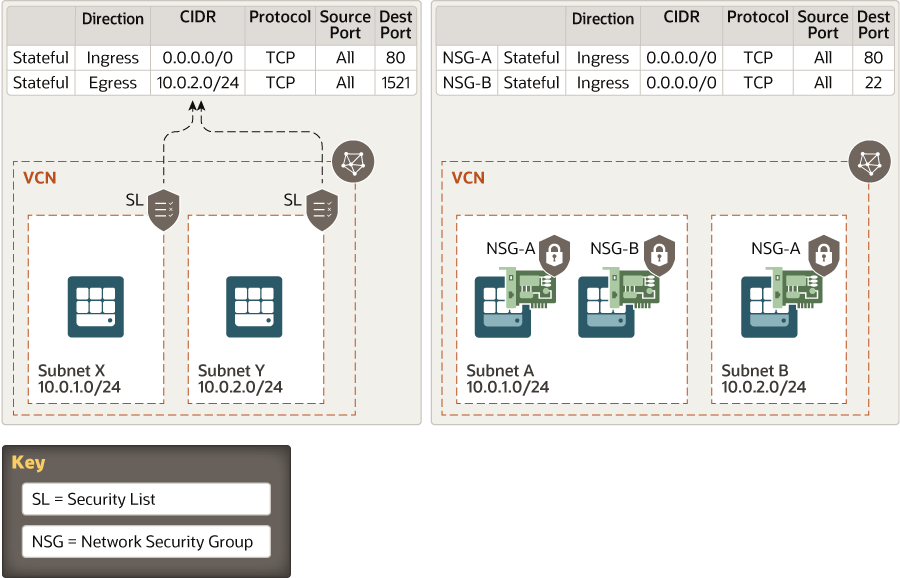
This architecture shows a virtual firewall implementation using security lists. The rules that you specify in a security list apply to all the VNICs in the subnet to which you attach the security list. If you need firewalls at a more granular level, use network security groups (NSGs). The rules in an NSG apply to only the VNICs that you specify. Oracle recommends that you use NSGs, because they enable you to separate the subnet architecture from your workload's security requirements.
The following example compares security lists and NSGs:
Use the following checklist to protect your network boundaries:
| Done? | Security Controls and Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Partition your VCN into private and public subnets. | |
| Define firewall rules to control access to your instances. | |
| Create and configure virtual routers for network connectivity. | |
| Use IAM policies to restrict access to network resources to only groups allowed to manage network resources. | |
| To control network access, use a tiered subnet strategy for the VCN. Use a demilitarized zone (DMZ) subnet for load balancers; a public subnet for externally accessible hosts, such as web servers; and a private subnet for internal hosts, such as databases. | |
| Use a NAT gateway for connectivity to the internet from private compute instances. | |
| Use a service gateway for connectivity to the Oracle Services Network. | |
| Use granular security rules for access within a VCN, communication with the internet, access with other VCNs through peering gateways, and access to on-premises networks through IPSec VPN and FastConnect. | |
| Set up an intrusion detection and protection system (IDS/IPS). | |
| Create and configure load balancers for high availability and transport layer security (TLS). | |
| Use a web application firewall (WAF). | |
| Create DNS zones and mappings. An important security consideration in load balancers is using customer TLS certificates to configure TLS connections to the customer’s VCN. | |
| Follow security best practices for external cloud connections. |
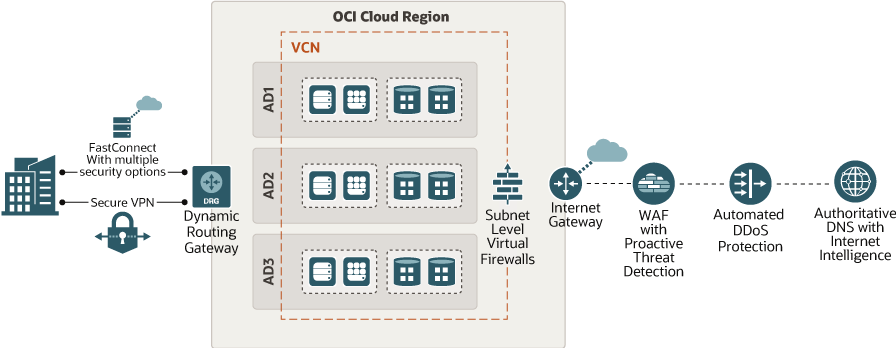
The following graphic shows network connectivity options with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.