Deploy a Retail Platform With Multicloud Integration on Oracle Cloud
Although outages of on-premises transaction systems cost retailers up to $100,000 per hour in losses, many retailers are reluctant to move their systems to the cloud.
For some retailers, the risks of business disruption from data center relocation, hardware upgrades, or refactored software can often obscure the benefits of running their retail systems by using managed cloud services.
But RedIron Technologies is working to change this perception by helping retailers move and manage their on-premises transaction systems to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Founded in 2000, RedIron Technologies helps its customers design, implement, integrate, and maintain their retail system platforms on OCI. RedIron's cloud retail platform RI Commerce, now available in Oracle Cloud Marketplace, displaces the cost and complexity of in-store technology with a cloud-centralized, real-time architecture that delivers comprehensive solutions for retailers, from merchandising through store execution, and point-of-sale.
By moving retail systems to OCI, RedIron helps its customers:
- Gain control: While RedIron is tasked with maintaining the retail systems in OCI, the company distributes the control of certain resources to retail system owners. In the cloud, RedIron can move or deploy a retail system into an isolated environment and, using policies, grant access as needed to retail system owners to make changes themselves.
- Increase database performance: After moving the retail system's Oracle Database to Oracle Base Database Service, RedIron increases database performance with fewer resources than were required on-premises. RedIron ensures that the Database Cloud Service is tuned to meet the customer's needs, without needing to add additional OCPU or RAM resources.
- Remove responsibility for managing licenses: RedIron uses OCI to manage licenses for included images for Oracle WebLogic Server and Database Cloud Service, removing this responsibility from their customers.
- Reduce risk of outages and loss of sales: RedIron offers standard practices to create production, QA/UAT, and development environments, which facilitate validation processes. Creating these environments on-premises would be complex, costly, and require additional resources. RedIron's ability to test and develop without affecting the production environment reduces the risks of outages and loss of sales.
- Tighten cost controls: On OCI, RedIron is able to standardize configurations for hardware, storage, and compute resources, helping its customers reduce maintenance costs, system complexity, and operations overhead.
Architecture
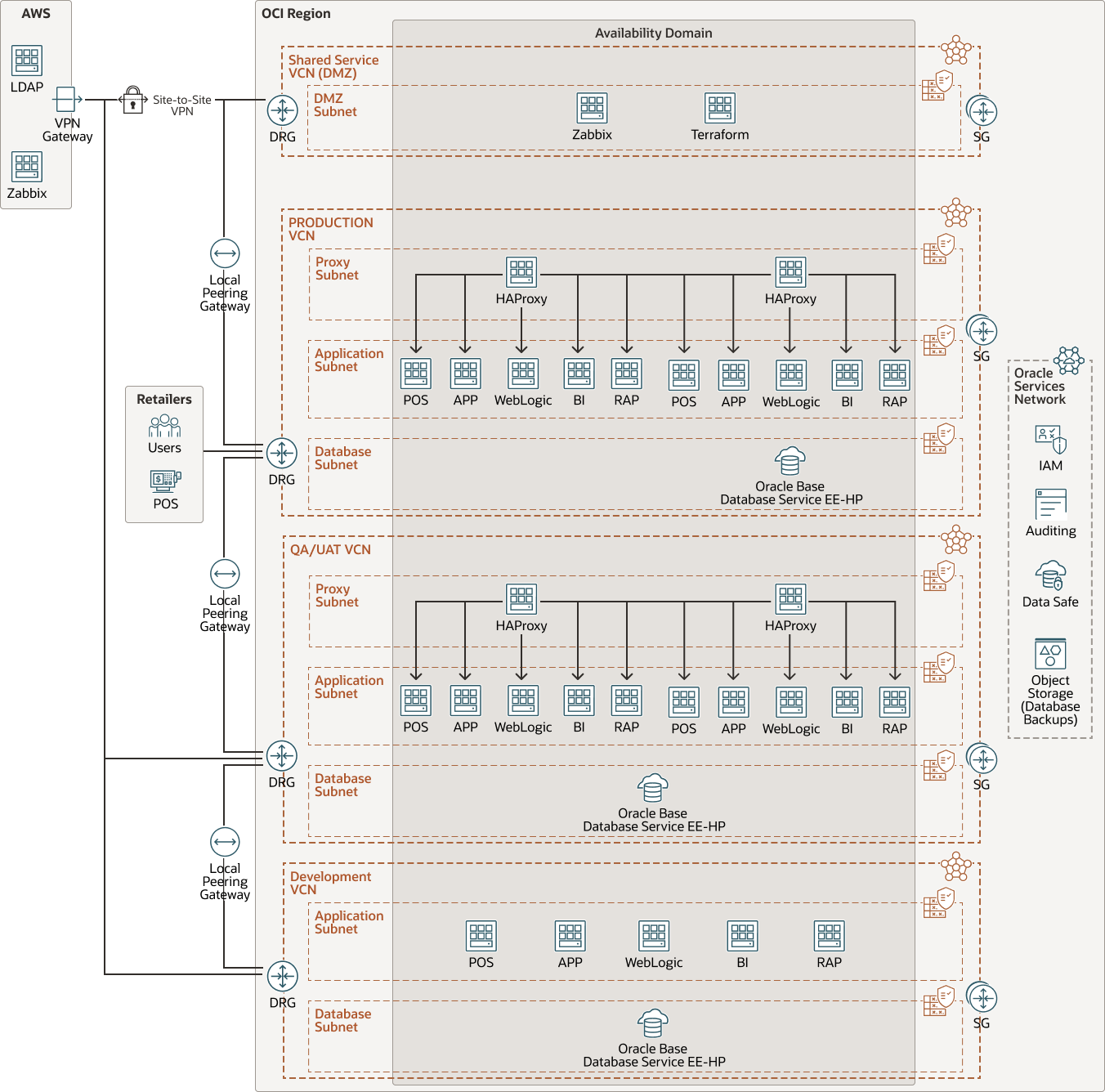
The architecture below is an example of a retail system deployment that RedIron Technologies moved from on-premises to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
The RedIron retail system consists of JBOSS and Oracle WebLogic Server instances for the front end and Oracle Base Database Service for the back end.
Four virtual cloud networks (VCNs) are provided: three VCNs provide isolated environments for production, QA/UAT, and development and a fourth VCN is used as a DMZ for shared services. The VCNs are connected by local peering gateways (LPGs). Using RedIron's virtual private network (VPN) gateway deployed in AWS, site-to-site VPNs are used to connect to each VCN. An AWS tenancy is used to provide LDAP services and monitoring services by using Zabbix. Point-of-sale (POS) systems located at retail locations connect privately by using the VPN or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect. Each VCN is segmented into application and database subnets.
HAProxy provides load balancing, high availability, and reverse proxy capabilities for the architecture. Customers can optionally choose to have high availability across multiple availability domains, which requires additional resources and incurs additional costs.
All Oracle Base Database Service instances are deployed and licensed with Enterprise Edition-High Performance (EE-HP) to take advantage of Oracle Cloud Management Packs. To save on costs, multiple instances are reduced to single instances and are deployed in the QA/UAT and development environments.
Zabbix is used for monitoring performance of the retail system application. With Zabbix, RedIron monitors and identifies any bottlenecks with the retail system. A terraform server is deployed to the Shared Services VCN to take advantage of Ansible for automation. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage is used for database backups. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit is used to track audit information from within the tenancy. Oracle Data Safe is deployed to manage security and compliance for Oracle databases.
The following diagram illustrates the architecture:
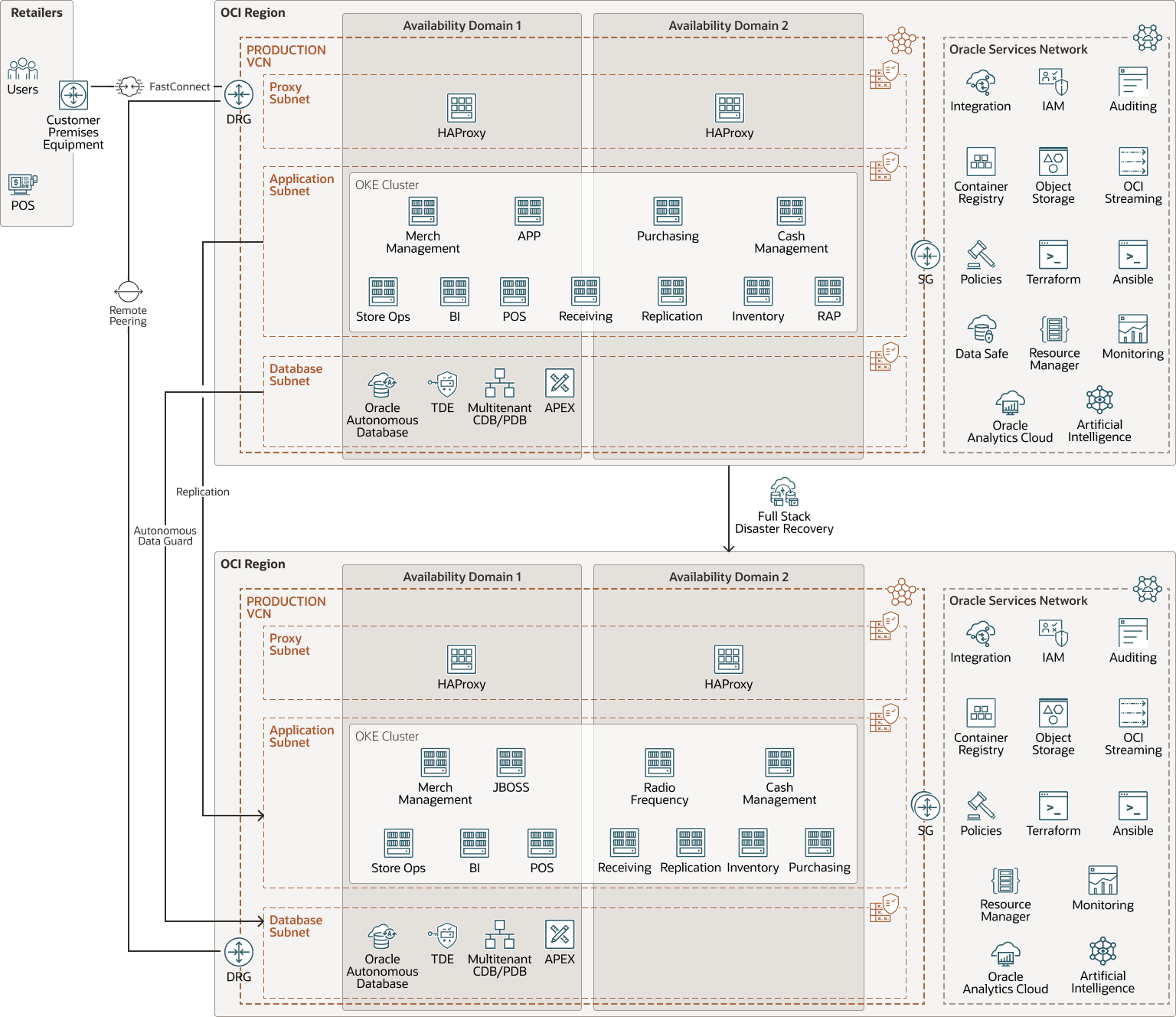
The future state architecture roadmap for RedIron includes:
- Terraform and Ansible: As RedIron's customer base grows, RedIron wants to take advantage of Terraform and Ansible to automate the scripting and deployment of their retail system to shorten deployment times.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine (OKE): RedIron is investigating how to refactor its retail application by using containers and OKE to take advantage of more automation, deploy features quicker, and use rollback features without disrupting sales.
- Oracle Autonomous Database (ADB): RedIron is looking to take advantage of ADB features such as self-tuning and autoscaling. With Autonomous Database, RedIron will also be able to take advantage of Oracle Autonomous Data Guard to provide disaster recovery for databases.
- Oracle Analytics Cloud and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure AI Services: RedIron is keen to enhance its retail application by providing built-in analytics and artificial intelligence.
- Multitenancy: For smaller retail customers, RedIron sees the benefit of creating a multitenant environment, enabling the company to host multiple retailers in a single OCI tenancy. These customers can share instances of Oracle WebLogic Server and databases to reduce licensing costs.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect: RedIron is looking to provide an option for retailers who require a dedicated connection.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Full Stack Disaster Recovery: RedIron is exploring options to automate the disaster recovery process for their implementations.
The following diagram illustrates the future state architecture:
The architecture has the following components:
- Tenancy
A tenancy is a secure and isolated partition that Oracle sets up within Oracle Cloud when you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. You can create, organize, and administer your resources in Oracle Cloud within your tenancy. A tenancy is synonymous with a company or organization. Usually, a company will have a single tenancy and reflect its organizational structure within that tenancy. A single tenancy is usually associated with a single subscription, and a single subscription usually only has one tenancy.
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain shouldn't affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnets
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN provides IPSec VPN connectivity between your on-premises network and VCNs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. The IPSec protocol suite encrypts IP traffic before the packets are transferred from the source to the destination and decrypts the traffic when it arrives.
- Internet gateway
The internet gateway allows traffic between the public subnets in a VCN and the public internet.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and does not traverse the internet.
- Local peering gateway (LPG)
An LPG enables you to peer one VCN with another VCN in the same region. Peering means the VCNs communicate using private IP addresses, without the traffic traversing the internet or routing through your on-premises network.
- Network security group (NSG)
Network security group (NSG) acts as a virtual firewall for your cloud resources. With the zero-trust security model of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, all traffic is denied, and you can control the network traffic inside a VCN. An NSG consists of a set of ingress and egress security rules that apply to only a specified set of VNICs in a single VCN.
- Compute
With Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute, you can provision and manage compute hosts in the cloud. You can launch compute instances with shapes that meet your resource requirements for CPU, memory, network bandwidth, and storage. After creating a compute instance, you can access it securely, restart it, attach and detach volumes, and terminate it when you no longer need it.
- Object storage
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Data Safe
Oracle Data Safe is a fully-integrated, regional cloud service focused that provides a complete set of features for protecting sensitive and regulated data in Oracle databases. Data Safe also supports on-premises databases, Oracle Exadata Database Service on Cloud@Customer, and multicloud deployments. All Oracle Database customers can reduce the risk of a data breach and simplify compliance by using Oracle Data Safe to assess configuration and user risk, monitor and audit user activity, and to discover, classify, and mask sensitive data.
- Integration
Oracle Integration is a fully managed, preconfigured environment that allows you to integrate cloud and on-premises applications, automate business processes, and develop visual applications. It uses an SFTP-compliant file server to store and retrieve files and allows you to exchange documents with business-to-business trading partners by using a portfolio of hundreds of adapters and recipes to connect with Oracle and third-party applications.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the access control plane for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and Oracle Cloud Applications. The IAM API and the user interface enable you to manage identity domains and the resources within the identity domain. Each OCI IAM identity domain represents a standalone identity and access management solution or a different user population.
- Audit
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit service automatically records calls to all supported Oracle Cloud Infrastructure public application programming interface (API) endpoints as log events. All OCI services support logging by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Audit.
- Oracle Base Database Service
Oracle Base Database Service is an is an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) database service that enables you to build, scale, and manage full-featured Oracle databases on virtual machines. A VM database system uses OCI Block Volumes storage instead of local storage and can run Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) to improve availability.
Explore More
Learn more about the features of this architecture and about related architectures.