About Secure TLS Certificate Deployment
When implementing secure TLS communication on web servers or application servers, it is essential to have access to the following components:
- The TLS certificate
- The root and intermediate (certificate chain)
- The corresponding private key
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers native certificate management services that enable the creation and lifecycle management of certificates intended for use within OCI-managed services. In this model, private keys are securely stored in OCI Vault and are not accessible to end users or external systems. While this enhances security, it limits flexibility in scenarios where full certificate and key control is required—such as deploying to external application servers or hybrid environments. It poses a challenge when attempting to use the certificate authority (CA) from OCI Certificates for systems that require direct access to both the certificate and the private key.
This becomes particularly problematic when integrating with services such as:
- Oracle Analytics Cloud
- Oracle Integration
- Web servers hosted on OCI Compute
- On-premises or edge applications
These platforms typically require full control over the TLS certificate, including the ability to access the private key, in order to support secure communication and termination of SSL/TLS sessions.
This solution playbook introduces a cross-product solution that addresses this limitation by enabling the use of OCI CA for hybrid environments:
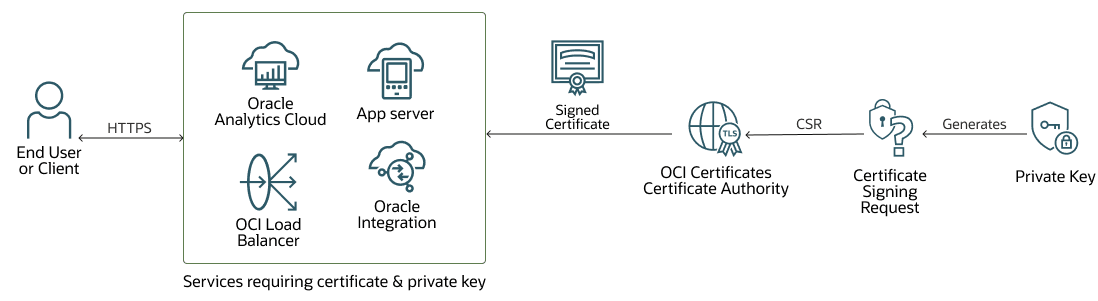
- You generate a private key and certificate signing request (CSR) locally, outside OCI.
- The CSR is then signed by the OCI Certificates CA, maintaining trust within the OCI ecosystem.
- The resulting signed certificate is combined with the locally generated private key and deployed to any service that requires it—whether in OCI, on-premises, or in another cloud.
The following diagram illustrates this flow.
This method is best for:
- Non-production setups where cost-effective self-signed certificates are sufficient.
- Environments that require both certificate and private key control (such as custom servers or on-premises integrations).
- Scenarios where OCI-managed certificates (which hide private keys) are not compatible with external systems.
Before You Begin
Before you begin, you need:
- An OCI Vault for securely storing private keys set up in OCI.
- An OCI Certificates certificate authority (CA) set up and fully functional in OCI.
- Access to the OpenSSL library on your local machine, so you can generate your private key.
About Required Services and Roles
This solution requires the following service and role:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
This is the role needed for the service.
| Service Name: Role | Required to... |
|---|---|
| Oracle Cloud Infrastructure: Administrator | Manage obects in compartments, and read or manage certificates, buckets, vaults, and keys (see below). |
You can use a simple policy for certificate authority administrators, or, set up both an administrator and a dynamic group policy to segregate roles and responsibilities and restrict them by compartment. For example:
### Simple Policy for Tenant Administrators
```
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to manage certificate-authority-family in tenancy
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to manage leaf-certificate-family in tenancy
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to read vaults in tenancy
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to read keys in tenancy
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to use key-delegate in tenancy
```Or:
### Policy for a Dynamic Group
```
Allow dynamic-group DynamicGroup to use keys in compartment DEF
Allow dynamic-group DynamicGroup to manage objects in compartment XYZ
```
### Policy for Compartment Administrators
```
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to manage certificate-authority-family in compartment ABC
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to read keys in compartment DEF
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to use key-delegate in compartment DEF
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to read buckets in compartment XYZ
Allow group CertificateAuthorityAdmins to read vaults in compartment DEF
```See Oracle Products, Solutions, and Services to get what you need.