Build an Agentic, High-Fidelity, Conversational AI Framework with Select AI and Oracle APEX
This AI-driven chatbot solution leverages an agentic framework that incorporates data visualization and reporting capabilities while minimizing hallucinations and ensuring high accuracy.
Natural language (NL) queries are translated into executable SQL statements for Oracle Database access, with a human-in-the-loop mechanism to validate SQL before execution. The solution is hosted on OCI, featuring an Oracle APEX Application Development user interface, LangChain-based AI agents running on OCI Compute, and integration with OCI Generative AI services and Oracle Autonomous AI Database. The architecture enables seamless natural language interaction with enterprise data, combining a responsive natural language processing front end with dynamic visualizations and a secure, high-performance back end for real-time data exploration.
This AI chatbot solution offers:
- Natural language query on the database with role-based access to data
- Dynamic data visualization and reporting
- Human-in-the-loop SQL validation
- Near zero hallucinations
Architecture
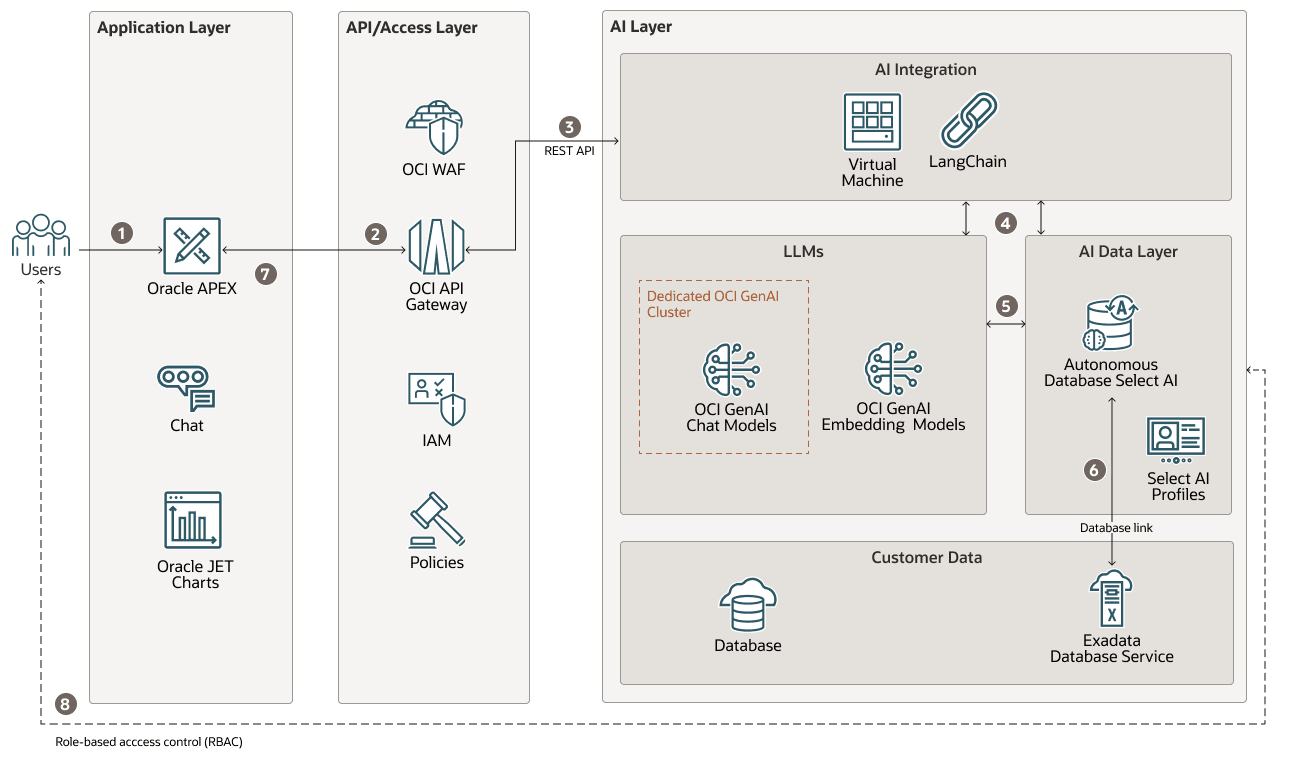
The agentic framework includes distinct, functional layers that handle user interaction, API access, AI processing, and data storage on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
The following diagram shows the functional layers and process flow:
select-ai-apex-architecture-oracle.zip
Workflow:
- The user signs in and submits a natural language query through the Oracle APEX Application Development front-end application.
- The request is routed through Oracle Cloud Infrastructure API Gateway to the orchestration engine.
- The request is routed from OCI API Gateway to OCI Compute that contains AI agents, developed with a framework like LangChain, running on an OCI Container Instances.
- The agent executes a workflow designed to ensure query accuracy and to mitigate inaccuracies (hallucinations).
- The agent invokes the Oracle Autonomous AI Database Select AI feature, which leverages OCI Generative AI to translate the natural language query and its metadata into an executable SQL statement.
- The source data resides on a separate, non-Autonomous Database such as Oracle Exadata Database Service. Oracle Autonomous AI Database functions as an intelligent sidecar, accessing this data by using secure database links. This architectural pattern enables the use of the Select AI capability on data stored in earlier database versions without requiring data migration.
- The results of the final SQL query are returned to the user by way of the application front end. Each response is formatted in natural language to emulate a chat-like experience, and is accompanied by data visualizations tailored to the specific query outcome.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) is enforced during this process. The agent selects a specific, Select AI profile corresponding to the user's role. Each profile is restricted to a specific subset of the source database's schema, ensuring that the generated SQL only accesses authorized data.
This architecture utilizes the following core OCI components:
- Oracle Autonomous AI Database
Provides the core of the AI data layer including:
- Data Integration: Accesses the non-Autonomous Database source by using database links (sidecar).
- Natural Language Interaction: Uses the built-in Select AI feature for natural language to SQL conversion.
- Vector Search: Employs the database's AI Vector Search capability for the retrieval augmented generation (RAG) feedback loop.
- Oracle APEX Application
Development
Provides a low-code platform for building the data-driven user interface. Tightly integrated with Autonomous Database, it serves as the front end for query input and visualization of results.
- OCI Compute w/ Python Runtime
Hosts the orchestration engine for the AI workflows. It receives requests from the APEX Service application by using the REST API, queries the database, and calls the OCI Generative AI. This component provides a persistent, low-latency runtime environment.
- OCI Generative AI
Provides access to large language models (LLMs) for three key functions:
- Natural Language to SQL: Serves as the inferencing engine for the Select AI feature.
- Feedback Vectorization: Generates embeddings from text for storage in the AI Vector Store.
- Back end LLM Services: Can be called directly by the Python back end for other generative tasks such as result summarization.
- OCI API Gateway
Provides a managed, secure endpoint for back end services, routing requests from the APEX Service front end to the orchestration engine on the OCI Container Instances.
- Oracle Exadata Database
Service
The high-performance database containing the source data to be queried.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web
Application Firewall (WAF)
OCI WAF acts as a critical security shield, inspecting all requests from the APEX Service front end to protect the API Gateway and back end services from malicious web-based attacks.
- OCI Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM policies are used for inspection, access control, and secure execution.
Agentic Workflow for Minimizing Hallucinations
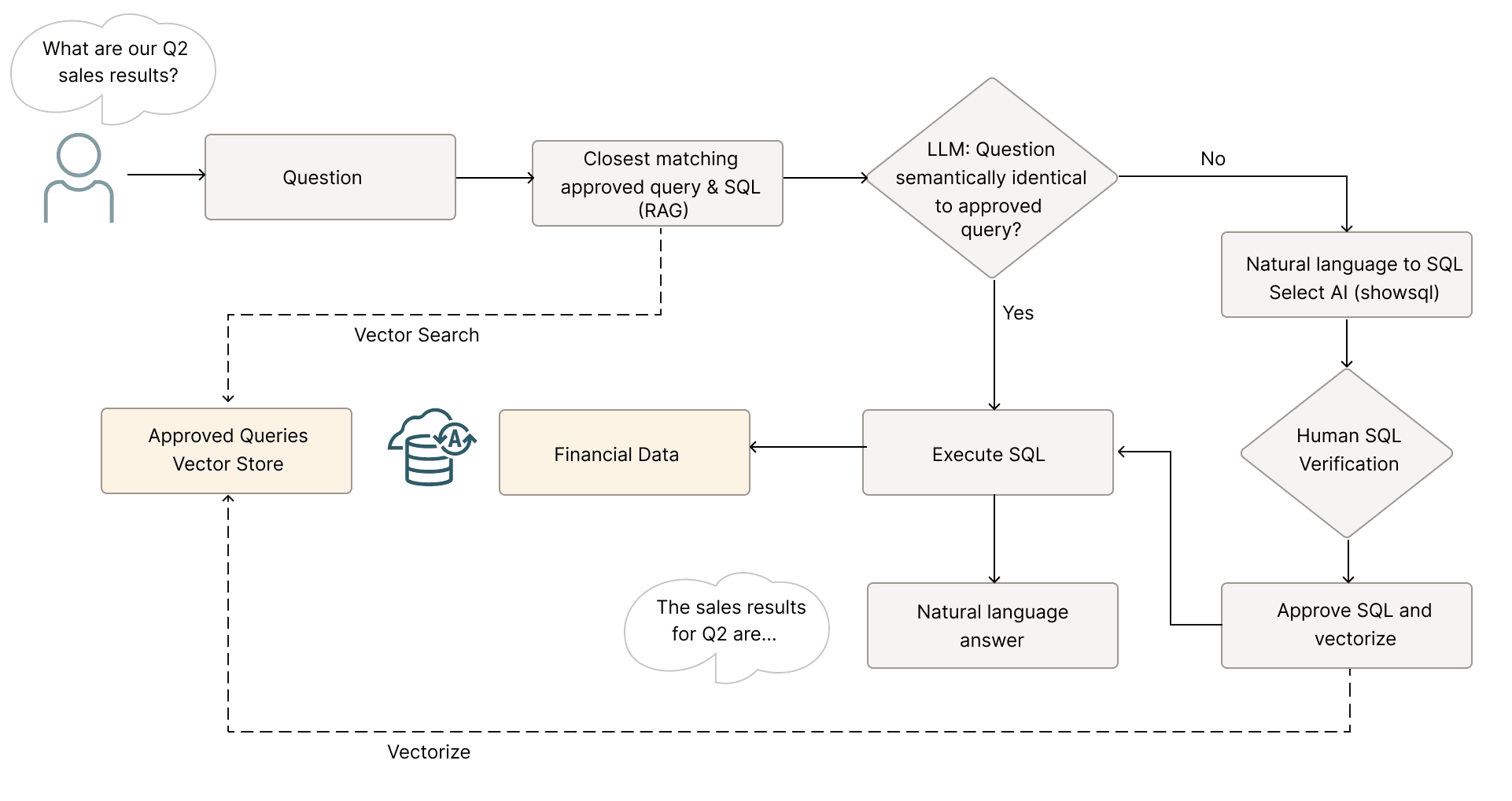
The following workflow outlines an agentic approach designed to achieve near-zero hallucinations in natural language (NL) query processing:
hallucination-reduction-workflow-oracle.zip
- User input: A user submits a natural language query through the APEX Service front end.
- RAG checkpoint: The query is first evaluated against the AI Vector Store in the Oracle Autonomous AI Database using semantic similarity search. If a closely matching, pre-validated query is found, its corresponding SQL is reused to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Natural language to SQL generation: If no match is identified, the orchestration engine triggers the Select AI feature in the Autonomous Database. This component leverages OCI Generative AI to translate the user's input into an executable SQL query.
- Query validation: The generated SQL is presented to the user for review and approval, introducing a human-in-the-loop safeguard before execution.
- Execution and data retrieval: After validation, the SQL query is executed against the Oracle Exadata Database Service. The resulting data is rendered in the APEX Service front end.
- Feedback loop: The validated natural language query and its corresponding SQL are embedded as vectors by using OCI Generative AI and are stored in the AI Vector Store. This enhances future RAG-based query resolution by expanding the repository of trusted query pairs.
This iterative workflow enables the system to continuously learn from user feedback, progressively reducing the likelihood of hallucinations over time.
Sidecar Pattern for Legacy Data Access
Oracle Autonomous AI Database acts as an AI sidecar with legacy databases, handling natural language to SQL translation and vector search, while federating queries to Exadata Database Service by using secure database links.
This approach eliminates the need to migrate legacy data, enabling enterprises to modernize query access without disrupting existing systems.
Leveraging APEX Service embedded Oracle JET for Dynamic Visualization
To support dynamic, data-driven visualizations, this architecture uses direct integration with Oracle JET rather than APEX Service’s declarative chart components. This enables required runtime rendering based on AI-generated data.
Oracle JET’s model-view-viewmodel (MVVM) architecture, which leverages Knockout.js, enables modular dependency management, asynchronous data binding, and runtime user interface composition. This allows the front end to respond dynamically to structured JSON outputs generated by AI-driven SQL queries.
By separating chart rendering from APEX Service’s declarative layer, we gain architectural control over the visualization pipeline. Chart types and data models are selected and introduced at runtime, enabling a responsive and extensible user experience aligned with modern analytics workflows.
Rendering Pipeline Overview:
- Model generation: AI-generated SQL results are transformed into structured JSON by using AI agents.
- JSON payloads: Stored in APEX Service page items for front end access.
- View composition: Chart type recommendations, for example bar, line, and pie charts, are retrieved by AI and stored in a APEX Service radio group item, allowing users to switch between different chart types.
- Runtime chart execution: The JavaScript function binds the JSON model to the Oracle JET chart component within a static region rendering the visualization in real time.
Recommendations
- Human-in-the-loop
Establish clear guidelines and interfaces for this interaction. Design intuitive review interfaces and define clear escalation criteria to ensure that human oversight is both efficient and effective. This fosters trust in the system and allows for continuous improvement through feedback loops.
- Feedback
Implement comprehensive analytics on the feedback logs generated by the system. This will provide insights into how the system is learning and evolving. Monitoring key performance indicators (KPI) such as query accuracy, user satisfaction, and response times will help in identifying areas for improvement and ensuring a high-quality user experience.
Considerations
Consider the following points when deploying this reference architecture on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI):
- Generative AI
- For predictable performance, especially in production environments, deploy dedicated AI clusters for model inference. These clusters are not shared with other tenants, ensuring consistent response times. For less critical tasks like embedding generation, the on-demand mode can be a more cost-effective option.
- For embeddings, you can either import pretrained models into Oracle Autonomous AI Database or generate embeddings externally using OCI Generative AI. Oracle Autonomous AI Database includes a built-in Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) runtime engine, allowing embedding models to run directly inside the database.
- High Availability
- AI Agents: To ensure high availability, the LangChain-based AI agents should be deployed across multiple compute instances in different fault domains or availability domains. We recommend using OCI Instance Pools for scalability and ease of management. An OCI Load Balancer distributes traffic among these instances and performs health checks.
- Managed Services: Other components in the architecture, such as Autonomous Database, APEX Service, OCI Generative AI, and OCI API Gateway, are fully managed services with built-in fault tolerance and high availability, requiring no additional configuration for redundancy.
- Disaster Recovery: For protection against site-wide outages, enable Oracle Autonomous Data Guard to replicate the database to another OCI region.
- Security and Compliance
- Layered Security Approach: Implement a multi-layered security strategy. This should include network security measures like using a Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall and following the principle of least privilege for all service interactions.
- Fine-Grained Access Control: In addition to the role-based access control (RBAC) implemented through AI profiles, consider using virtual private database (VPD) policies for more granular control over data access.
Explore More
Learn more about the features of this architecture and about related architectures.