5 Working with Alerts
An alert is a message that notifies you when a specified event or condition occurs for one or more Oracle GoldenGate components. This section describes how to use Oracle GoldenGate Monitor's the alerts. It contains the following topics:
5.1 About Alerts
An alert is a message that notifies you when a specified event or condition occurs for one or more Oracle GoldenGate components. Some examples of alerts:
-
An alert that notifies you when the lag of a Capture or Delivery group reaches a certain threshold.
-
An alert that notifies you when there is a failure within the Oracle GoldenGate instance.
-
An alert that notifies you when Capture has reached the end of the transaction log.
Oracle GoldenGate Monitor supports these notification types:
-
Oracle GoldenGate Monitor console
-
email
-
SNMP
-
Command-line Interface (CLI)
You determine the content of an alert when you create the alert definition.
Note:
Instance level security is not added for Alerts generations.You can create alerts for the instance objects that are not accessible to that userThis topic contains the following information:
5.1.1 Creating Console Alerts
By default, alerts are sent to the Data and Alerts View and Problem Summary tabs of Oracle GoldenGate Monitor. Whenever there is an alert, an animated bell icon appears in the Status Bar, which is visible no matter which tab of the application is active.
| Warning-level alert | |
| Error-level alert |
If no other notification protocol is required beyond the built-in alert views, you are ready to create your alert definitions. For instructions, see Managing Alert Definitions.
5.1.2 Creating email Alerts
You can configure Oracle GoldenGate Monitor to send email alerts to one or more Oracle GoldenGate Monitor users. For instructions, see Configuring email Alerts.
5.1.3 Creating SNMP Alerts
You can configure the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor SNMP interface to send alerts in the form of datagrams to any SNMP server. The datagrams are received by a trap recipient that is listening on a specific port. Versions 1 and 2a of SNMP are supported. For instructions, see Configuring SNMP Alerts.
5.1.4 Creating CLI Alerts
You can configure the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor Command Line Interface (CLI) to execute a script or binary file on the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor Server when an alert is triggered. (Creating CLI alerts does not support authentication.) For instructions, see Configuring CLI Alerts.
5.2 Managing Alert Definitions
Use the Alert Definition tab to create, view, and modify alert definitions. Super Administrators, Administrators, and Power Operators can configure alert definitions.
-
The Manage Alert Definitions table on this tab displays the existing alert definitions, with the following columns:
-
Definition Name: The name of the alert.
-
Assigned Users: The Oracle GoldenGate Monitor users that can receive the alert.
-
Object Type: The type of Oracle GoldenGate object for which this alert will be triggered (such as a Database or Capture object). See About the Objects.
-
Assigned Objects: Depending on how the alert was defined, this value can be "All objects" (the alert applies to all instances of the Object Type) or it can be the names of specific instances of the Object Type (such as the name of a database or the group name of a Capture object).
On the Alert Definition tab, you can take the following actions:
-
To create an alert definition, click New Alert Definition. See Configuring an Alert Definition.
-
To edit an alert definition, click its name in the list to open the Edit Alert Definition screen. See Configuring an Alert Definition.
-
To delete an alert definition, select the check box next to its name, and then click Remove Definition(s).
5.3 Configuring an Alert Definition
An Oracle GoldenGate Monitor user with the Administrator or Power Operator role can create or edit an alert definition. You can create as many alert definitions as you like.
Note:
When creating an alert, the following steps are displayed as the New Alert Definition screen. When editing an alert, the steps are displayed as the Edit Alert Definition screen. The functionality for the two are identical, except that default values are shown when creating a new alert, but current values are shown when editing an alert.To create or edit an alert definition
-
On the Alert Definition tab, click New Alert Definition. The New Alert Definition screen appears. To expand and collapse any section of this screen, click the arrow next to the section name. At the top of the screen, you will see the General Info section of the screen:
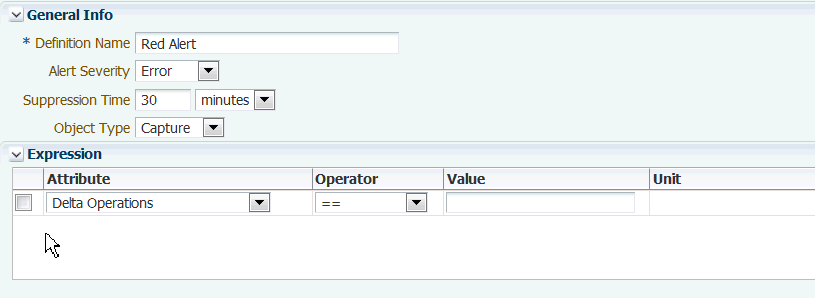
Description of the illustration new_alert_def_gen_info.gif
-
For Definition Name, type a name for this alert. You can use up to 30 characters, including numbers, symbols, and uppercase and lowercase letters. This field is mandatory.
-
For Alert Severity, select either Error or Warning. Any condition (as represented by this alert) can be treated as an error or warning, depending on your business protocols.
-
For Suppression Time, specify an interval of time during which you only want to receive one instance of this alert. This prevents multiple notifications of the same kind from filling the alert consoles and from being sent to email, SNMP, or CLI targets that are enabled.
-
For Object Type, select the type of object for which this alert will be triggered (such as Capture or Instance). You can specify an alert definition even before any object types are registered in the system. See About the Objects
-
In the Expression table, specify the condition (or multiple conditions) that will trigger the alert. Different conditions that are used in one expression are combined with logical AND operators, and the alert will be triggered when both of the conditions is satisfied.
-
For Attribute, select the attribute that triggers the alert. See About the Metrics.
-
For Operator, select a standard relational operator that clarifies the value that you will supply. See About the Alert Operators.
-
For Value, specify or select a value that, together with Attribute and Operator, will determine the complete condition. For some attributes, you must type a value. For others, a drop-down selection list is shown. Date-time values can be specified with the help of a calendar selector.
-
A value for Unit will appear automatically if the metric has one, such as Lag.
-
-
(Optional) To add more conditions to this Expression, click New Condition and then repeat the previous step to build the new condition. To remove any condition, select the check box next to it and then click Remove Condition(s).
-
(Optional) Collapse the Expression section to expose the next sections of the page. Your conditions will remain in place. The User Assignment section will now be at the top of the screen:
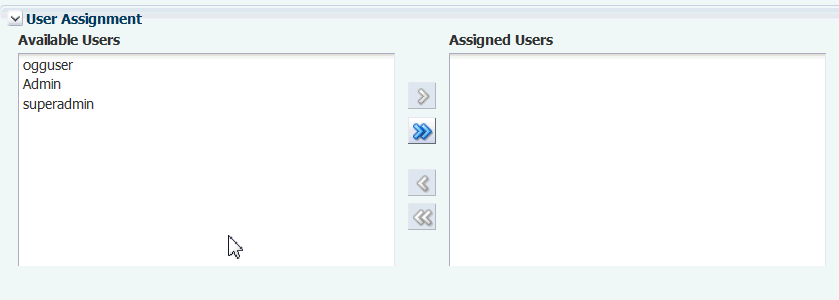
Description of the illustration new_alert_def_use_asgt.gif
-
Under Available Users, select the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor users that will receive this alert, and then move them to the Assigned Users panel. To move one user, select the name and then click the single arrow. To move more than one user, select them by using your operating system's standard selection methods and then click the single arrow. To move all users at once, click the double arrows (you do not need to select anything in the Available Users list.
Note:
By linking a user to an alert, you enable that user to view the alert in the Oracle GoldenGate Monitor user interface. To enable a user to receive an alert by email, SNMP, or CLI, that user must specify the notification method in his or her User Profile. For instructions, see Managing Your User Profile. -
(Optional) Collapse the User Assignment section to expose the next sections of the page. Your user assignments will remain in place. The next section is the Object Assignment section:
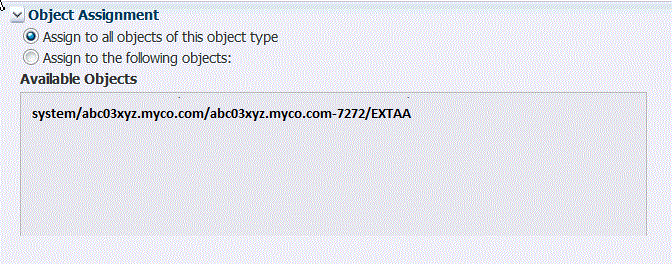
Description of the illustration new_alert_def_obj_asgt.gif
-
Under Object Assignment, do one of the following:
-
Select Assign to all objects of this object type to assign this alert to all objects of the object type that you selected in the Object Type field. For example, if you selected Capture for Object Type, the alert will be triggered for all Capture instances (for example Capture group "ext01", Capture group "ext02," and so forth). This is the default object assignment.
-
Select Assign to the following objects to activate a selection area, where you can select specific named objects that will trigger this alert. Select the names from Available Objects and then move them to Assigned Objects. To move one object, select it and then click the single arrow. To move more than one object, select them using the standard selection methods of the operating system, and then click the single arrow. To move all objects at once, use the double arrows (or just select Assign to all objects of this object type).
-
-
(Optional) Collapse the Object Assignment section to expose the next sections of the page. Your object assignments will remain in place. The next section is the Additional Notice Attributes section:
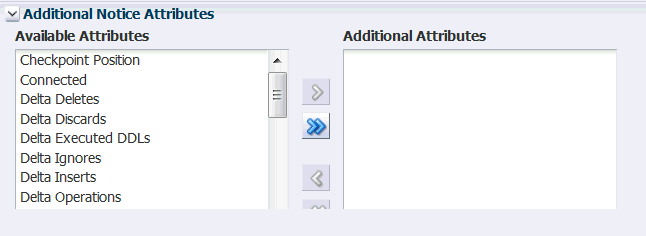
Description of the illustration new_alert_def_add_not.gif
-
(Optional) Under Additional Notice Attributes, you can specify additional attributes that are to be included in the alert. See About the Metrics.
The value of the additional metric will be its current value at the moment that the alert triggers. For example, if you are configuring this alert for Lag in a Capture Object Type, you could also include the Total Row Fetch Attempts and Total Row Fetch Failures attributes to indicate whether excessive fetching is causing the lag. You could also include the Checkpoint Position metric to see where Capture last created a checkpoint in the transaction log.
-
(Optional) Examine your alert definition. You can always edit it later if needed.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To create the alert definition, click Submit. The new alert is displayed in the Manage Alert Definitions table.
-
To remove all of the information that you have specified and restore all fields to their defaults, click Clear.
-
To remove all of the information that you have specified and exit the screen without creating the alert, click Cancel.
-
5.4 About the Alert Operators
Oracle GoldenGate Monitor uses the following operators to establish a relationship between an metric and a value for that metric when creating alert criteria.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| < | Less than. For example: Mapped Total Updates < 10000 |
| <= | Less than or equal to. For example: Start Time <= 06/01/2010 12:00 PM |
| > | Greater than. For example: Lag > 3 sec |
| >= | Greater than or equal to. For example: Last Checkpoint Timestamp >= 06/01/2010 12:00 PM |
| != | Not equal to. For example: Status != Running |
| == | Equal to. For example: Group Name = ext01 |