Oracle® Healthcare Foundation
Quick Reference Guide for Oracle Data Integrator
Release 7.2.1
F11017-01
October 2018
This guide provides the configuration details and the process for data loading.
Prerequisite
Set the database properties according to the Oracle Healthcare Foundation configuration recommendations. For the configuration recommendations, see Oracle Healthcare Foundation Configuration Guide.
Terminology Loaders
Configuration Table
Modify the SDE_ETL_LOAD_ PARAM_G table, in the HMC schema, to configure the Terminology Loader.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VAR_SOURCE_FOLDER_NAME | Location of Terminology Loader data files. |
| VAR_ARCHIVE_ FOLDER_NAME | Location where Terminology Loader data files are archived after successful data load. |
Setting Up the Environment for the ETL Execution
Before executing any ETLs, run the GENERATE ALL SCENARIOS package. This is a one-time step.
-
Navigate to EHA_HLI_Integration > Global.
-
Expand the Packages folder.
-
Right-click GENERATE ALL SCENARIOS, and select Execute.
ETL Execution
Before executing the ETL, make sure that the Terminology Loaders source files are available in the source directory.
You can execute the Terminology Loader ETLs by using:
-
Scheduler: For information, see Executing Terminology Loader ETLs Using the Scheduler.
-
Oracle Data Integrator Console: For information, see Executing the Terminology Loader ETLs Using the Oracle Data Integrator Studio.
Executing Terminology Loader ETLs Using the Scheduler
You can schedule ETLs on any enterprise scheduler to match the frequency (daily, weekly, and so on) of the source data acquisition.
To schedule ETLs:
Note:
You can schedule the default MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN provided with OHF to execute all Terminology Loader ETLs. Alternatively, you can build a similar MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN that includes selected ETLs of your choice and schedule that.-
Connect to the Terminology Loaders Work Repository, and select Designer.
-
Expand EHA_HLI_Integration project > Global > Packages > MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN > Scenarios
-
Expand the desired scenario.
-
Right-click Scheduling, and select New Scheduling to build the schedule.
Executing the Terminology Loader ETLs Using the Oracle Data Integrator Studio
Executing a Single Terminology Loader ETL
-
Connect to the Terminology Loaders Work Repository, and select Designer.
-
Select the EHA_HLI_Integration project, and select the folder containing the ETL.
-
Expand Packages > Scenarios.
-
Right-click the desired scenario, and select Execute.
Executing All Terminology Loader ETLs
-
Connect to the Terminology Loaders Work Repository, and select Designer.
-
Navigate to EHA_HLI_Integration project > Global.
-
Expand the Packages folder > MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN package > Scenarios.
-
Right-click MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN, and select Execute.
Note:
Execute the MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN package or scenario from the ODI hosting machine and not from the remote machine.
System Monitoring and Error Handling
-
ETL execution error logging:
The ETL creates an error table for every HDI table that the Terminology Loader ETLs load. During the data processing, if a source record fails due to a system error or an incorrect data, the ETL loads this record to the E$_<Interface Table Name> table.
-
ETL execution error correction:
-
ETLs do not fail for any data issues if the file structure is maintained. If an ETL fails for any database related issues, correct the issues, note the step that failed in the MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN, and follow the instructions appropriate to that step:
Failed in LOAD_HLI_STAGE_TABLES:
-
Failed in the HLI_Archive.sh command task - Check the HLI_Archive.log file in the VAR_SOURCE_ FOLDER_NAME source file directory.
-
Failed before or during the HLI archive - Run the MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN package.
-
Failed after the HLI archive - Run the LOAD_HLI_STAGE_TAB_WITHOUT_ FILE_PRE_PROCESS package and then the MASTER_EXECUTION_PLAN_STAGE_TO_HDI package.
Failed after LOAD_HLI_STAGE_TABLES:
-
Failed before or during LOAD_HDI_CD_DESC - Run the MASTER_ EXECUTION_PLAN_STAGE_TO_HDI package.
-
Failed after LOAD_HDI_CD_DESC - Run the failed ETL and remaining ETLs individually according to the load order.
-
-
When a particular source record fails during the data processing and gets rejected, the ETL logs an exception into the error table. Every exception has a message and a description, which can be configured. If a record fails due to one error, the ETL creates only one exception. If a record fails due to multiple errors, the ETL creates multiple exceptions in the error table.
-
Warehouse Integration Loaders
The Warehouse Integration Loaders include a comprehensive set of ETLs that provide a data integration solution to process data from diverse source systems through the Interface Tables to the Healthcare Data Warehouse.
Prerequisites
Update Global Settings
Review and update the following configurations in the HDI_ETL_GLBL_PARAM_G table of the HMC schema:
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ALLOW_INVALID_CODE | Controls the way data is loaded to the target when the source code is not resolved against HDM_CD_REPOSITORY.
Yes - Loads the record to the target with a NAV value for the HDM code attributes. No - Rejects the record. |
| ALLOW_INVALID_REFERENCES | Controls the way data is loaded to the target when the source reference is not resolved against the HDM table. This is applicable for optional references only.
Yes - Loads the record to the target with a NAV value for the HDM reference attributes. No - Rejects the record. |
| VERSIONING | Applicable for the incremental ETLs only when a changed record is from the source system.
Yes - Creates a new version of the record. No - Overwrites the existing record. |
| RULE_IDS_TO_BE_REPROCESSED | List of Rule IDs, separated by commas, to be automatically reprocessed if the ETL fails. For example, -9998, -9993. NULL indicates no rules should be reprocessed. |
| MAX_REPROCESS_CNT | Number of times a record can be reprocessed before rejecting. You must configure this in conjunction with RULE_IDS_TO_BE_REPROCESSED. |
| PARALLEL_DEGREE | Parallel degree for the session level parallelism. |
Configure Rules and Terminology
-
Review and enable or disable the default data validation rules in the HDI_ETL_RL_G table of the HMC schema as needed.
-
Review the seeded terminology standardization configurations in the HDI_ATRB_CD_SYS_LKUP_G and HDM_ATRB_CD_SYS_LKUP_G tables in the HDI and HDM schemas respectively.
You must disable the seeded configurations if the terminology standardization feature is not used or the seeded configurations are not relevant.
-
Review the seeded terminology validation configurations in the HDI_ATRB_CD_TYP_LKUP_G and HDM_ATRB_CD_TYP_LKUP_G tables in the HDI and HDM schemas respectively.
You must disable the seeded configurations if the terminology validation feature is not used or the seeded configurations are not relevant.
-
(Optional) Configure the late arriving data rules in the HDI_RL_REFRNTL_INTGRTY_G table in the HMC schema
For more information, see Oracle Healthcare Foundation Administrator's Guide.
Schedule Load Plans
A load plan is a group of related package scenarios. You can modify the load plans to disable, delete, insert, or modify a package scenario.
Note:
You can schedule the default Load Plans provided with OHF to execute the ETLs that are required to load HCD or CDM data mart. Alternatively, you can build similar Load Plans that includes specific ETLs of your choice and schedule that.| Load Plan | Description |
|---|---|
| OHF_WIL_MASTER_DATA_LOAD_PLAN | Includes the master data, rules, and configuration ETLs. |
| OHF_WIL_INITIAL_LOAD_PLAN | Includes the HCD or CDM specific ETLs for the initial load in the Party Not Available mode. |
| OHF_WIL_INCREMENTAL_LOAD_PLAN | Includes the HCD or CDM specific ETLs for the incremental load in the Party Not Available mode. |
| OHF_WIL_INITIAL_PARTY_AVAILABLE_LOAD_PLAN | Includes the HCD or CDM specific ETLs for the initial load in the Party Available mode. |
| OHF_WIL_INCREMENTAL_PARTY_AVAILABLE_LOAD_PLAN | Includes the HCD or CDM specific ETLs for the incremental load in the Party Available mode. |
You can schedule any of the load plans as per your execution frequency.
Setting Up the Environment for the First ETL Execution
-
Gather statistics on all Interface Tables.
-
Disable the automatic statistics gathering option on the HDM schema.
-
Delete and lock statistics on the HDM schema.
-
Set the parallel degree in the HDI_ETL_GLBL_PARAM_G table.
-
Review and modify the global parameters.
Executing Master Data Management ETLs
The Master Data Management (MDM) ETLs load data to the MDM tables, such as User, Data Source, Code System, Code Repository, Cross Map, and other Code related tables. The MDM ETLs are grouped under the DI_MASTER_DATA_MANAGEMENT folder in the Warehouse Integration Loaders repository.
You can choose to run the MDM ETLs as needed only when there is a change.
Executing Rules and Configurations ETLs
You can create late arriving data rules, data validation rules, and terminology configurations when they are needed, and run the ETLs accordingly. These ETLs are grouped under the DI_MASTER_DATA_MANAGEMENT folder in the Warehouse Integration Loaders repository.
Global Packages for Transaction ETLs
The following packages are in the SETUP folder:
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PKG_GLOBAL_REFRESH_VARIABLES | Run this to refresh the common variables used in the transaction ETLs. |
| PKG_GLOBAL_REFRESH_PROCEDURE | Run this when the standardization or type validation is configured. |
Executing the Initial Load ETLs for Transaction Entities
The initial load ETLs process historical data and perform data loading in an optimal way.
Setting Up the Environment
-
Drop the foreign keys according to the guidelines in the Oracle Healthcare Foundation Administrator's Guide.
-
Make sure that the HDI data load is complete.
-
Make sure that the source data does not contain multiple versions of the same record. The initial load ETLs cannot handle multiple versions.
-
Process necessary rules and configurations, and load the master data tables to the HDM tables.
Executing ETLs
When you use an enterprise scheduler, ETLs start automatically at the scheduled time or after the HDI data load is complete. You can monitor the progress of ETLs through the ODI Operator Window.
Restarting Failed ETLs
The Warehouse Integration Loaders do not automatically restart ETLs for an initial load. If an ETL fails in the middle of the data load, delete the data loaded for the current request ID, and restart the ETL.
-
When an ETL fails while loading the master table, clean up the target table, and restart the complete ETL.
-
When an ETL fails while loading any other child table, clean up that target table, and restart the ETL from that child scenario.
Use the following script to clean up the target table:
DELETE FROM <TARGET_TABLE> WHERE REQUEST_ID= (SELECT REQUEST_ID FROM<ETLSCHEMA>.HDI_ETL_LOAD_DT_G WHERE PACKAGE_NM='PKG_<Interface Table Name>');COMMIT; -
When an ETL is connected with multiple parallel scenarios, and if a scenario fails in that group, clean up the corresponding target table, and execute the scenario. Perform this for each failed scenario in the group, and then restart the main ETL.
Executing the Incremental Load ETLs for Transaction Entities
Setting Up the Environment
-
For the first incremental load, create the foreign key indexes on the HDM table according to the guidelines in the Oracle Healthcare Foundation Administrator's Guide.
-
Schedule an automatic statistics gathering for the HDM and HDI schema using the stale option.
-
Make sure that the HDI data load is complete.
-
Process any additional rules and configurations, and load the master data tables to the HDM tables.
Executing ETLs
When you use an enterprise scheduler, ETLs start automatically at the scheduled time or after the HDI data load is complete. You can monitor the progress of ETLs through the Operator window.
Restarting Failed ETLs
You can restart the package if an incremental ETL fails.
| Package Name | Interface Name | Interface Type |
|---|---|---|
| INCR_PKG_HDI_PROD_CTLG | INT_HDI_PROD_CTLG_HDM_PROD_ CTLG | First Interface (Linked to the package) |
| INCR_PKG_HDI_PROD_CTLG | INT_HDI_PROD_CTLG_HDM_ITM_ CTLG | Child Interface |
| INCR_PKG_HDI_PROD_CTLG | INT_HDI_PROD_CTLG_HDM_PURSVC_ CTLG | Child Interface |
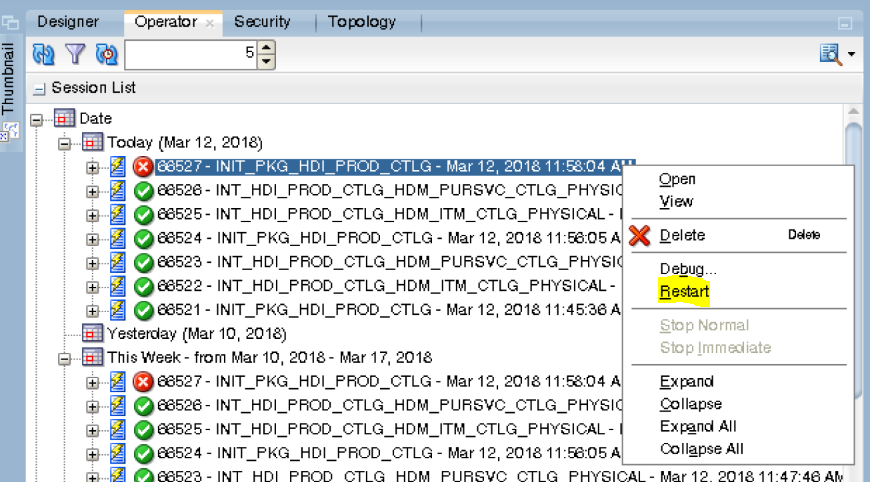
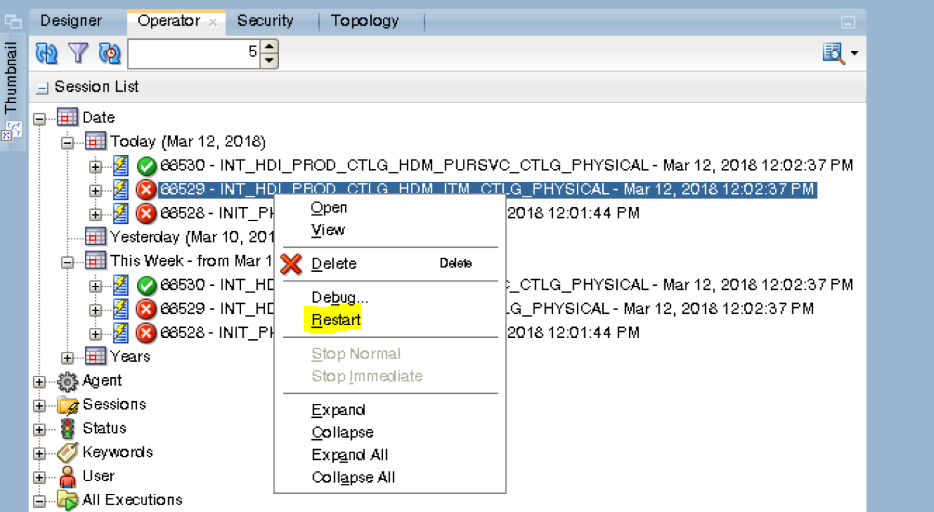
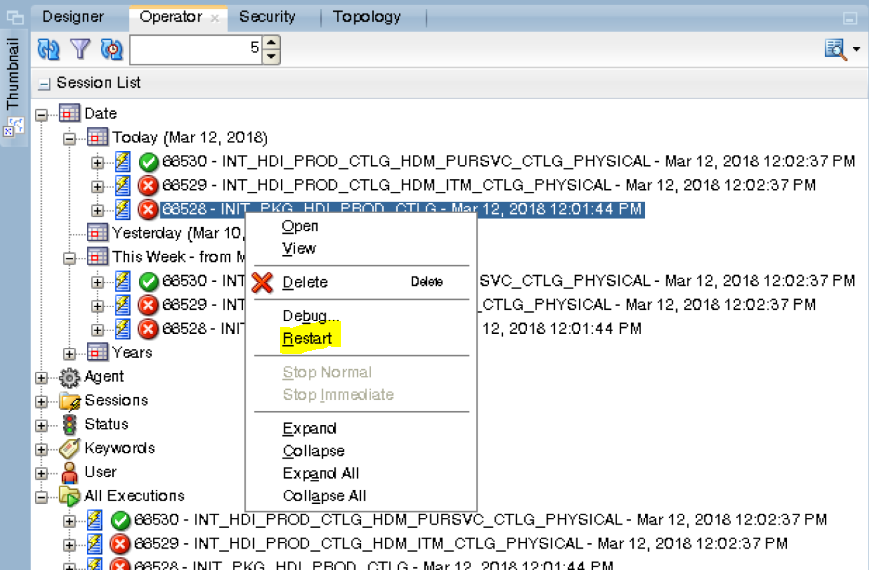
If the execution fails at the first interface, that is, INIT_PKG_HDI_PROD_CTLG in the below example, restart the failed package.
If the execution fails at a child interface, that is, INT_HDI_PROD_CTLG_HDM_ITM_CTLG or INT_HDI_PROD_CTLG_HDM_PURSVC_CTLG in the above example:
-
Restart the failed scenarios associated with that package.
Note:
When a package has multiple interfaces, and if any of the scenario associated with the respective interfaces fails, perform the above steps for each failed scenario. -
Once all the child scenarios are successfully complete, restart the failed package, INIT_PKG_HDI_PROD_CTLG.
Monitoring and Logging
You can monitor the progress of the ETL execution through the ODI Operator.
Load Summary
The Warehouse Integration Loaders capture the ETL execution summary in JB table of the enterprise schema and in the EXCPTN table.
The execution statistics includes component (Warehouse Integration Loaders and Application Toolkit), job group name (package name), job name (interface name), job type (initial or incremental), job start date, job end data, job status (running, succeeded, or failed), source record count, and target record count.
The exception statistics includes exception type (reject, reprocess, or suspend) and the exception count.
ETL Exceptions
When a source record fails a validation, the ETL rejects it and logs an exception in the error table. Every exception has a message and a description, which can be configured.
If a record fails only one validation, the ETL creates one exception. If a record fails multiple validations, the ETL creates multiple exceptions.
Application Toolkit Loaders
The Application Toolkit Loaders include a comprehensive set of ETLs that provide a data integration solution to process data from Healthcare Data Warehouse to Healthcare Common Data mart (HCD).
Updating Configurations
-
Review and update the configurations in the HCD_ETL_ENTY_SELCTN_PARAM_G table of the HMC schema as needed.
Parameter Name Description MSTR_ENTY_NM Entity which uses the parameterized attribute value. ATTRIB_NM Name of the attribute to be parameterized. ATTRIB_VAL Value of the parameterized attribute. ENTERPRISE_ID Unique identifier for an enterprise in a multi-enterprise environment. -
Set the degree of parallelism in the HCD_GLBL_PARAM_G table in the HMC schema to parallelize the SQL executions.
Parameter Name Default Value Description PARALLEL_QUERY_NO 1 This parameter is used for performance enhancement for the initial load ETLs. Set this value to an exponential value of 2, that is, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and so on.
For Exadata environment, set this value to 16 or 32. For non-Exadata environment, set this value to 2 or 4.
HDWF_SCHEMA_NAME HDM Specifies the Healthcare Data Warehouse schema name. HMC_SCHEMA_NAME HMC Specifies the ETL configuration schema name. PROXY_USER_ENABLED NO Indicates whether the Application Toolkit ETLs have to be executed through a proxy user. Update this parameter to YES if you want ETLs to be executed through a proxy user. HCD_SCHEMA_NAME HCD Specifies the HCD schema name.
Scheduling Load Plans
You can schedule load plans on any enterprise scheduler to match the frequency (daily, weekly, and so on) of the source data acquisition.
-
Connect to the Application Toolkig (HCD) Work Repository, and select Designer.
-
Go to the Load Plans and Scenarios section.
-
Expand the desired load plan (e.g. HCD_INITAL_LOAD_MASTER_EXEC_PLAN).
-
Right-click Scheduling, and select New Scheduling to build the schedule.
You can modify the load plan to disable, delete, or modify any package scenario. The following load plans are in the HCD work repository:
-
Initial - HCD_INITAL_LOAD_MASTER_EXEC_PLAN
-
Incremental - HCD_INCREMENTAL_LOAD_MASTER_EXEC_PLAN
-
Hierarchy - HCD_HIERARCHY_LOAD
Executing ETLs Using the Oracle Data Integrator Operator
-
Connect to the HCD Work Repository, and select Designer.
-
Expand Project, and expand the required folder.
-
Expand Packages > Scenario.
-
Right-click the package scenario to execute, and select Execute.
Setting Up the Environment for the First ETL Execution
-
Gather statistics on all HDM tables.
-
Disable the automatic statistics gathering option on the HDM schema.
-
Delete and lock the statistics on the HCD schema.
-
Set the parallel degree in the HCD_GLBL_PARAM_G table.
-
Review and modify the global parameters.
Executing the Initial Load ETLs for Transaction Entities
The initial load ETLs process historical data and perform data loading in an optimal way.
Setting Up the Environment
-
Drop the foreign keys according to the guidelines in the Oracle Healthcare Foundation Administrator's Guide.
-
Make sure that the HDM data load is complete.
-
Make sure that the selection or inline code configurations are valid in the HCD_ETL_ENTY_SELCTN_PARAM_G entity.
Executing Incremental Load ETLs
The incremental ETLs process data acquired on a regular basis.
Setting Up the Environment
-
For the first incremental load, create the foreign key indexes on the HDM table according to the guidelines in the Oracle Healthcare Foundation Administrator's Guide.
-
Schedule an automatic statistics gathering for the HDM and HCD schema using the stale option.
-
Make sure that the HDM data load is complete.
Monitoring and Logging
You can log in to the HCD_WORK repository through the ODI Operator to monitor the progress of the ETL execution.
For the load summary details, see Load Summary.
Cohort Data Mart Loaders
Updating Configurations
-
Review and update the configurations in the C_LOAD_PARAM table of the HDM schema as needed.
-
Set the degree of parallelism in the C_LOAD_CONFIG table in CDM schema to parallelize SQL executions.
Scheduling Load Plans
The CDM ETL contains the following load plan to load the data into CDM:
-
CDM_LOAD_PLAN - Use this load plan in the scheduler for initial or incremental executions.
Executing ETLs Using the Oracle Data Integrator Console
-
Connect to the CDM work repository, and select Designer.
-
Expand the Oracle Healthcare Analytics project, and expand the required folder.
-
Expand Packages > Scenario.
-
Right-click the scenario to execute, and select Execute.
Setting Up the Environment for the First ETL Execution
-
Gather statistics on all HDM tables.
-
Review and modify the global parameters.
Executing the Initial Load ETLs
CDM has a load plan, CDM_LOAD_PLAN, to load data in the initial load.
Running ETLs
When you use an enterprise scheduler, ETLs start automatically at the scheduled time or after the HDM data load is complete. You can monitor the progress of ETLs through the ODI operator.
Note:
When upgrading to OHF 7.2.1 or later, you must truncate and reload the CDM tables for which the ETL is optimized.Restarting Failed ETLs
When an ETL fails during the data loading process, rerun the failed ETL.
Executing Incremental Load ETLs
CDM has a load plan, CDM_LOAD_PLAN, for incremental ETLs to process the data acquired on a regular basis.
Monitoring and Logging
You can monitor the progress of the ETL execution through the ODI Operator.
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Oracle customers that have purchased support have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle Healthcare Foundation Quick Reference Guide for Oracle Data Integrator, Release 7.2.1
F11017-01
Copyright © 2018, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle.