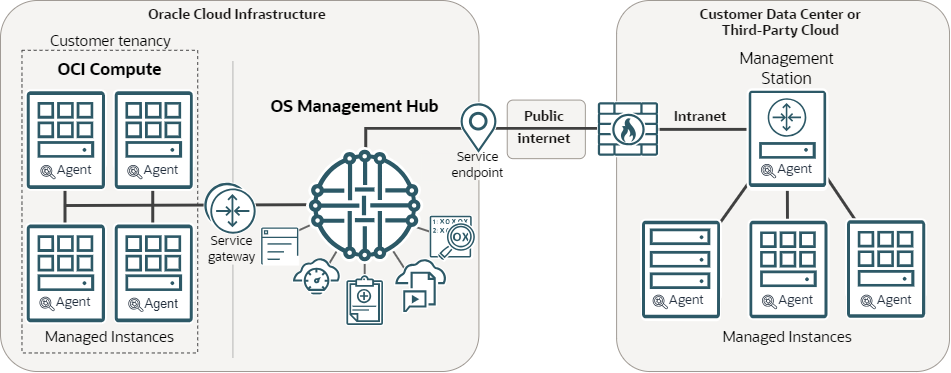
Architectural Overview
OS Management Hub is the next generation management solution for operating system environments. OS Management Hub is delivered as an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service to expand capabilities and reduce complexity. The service supports managing instances in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), private data centers, and supported third-party clouds.
Understanding the Agent Plugin
OS Management Hub uses an agent plugin for managing and applying updates. The plugin is the agent that interacts with the OS content on an instance as directed by OS Management Hub and reports data and results back to the service. The agent differs between OCI and on-premises or third-party cloud.
For OCI instances, OS Management Hub uses the Oracle Cloud Agent plugin. To use OS Management Hub, you must enable the plugin. See Registering an OCI Instance.
OS Management Hub requires minimum Oracle Cloud Agent version 1.40. For instances using platform images released before April 2024, upgrade the Oracle Cloud Agent to 1.40 or later.
For on-premises or third-party cloud instances, OS Management Hub uses a plugin to the Management Agent installed on the instance. To use OS Management Hub, you must install the Management Agent and activate the OS Management Hub plugin, and register the instance with the service. See Registering a Non-OCI Instance.
To check the version of the OS Management Hub plugin running on an instance, see Verifying the OS Management Hub Plugin Version.
Features in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Using the OCI Console, CLI, and API, you interact with the OS Management Hub service to:
- Configure the service.
- Monitor instances and resources.
- Create update jobs for security and bug fixes and deploy new software content.
- Run reports.
The OS Management Hub configuration is stored and backed up by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, including:
- The software source content used by the service, such as the vendor software sources that you select and the custom software sources that you create.
- The management station configurations.
- Group and lifecycle environments that you create to align content across multiple instances.
- Scheduled and recurring jobs that you create to modify and update instant content.
What Data Is Stored in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for Instances?
The following information about instances managed by OS Management Hub is stored in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Hostname
- OS vendor, version, and architecture
- Inventory of installed packages
-
Software sources (repositories) assigned to the instance based on the registration profile or changes made after registration by an administrator.
Note
Third-party (private) repositories aren't tracked or stored by OS Management Hub. - Module stream status and module stream profiles (Oracle Linux 8 and Oracle Linux 9)
- Inventory of available updates
- Inventory of available errata
- Kernel version
- Ksplice effective kernel version
- Yum and DNF command output (in job history)
- Ksplice command output (in job history)
- Uptime
What Runs in the Customer Data Center?
When using on-premises or third-party cloud instances, some OS Management Hub components are physically present in the customer data center, including one or more management stations and the instances managed by the service.
Management stations are a proxy for OS Management Hub traffic to and from the customer data center or third-party cloud. Only management stations are required to communicate directly with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Instances in the data center send and receive requests and responses through the management station.
A management station also acts as yum and DNF mirror for Oracle Linux content in a customer data center and distributes it locally to instances, reducing the amount of bandwidth used for patching instances. The content that's mirrored is based on the number of OS versions and software sources used by the instances in the data center, which is bound to grow over time.
OS Management Hub traffic is proxied to the management station through Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. A management station must have connectivity with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Instances communicate directly with their local management station and receive their OS content from the management station and don't require direct connectivity with the service. All package transfers are local to the customer data center. When creating management stations, you have full control over the TCP ports used for traffic between the management stations and instances.
The OS Management Hub plugin is a service plugin to the Management Agent and runs on the instances in the customer data center. The OS Management Hub plugin is the agent that interacts with the OS content on an instance as directed by OS Management Hub and reports data and results back to the service.
What Data Is Stored in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for Management Stations?
OS Management Hub stores the following information about management stations in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure:
- Hostname
- Permitted proxy addresses
- Proxy listening port
- Proxy forwarding port
- Path to software source mirror
- Capacity (percentage free) of mirror storage
- Mirror listening ports
- SSL certification path (if provided)
reposynccommand output
If the management station is also being managed and updated using OS Management Hub, its instance information is also stored. See What Data Is Stored in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for Instances?.
Instance Activity and Status
An instance registered with OS Management Hub checks in periodically with the service using the OS Management Hub plugin.
The following status values are used based on when the instance last checked in with the service:
- Active: An instance that's actively checking in with the service. An active instance checks in with the service at an interval of every 2 minutes.
- Offline: An instance that hasn't checked in with the service for 24 hours (or longer).
- Inactive: An instance that hasn't checked in with the service in 30 minutes (or longer).
- Registering: An instance that's in the process of registering with the service.
- Registration failed: An instance that failed to register with the service.
- Unregistering: An instance that's unregistering from the service. Once unregistered, OS Management Hub will no longer manage the instance.
The status of instances is displayed on the Instances page and can be viewed in reports.