Replicare i dati tra database cloud nella stessa area
Scopri come impostare Oracle Cloud Infrastructure GoldenGate per replicare i dati tra due database AI autonomi.
Panoramica
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure GoldenGate ti consente di replicare i database supportati all'interno della stessa area. I passi riportati di seguito illustrano come creare un'istanza di un database di destinazione utilizzando Oracle Data Pump e replicare i dati dall'origine alla destinazione.
Questa Quickstart è disponibile anche come LiveLab: Visualizza il workshop.
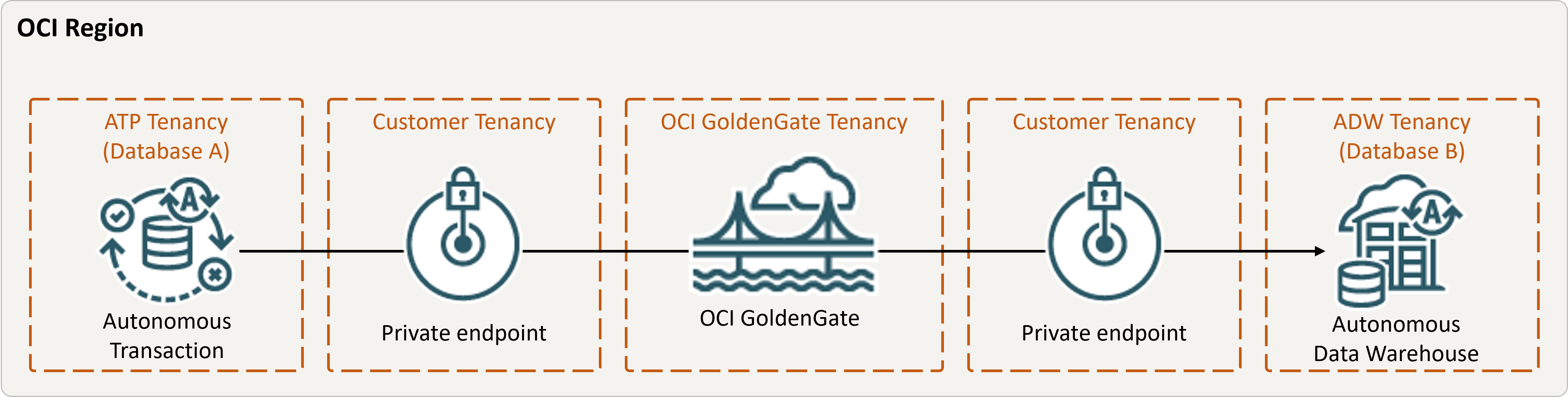
Descrizione dell'illustrazione same-region.png
Prima di iniziare
Per continuare, è necessario disporre dei seguenti elementi:
- Un database di origine esistente
- Un database di destinazione esistente
- Il database di origine e di destinazione deve trovarsi in una singola tenancy, nella stessa area
- Se sono necessari dati di esempio, scaricare Archive.zip, quindi seguire le istruzioni riportate in Lab 1, Task 3: Carica lo schema ATP.
Task 2: Creare l'estrazione integrata
Un'estrazione integrata acquisisce le modifiche in corso al database di origine.
Task 3: Esportare i dati utilizzando Oracle Data Pump (ExpDP)
Utilizzare Oracle Data Pump (ExpDP) per esportare i dati dal database di origine nell'area di memorizzazione degli oggetti Oracle.