Configura replica bidirezionale
Dopo aver impostato una replica unidirezionale, sono disponibili solo alcuni passaggi aggiuntivi per replicare i dati nella direzione opposta. Questo esempio rapido utilizza Autonomous AI Transaction Processing e Autonomous AI Lakehouse come due database cloud.
Argomenti correlati
Prima di iniziare
Per procedere con questo avvio rapido, è necessario disporre di due database esistenti nella stessa tenancy e area. Se sono necessari dati di esempio, scaricare Archive.zip, quindi seguire le istruzioni riportate in Lab 1, Task 3: Caricamento dello schema ATP
Panoramica
I passi riportati di seguito descrivono come creare un'istanza di un database di destinazione utilizzando Oracle Data Pump e impostare la replica bidirezionale (a due vie) tra due database nella stessa area.
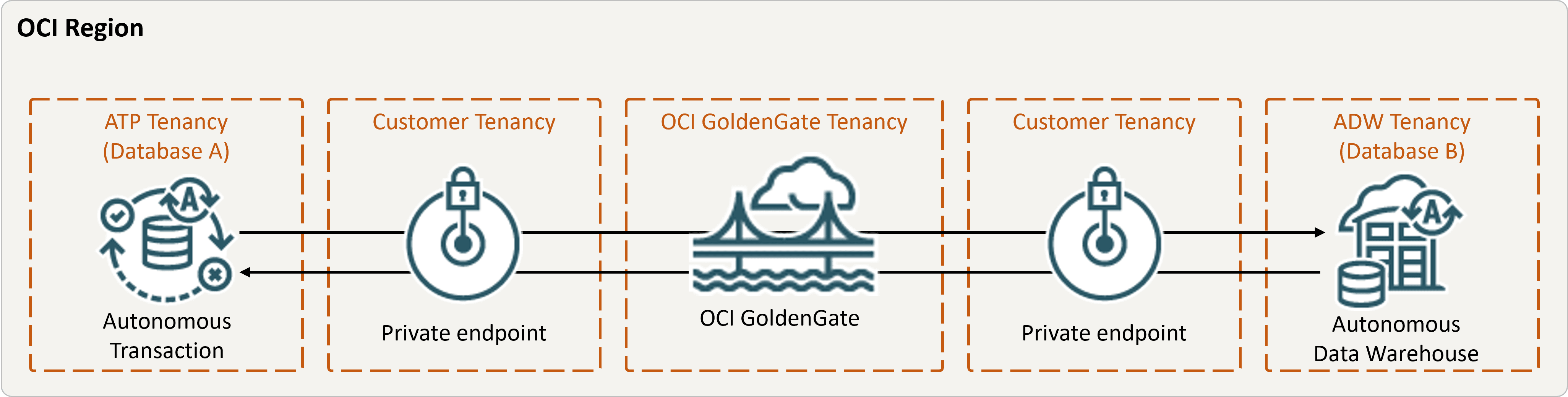
Descrizione dell'immagine bidirectional.png
Task 2: Aggiungere informazioni sulle transazioni e una tabella di checkpoint per entrambi i database
Nella console di distribuzione OCI GoldenGate andare alla schermata Configurazione per il servizio di amministrazione, quindi completare quanto riportato di seguito.
Task 3: Creazione dell'estrazione integrata
Un'estrazione integrata acquisisce le modifiche in corso al database di origine.
Task 4: Esportare i dati utilizzando Oracle Data Pump (ExpDP)
Utilizzare Oracle Data Pump (ExpDP) per esportare i dati dal database di origine in Oracle Object Store.
Task 5: creare un'istanza del database di destinazione utilizzando Oracle Data Pump (ImpDP)
Utilizzare Oracle Data Pump (ImpDP) per importare i dati nel database di destinazione dal file SRC_OCIGGLL.dmp esportato dal database di origine.
Task 6: Aggiunta ed esecuzione di un Replicat non integrato
- Aggiungere ed eseguire Replicat.
- Eseguire alcune modifiche al database A per visualizzarle replicate nel database B.