ノート:
- このチュートリアルではOracle Cloudへのアクセスが必要です。無料アカウントにサインアップするには、Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tierの開始を参照してください。
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure資格証明、テナンシおよびコンパートメントの値の例を使用します。演習を完了する場合は、これらの値をクラウド環境に固有の値に置き換えてください。
OCI Data Scienceのインタラクティブなノートブックを使用して、OCI Data Flowで分析を実行
イントロダクション
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Data Flowはフルマネージド・ビッグ・データ・サービスであり、Apache Sparkアプリケーションを任意の規模で実行でき、管理はほぼ不要です。Sparkは主要なビッグ・データ処理フレームワークになり、OCIデータ・フローはOracle CloudでSparkを実行する最も簡単な方法です。開発者はインストールや管理ができないためです。
目標
このチュートリアルの目的は、OCIデータ・サイエンス・ノートブック・セッションを介してOCIデータ・フロー・セッションにアクセスするために必要な設定を順を追って説明することです。これらのセッションでは、Apache Livy統合を介して、長期にわたるデータ・フロー・クラスタ上で対話型のSparkワークロードを実行できます。
また、OCI Data Flow Sparkセッションが作成されたら、OCI Object StorageおよびOracle Autonomous Data WarehouseでSpark操作を実行するためのサンプル・コードも確認します。
タスク1: OCIデータ・フローを使用したOCIデータ・サイエンス・ノートブックの設定
OCIデータ・フロー・コンダ環境の作成および設定
-
必要なバケットを作成します。
a.テナンシにdataflow-logsという名前のバケットを作成します。
b.テナンシにdataflow-warehouseという名前のバケットを作成します。
-
特定のコンパートメントに動的グループを作成します。
ALL {resource.type='dataflowrun', resource.compartment.id='<compartment_id>'} ALL {resource.type='datasciencenotebooksession', resource.compartment.id='<compartment_id>'} Any {resource.type = 'datacatalogmetastore'} -
OCIデータ・フローおよびOCIデータ・サイエンスからOCIリソースを管理するポリシーを作成します。
-
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP <df-dynamic-group> TO MANAGE objects IN TENANCY WHERE ANY {target.bucket.name='<bucket_name>',target.bucket.name ='dataflow-logs,target.bucket.name='dataflow-warehouse'} -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<ds-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE dataflow-family in compartment '<your-compartment-name>' -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<df-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE data-catalog-metastores IN TENANCY -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<dcat-hive-group>' TO READ buckets IN TENANCY -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<dcat-hive-group>' TO MANAGE object-family IN TENANCY WHERE ANY { target.bucket.name = '<bucket_name>',target.bucket.name = '<managed-table-location-bucket>',target.bucket.name = '<external-table-location-bucket>'} -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<ds-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE objects IN TENANCY WHERE ALL {target.bucket.name='ds-conda-env'} -
ALLOW DYNAMIC-GROUP '<df-dynamic-group>' TO MANAGE objects IN TENANCY WHERE ALL {target.bucket.name='ds-conda-env'}
-
-
OCI Data Scienceプロジェクトおよびセッションを作成します。
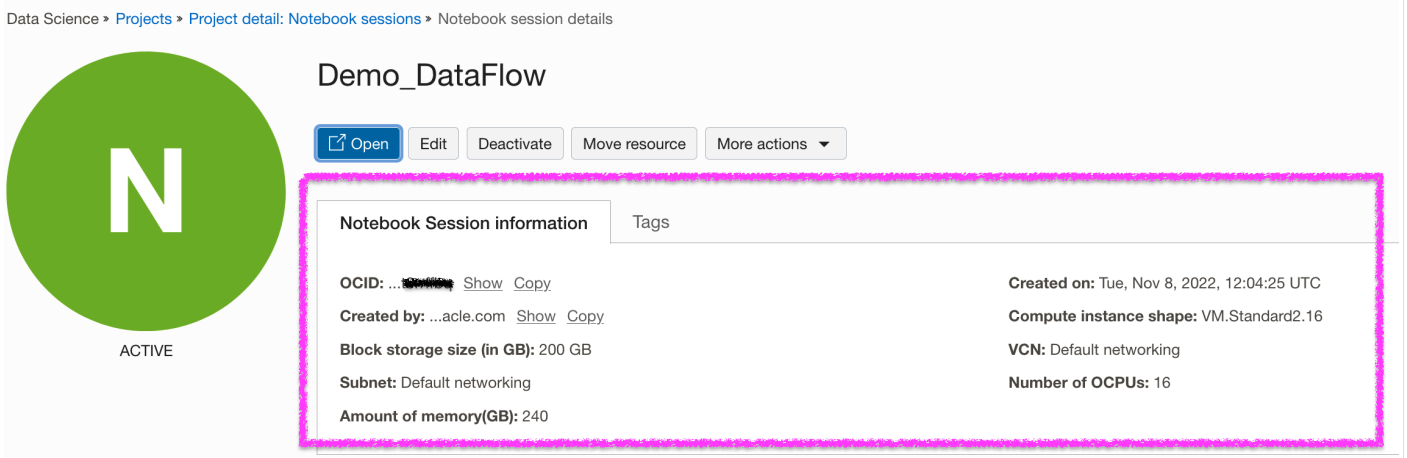
-
新しいOCIデータ・サイエンス・セッションを開きます。「ファイル」メニューから「新規ランチャ」を選択し、「ターミナル」をクリックします。

-
端末から
pyspark32_p38_cpu_v1Conda環境をインストールしてアクティブ化します。odsc conda install -s pyspark32_p38_cpu_v1 source activate /home/datascience/conda/pyspark32_p38_cpu_v1 -
Condaをアクティブ化したら、「新規ランチャ」タブに移動し、「設定」をクリックします。Condaパッケージをアップロードして保存するオブジェクト・ストレージに関する必要な情報を入力します。

-
Conda環境を公開します。
odsc conda publish -s pyspark3_2anddataflowv1_0ノート: 公開には時間がかかります。完了すると、Object StorageバケットにCondaパッケージがアップロードされることがわかります。
Livyサービスを使用したOCIデータ・フローSparkセッションの設定および作成
新しいランチャからカーネルとして"PySpark and DataFlow"を使用してノートブックを開き、次のコマンドを実行して、Livyサービスを使用してOCIデータ・フローSparkセッションを設定および作成します:
-
ADSを使用して認証を設定します。
import adsads.set_auth("resource_principal") # Supported values: resource_principal, api_key -
延長のロード。
%load_ext dataflow.magics -
OCI Data Scienceノートブックを介してLivyサービスを使用してOCI Data Flow Sparkセッションを作成します。
import json command = { "compartmentId": "ocid1.compartment.oc1..xxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "displayName": "Demo_DataFlow_Spark_v1", "sparkVersion": "3.2.1", "driverShape": "VM.Standard.E3.Flex", "executorShape": "VM.Standard.E3.Flex", "driverShapeConfig":{"ocpus":1,"memoryInGBs":16}, "executorShapeConfig":{"ocpus":1,"memoryInGBs":16}, "numExecutors": 1, "logsBucketUri": "<oci://bucket@namespace/>", "archiveUri": "<oci://bucket@namespace/archive.zip>" "configuration":{"spark.archives":"<oci://bucket@namespace/>#conda", "spark.oracle.datasource.enabled":"true"} } command = f'\'{json.dumps(command)}\'' print("command",command) #"configuration":{ # "spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"true", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.shuffleTracking.enabled":"true", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors":"1", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors":"4", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.executorIdleTimeout":"60", # "spark.dynamicAllocation.schedulerBacklogTimeout":"60", # "spark.dataflow.dynamicAllocation.quotaPolicy":"min" }}' %create_session -l python -c $command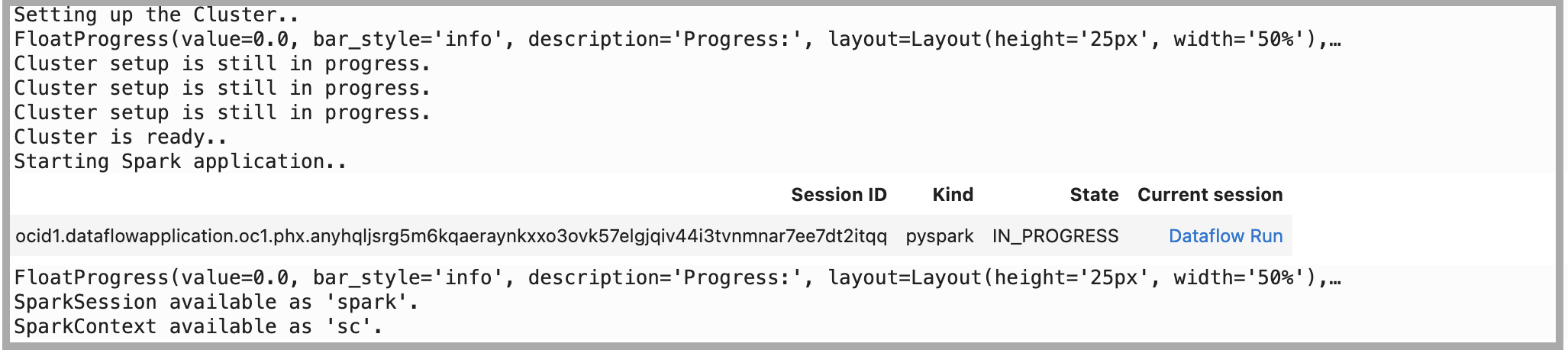
タスク2: サンプル・コードを使用したOCIオブジェクト・ストレージでのSpark操作の実行
-
セッションで依存ライブラリをインポートします。
%%spark #Import required libraries. import json import os import sys import datetime import oci import pyspark.sql from pyspark.sql.functions import countDistinct from delta.tables import * -
オブジェクト・ストレージでSpark読取り操作を実行します。Livyセッションから
spark.readを使用してオブジェクト・ストレージ・ファイルを読み取ります。%%spark -o df_Bronze_Insurance_Data #Read Claim Insurance files from OCI Object Storage in Spark Dataframe. df_Bronze_Insurance_Data = spark.read.format("csv").option("header", "true") \ .option("multiLine", "true").load("oci://test-demo@OSNamespace/insur_claim/claim.csv*") print("df_RawZone_Data",df_Bronze_Insurance_Data) df_Bronze_Insurance_Data.show(5) -
オブジェクト・ストレージでSpark書込み操作を実行します。
%%spark df_Bronze_Insurance_Data.write.format("json").option("mode","overwrite").save("oci://test-demo@OSNamespace/insur_claim/claim_curated")
タスク3: サンプル・コードを使用したOracle Autonomous Data Warehouseでの読取りおよび書込み操作の実行
-
Secret Vault for Walletを使用してOracle Autonomous Data Warehouseにデータをロードします。次のコードをそのままコピーします。詳細は、GitHubサンプルを参照してください。
%%spark def get_authenticated_client(token_path, client, file_location=None, profile_name=None): """ Get an an authenticated OCI client. Example: get_authenticated_client(token_path, oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient) """ import oci if not in_dataflow(): # We are running locally, use our API Key. if file_location is None: file_location = oci.config.DEFAULT_LOCATION if profile_name is None: profile_name = oci.config.DEFAULT_PROFILE config = oci.config.from_file(file_location=file_location, profile_name=profile_name) authenticated_client = client(config) else: # We are running in Data Flow, use our Delegation Token. with open(token_path) as fd: delegation_token = fd.read() signer = oci.auth.signers.InstancePrincipalsDelegationTokenSigner( delegation_token=delegation_token ) authenticated_client = client(config={}, signer=signer) return authenticated_client def get_password_from_secrets(token_path, password_ocid): """ Get a password from the OCI Secrets Service. """ import base64 import oci secrets_client = get_authenticated_client(token_path, oci.secrets.SecretsClient) response = secrets_client.get_secret_bundle(password_ocid) base64_secret_content = response.data.secret_bundle_content.content base64_secret_bytes = base64_secret_content.encode("ascii") base64_message_bytes = base64.b64decode(base64_secret_bytes) secret_content = base64_message_bytes.decode("ascii") return secret_content def get_delegation_token_path(spark): """ Get the delegation token path when we're running in Data Flow. """ if not in_dataflow(): return None token_key = "spark.hadoop.fs.oci.client.auth.delegationTokenPath" token_path = spark.sparkContext.getConf().get(token_key) if not token_path: raise Exception(f"{token_key} is not set") return token_path def get_temporary_directory(): if in_dataflow(): return "/opt/spark/work-dir/" else: import tempfile return tempfile.gettempdir() def in_dataflow(): """ Determine if we are running in OCI Data Flow by checking the environment. """ if os.environ.get("HOME") == "/home/dataflow": return True return False def download_wallet(spark, wallet_path): """ Download an Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse/ATP wallet file and prepare it for use in a Data Flow application. """ import oci import zipfile # Get an object store client. token_path = get_delegation_token_path(spark) object_store_client = get_authenticated_client( token_path, oci.object_storage.ObjectStorageClient ) # Download the wallet file. from urllib.parse import urlparse parsed = urlparse(wallet_path) bucket_name, namespace = parsed.netloc.split("@") file_name = parsed.path[1:] response = object_store_client.get_object(namespace, bucket_name, file_name) temporary_directory = get_temporary_directory() zip_file_path = os.path.join(temporary_directory, "wallet.zip") with open(zip_file_path, "wb") as fd: for chunk in response.data.raw.stream(1024 * 1024, decode_content=False): fd.write(chunk) # Extract everything locally. with zipfile.ZipFile(zip_file_path, "r") as zip_ref: zip_ref.extractall(temporary_directory) # Distribute all wallet files. contents = "cwallet.sso ewallet.p12 keystore.jks ojdbc.properties sqlnet.ora tnsnames.ora truststore.jks".split() spark_context = spark.sparkContext for file in contents: spark_context.addFile(os.path.join(temporary_directory, file)) return temporary_directory -
Oracle Autonomous Data WarehouseインスタンスおよびWalletに関連する次のパラメータを設定します。
%%spark PASSWORD_SECRET_OCID = "ocid1.vaultsecret.oc1.phx.xxxxxxx" TARGET_TABLE = "ADMIN.TB_NAME" TNSNAME = "demolakehouseadw_medium" USER = "admin" WALLET_PATH = "oci://bucketname@osnamespace/Wallet_DemoLakeHouseADW.zip" # Download and distribute our wallet file. wallet_path = download_wallet(spark, WALLET_PATH) adw_url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@{}?TNS_ADMIN={}".format(TNSNAME, wallet_path) -
シークレット・サービスを使用してパスワードを取得します。
%%spark # Get our password using the secret service. print("Getting wallet password") token_path = get_delegation_token_path(spark) password = get_password_from_secrets(token_path, PASSWORD_SECRET_OCID) print("Done getting wallet password") # Save the results to the database. print("Saving processed data to " + adw_url) properties = { "driver": "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver", "oracle.net.tns_admin": TNSNAME, "password": password, "user": USER } -
Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouseのサンプル表をお読みください。
%%spark SOURCE_TABLE = "ADMIN.RETAILPOS" df_RetailPOS_15min = spark.read.jdbc(url=adw_url, table=SOURCE_TABLE, properties=properties) -
前述のデータフレームをOracle Autonomous Data Warehouseにロードします。
%%spark #Load into Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse: TARGET_TABLE = "ADMIN.RETAILPOS_15MINUTES" print("TARGET_TABLE : ",TARGET_TABLE) # Write to Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse. print("Write to Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse : ") df_RetailPOS_15min.write.jdbc(url=adw_url, table=TARGET_TABLE, mode="Append", properties=properties) print("Writing done to Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse : ")
次のステップ
-
OCIデータ・フローを使用すると、データ・フローに対して対話形式でアプリケーションを実行するようにOCIデータ・サイエンス・ノートブックを構成できます。Data Flow Studioでのデータ・サイエンスの使用に関するチュートリアル・ビデオをご覧ください。
-
データ・サイエンスとデータ・フローの統合の詳細は、Oracle Accelerated Data Science SDKドキュメンテーションも参照してください。
-
その他の例は、GitHubからデータ・フロー・サンプルおよびデータ・サイエンス・サンプルとともに使用できます。
-
今日から開始するには、Oracle Cloud無料トライアルにサインアップするか、アカウントにサインインしてOCIデータ・フローを試してください。データ・フローのインストール不要の15分間のチュートリアルを試して、Oracle Cloud InfrastructureでSparkの処理がどの程度簡単であるかを確認してください。
関連リンク
謝辞
作成者 - Kumar Chandragupta (OCIシニア・クラウド・エンジニア)
その他の学習リソース
docs.oracle.com/learnで他のラボをご覧いただくか、Oracle Learning YouTubeチャネルでより無料のラーニング・コンテンツにアクセスしてください。また、education.oracle.com/learning-explorerにアクセスして、Oracle Learning Explorerになります。
製品ドキュメントについては、Oracle Help Centerを参照してください。
Perform your analytics on OCI Data Flow using OCI Data Science interactive notebook
F79466-01
March 2023
Copyright © 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.