주:
- 이 사용지침서에서는 Oracle Cloud에 액세스해야 합니다. 무료 계정에 등록하려면 Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier 시작하기를 참조하십시오.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure 인증서, 테넌시 및 구획에 대한 예제 값을 사용합니다. 실습을 마치면 이러한 값을 자신의 클라우드 환경과 관련된 값으로 대체합니다.
Terraform을 사용하여 PostgreSQL 서비스로 OCI 관리 데이터베이스 배치
소개
널리 인정받는 오픈 소스 객체 관계형 데이터베이스인 PostgreSQL는 강력한 아키텍처와 확고한 데이터 무결성으로 인해 눈에 띄는 위치를 유지하므로 엔터프라이즈 환경에서 선호하는 선택입니다. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure(OCI)에서 제공되는 이 서비스는 지능형 크기 조정, 비용 효율적인 튜닝 및 내구성을 갖춘 완전 관리형 고성능 데이터베이스 서비스를 도입했습니다. PostgreSQL 기업, SMB(중소, 중견, 성장 기업) 및 광범위한 개발 환경을 지원하여 적응력과 견고성을 입증합니다.
이 자습서에서는 OCI 클라우드 테넌시에 OCI 관리형 PostgreSQL 데이터베이스 시스템의 세 노드를 배포하고 Terraform 스크립트를 사용하여 컴퓨트 인스턴스를 통해 전용으로 연결하는 방법에 대해 알아봅니다.
목표
-
PostgreSQL 및 컴퓨트 인스턴스로 OCI 관리 데이터베이스를 배포하여 Terraform 스크립트를 사용하여 전용으로 데이터베이스 서비스를 연결합니다. Terraform 코드를 사용하여 OCI에서 다음 아키텍처를 배포할 예정입니다.
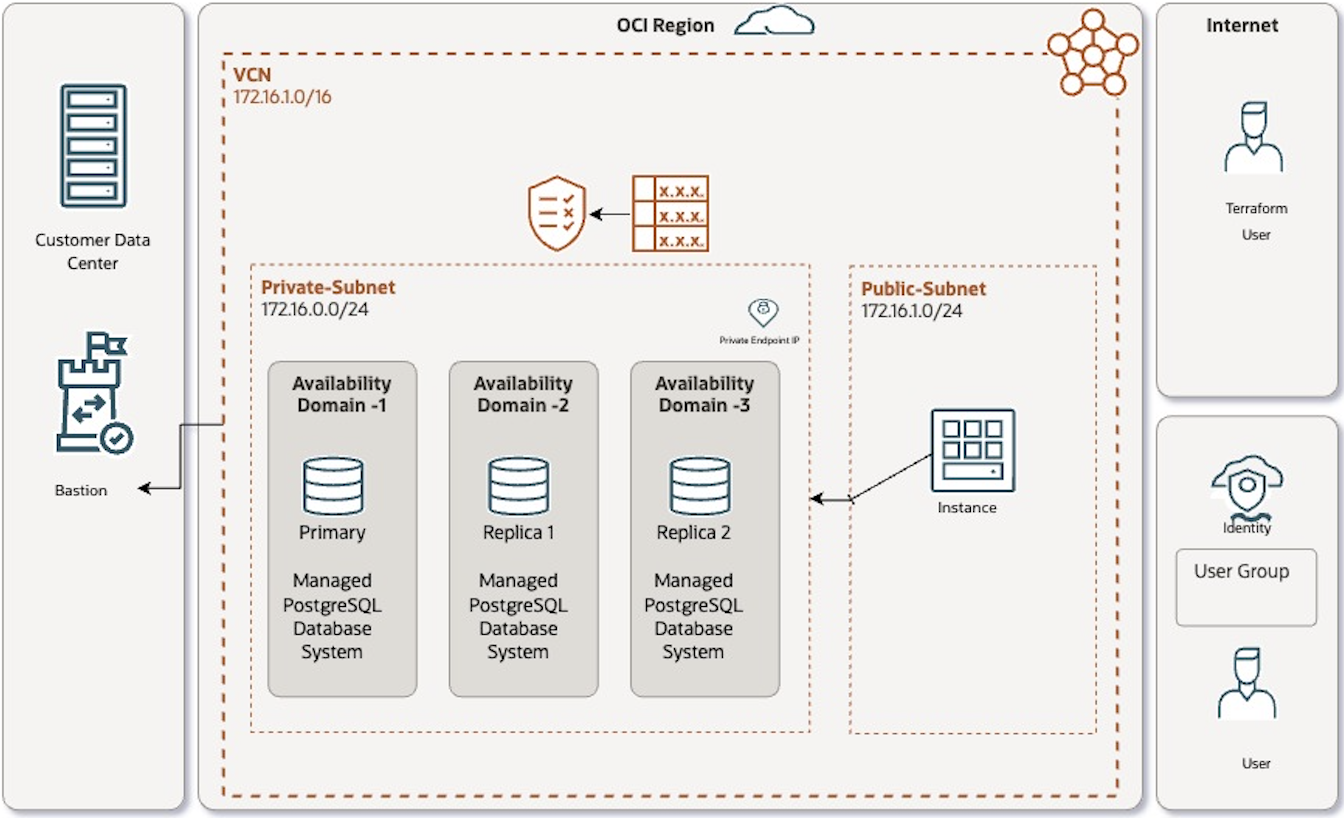
주: 선택한 영역에 단일 가용성 도메인이 있는 경우, 고가용성 데이터베이스 시스템을 생성하면 AD별 서브넷이든 지역별 서브넷이든 관계없이, 모든 PostgreSQL 인스턴스가 영역의 모든 결함 도메인에 분산됩니다.
필요 조건
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure 테넌시.
-
사용자 생성, 사용자 그룹에 사용자 추가, 보안 정책 생성 권한이 있는 사용자 계정입니다.
-
사용자에게 OCI IAM 권한이 있어야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 PostgreSQL 정책이 포함된 OCI 데이터베이스를 참조하십시오.
작업 1: 폴더에 Terraform 스크립트 파일 생성
-
providers.tf스크립트를 만듭니다.먼저
providers.tf파일을 만듭니다. 로컬 폴더를 생성하고 생성된 파일에 아래 코드를 복사합니다. tenancy_id, user_id, region 등의 값은 이후 단계에서 생성할variables.tf파일에서 바뀝니다. OCI 구성 값을 가져오려면 사용자 설정에 액세스하여 OCI에서 API 키를 생성하고, API 키 쌍을 생성하고, 전용 키를 안전하게 다운로드한 후, 인증을 위해 Terraform 코드의 사용자 및 테넌시 OCID와 함께 사용하여 OCI 리소스를 배치합니다. 자세한 내용은 API 서명 키 생성을 참조하십시오.terraform { required_providers { oci = { source = "oracle/oci" version = "5.22.0" } } } # Provider configuration for Tenancy provider "oci" { tenancy_ocid = var.tenancy_id user_ocid = var.user_id fingerprint = var.api_fingerprint private_key_path = var.api_private_key_path region = var.region } -
vcn.tf스크립트를 만듭니다.OCI PostgreSQL 데이터베이스 시스템을 배포하고 액세스하려면 전용 및 공용 서브넷이 있는 VCN 네트워크가 필요합니다. PostgreSQL 데이터베이스는 전용 서브넷에만 배포됩니다. 다음 코드를 사용하여
vcn.tf라는 파일을 생성합니다. 이 코드는 VCN CIDR만 PostgreSQL용 포트 5432에 액세스할 수 있으며 보안 목록 내 포트 22의 SSH를 통해 컴퓨트 인스턴스에 액세스할 수 있도록 합니다. 여기서 값을 바꿀 필요가 없습니다.variables.tf파일에서 값을 바꿀 수 있습니다.resource oci_core_vcn psql_vcn_tf { #Required compartment_id = var.compartment_id #Optional cidr_block = var.vcn_cidr_block display_name = var.vcn_display_name } resource oci_core_subnet public_subnet { #Required cidr_block = var.public_subnet_cidr_block compartment_id = var.compartment_id vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id #Optional display_name = var.public_subnet_display_name route_table_id = oci_core_route_table.tf_public_route_table.id } resource oci_core_subnet private_subnet { #Required cidr_block = var.private_subnet_cidr_block compartment_id = var.compartment_id vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id display_name = var.private_subnet_display_name route_table_id = oci_core_route_table.tf_private_route_table.id prohibit_internet_ingress = true security_list_ids = [oci_core_security_list.tf_private_security_list.id] } resource oci_core_internet_gateway vcntf_igw { vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = var.internet_gateway_name } resource oci_core_nat_gateway tf_nat_gateway { vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = example-ngw # Add route tables to direct traffic through this NAT gateway } data oci_core_services test_services { } variable create_service_gateway { description = whether to create a service gateway. If set to true, creates a service gateway. default = true type = bool } data oci_core_services all_oci_services { filter { name = name values = [All .* Services In Oracle Services Network] regex = true } count = var.create_service_gateway == true ? 1 : 0 } resource oci_core_service_gateway service_gateway { compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = var.service_gateway_displayname services { service_id = lookup(data.oci_core_services.all_oci_services[0].services[0], id) } vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id count = var.create_service_gateway == true ? 1 : 0 } resource oci_core_security_list tf_public_security_list { vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = var.public_subnet_security_list_display_name ingress_security_rules { protocol = 6 # TCP protocol for SSH source = 0.0.0.0/0 # Allow inbound traffic from all sources tcp_options { #Optional max = 22 min = 22 } description = Allow SSH from all sources } } resource oci_core_security_list tf_private_security_list { vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = var.private_subnet_security_list_disply_name ingress_security_rules { protocol = 6 # TCP protocol to connect Postgress service from compute instance in public subnet source = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.cidr_block # Allow inbound traffic from CIDR Block of VCN sources tcp_options { #Optional max = 5432 min = 5432 } description = Allow psql service connections from all ranges cidr vcn } } resource oci_core_route_table tf_public_route_table { vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = var.public_subnet_route_table_display_name route_rules { // Define route rules for public subnet network_entity_id = oci_core_internet_gateway.vcntf_igw.id destination = 0.0.0.0/0 destination_type = CIDR_BLOCK } } resource oci_core_route_table tf_private_route_table { vcn_id = oci_core_vcn.psql_vcn_tf.id compartment_id = var.compartment_id display_name = var.private_subnet_route_table_display_name route_rules { // Define route rules for private subnet network_entity_id = oci_core_nat_gateway.tf_nat_gateway.id destination = 0.0.0.0/0 destination_type = CIDR_BLOCK } route_rules { network_entity_id = oci_core_service_gateway.service_gateway.0.id destination = all-iad-services-in-oracle-services-network destination_type = SERVICE_CIDR_BLOCK } } resource oci_core_route_table_attachment public_route_table_attachment { #Required subnet_id = oci_core_subnet.public_subnet.id route_table_id =oci_core_route_table.tf_public_route_table.id } resource oci_core_route_table_attachment private_route_table_attachment { #Required subnet_id = oci_core_subnet.private_subnet.id route_table_id =oci_core_route_table.tf_private_route_table.id depends_on = [oci_core_service_gateway.service_gateway] } -
instance.tf스크립트를 만듭니다.PostgreSQL 데이터베이스에 액세스하려면 공용 서브넷에 컴퓨트 인스턴스가 필요합니다. 인스턴스에 접속한 다음 PostgreSQL에 액세스합니다. 전용 서브넷을 통해서만 액세스할 수 있기 때문입니다. 이렇게 하려면 다음 코드를 사용하여
instance.tf라는 파일을 만듭니다. 나중에variables.tf파일에서 컴퓨트 변수 값을 쉽게 업데이트할 수 있습니다.# Resources data "oci_identity_availability_domains" "ads" { compartment_id = var.compartment_id } resource "oci_core_instance" "tf_compute" { # Required availability_domain = data.oci_identity_availability_domains.ads.availability_domains[0].name compartment_id = var.compartment_id shape = var.compute_shape source_details { source_id = var.source_operating_system_image_id source_type = "image" } display_name = var.compute_instance_display_name shape_config { ocpus = var.compute_cpus memory_in_gbs = var.compute_memory_in_gbs } create_vnic_details { subnet_id = oci_core_subnet.public_subnet.id assign_public_ip = true } metadata = { ssh_authorized_keys = file(var.compute_ssh_authorized_keys) } preserve_boot_volume = false provisioner "remote-exec" { inline = [ "sudo dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm", "sudo dnf -qy module disable postgresql", "sudo dnf install -y postgresql16-server", "sudo /usr/pgsql-16/bin/postgresql-16-setup initdb", "sudo systemctl enable postgresql-16", "sudo systemctl start postgresql-16" ] connection { type = "ssh" host = self.public_ip user = "opc" private_key = file(var.api_private_key_for_ssh) } } } # Outputs output "compute_id" { value = oci_core_instance.tf_compute.id } output "compute_state" { value = oci_core_instance.tf_compute.state } output "compute_public_ip" { value = oci_core_instance.tf_compute.public_ip } -
postgresql.tf스크립트를 만듭니다.postgresql.tf라는 파일에 Terraform 코드를 추가하여 OCI PostgreSQL 데이터베이스 시스템을 설정해 보겠습니다. 이 코드는 구성, 코어 및 노드를 포함하여 시스템 구성에 대해 자세히 설명합니다. 최적화된 설정의 경우 3노드 데이터베이스 시스템(기본 노드 1개와 가용성 영역 2개)을 고려합니다. 먼저postgresql.tf파일을 생성하고 제공된 코드를 삽입합니다.variables.tf파일에 PostgreSQL 데이터베이스의 변수 값을 쉽게 추가하여 특정 요구사항을 충족할 수 있습니다.resource "oci_psql_db_system" "test_db_system" { #Required compartment_id = var.compartment_id db_version = var.db_system_db_version display_name = var.db_system_display_name network_details { #Required subnet_id = oci_core_subnet.private_subnet.id } shape = var.db_system_shape storage_details { #Required is_regionally_durable = var.db_system_storage_details_is_regionally_durable system_type = var.db_system_storage_details_system_type #Optional # availability_domain = var.db_system_storage_details_availability_domain # iops = var.db_system_storage_details_iops } credentials { #Required password_details { #Required password_type = var.db_system_credentials_password_details_password_type #Optional password = var.db_system_credentials_password_details_password } username = var.db_system_credentials_username } instance_count = var.db_system_instance_count instance_memory_size_in_gbs = var.db_system_instance_memory_size_in_gbs instance_ocpu_count = var.db_system_instance_ocpu_count } -
variables.tf스크립트를 만듭니다.이 섹션에서는 사용자가 OCI 테넌시 내에 생성할 리소스의 값을 조정하고 업데이트해야 합니다.
variables.tf파일을 생성하고 다음 코드를 추가합니다. 이 파일은 동일한 폴더에 생성되는 최종 파일입니다. 요구 사항에 따라 각 변수를 주의 깊게 검토하고 수정합니다. 일부 값은 각 코드의 '값' 섹션에 미리 채워지고, 다른 값은 사용자의 필요에 따라 입력해야 합니다. 파일에서 모든 값이 추가되거나 수정되면 실행 단계로 진행합니다.# Provider identity parameters - Replace these values from API Key Values from OCI User variable "api_fingerprint" { description = "Fingerprint of OCI API private key for Requestor Tenancy" type = string default = "" } variable "api_private_key_path" { description = "Path to OCI API private key used for Requestor Tenancy" type = string default = "" } variable "tenancy_id" { description = "Tenancy ID where to create resources for Requestor Tenancy" type = string default = "" } variable "user_id" { description = "User ID that Terraform will use to create resources for Requestor Tenancy" type = string default = "" } variable "region" { description = "OCI region where resources will be created for Requestor Tenancy" type = string default = "us-ashburn-1" # example value # check this document, if you want to use different region - https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/General/Concepts/regions.htm#About } # compartment OCID - Replace these values variable "compartment_id" { description = "Compartment ID where to create resources for Requestor Tenancy" type = string default = "" } variable "db_system_db_version" { description = "Version" type = number default = 14 } variable "db_system_display_name" { description = "postgress db service name" type = string default = "psqlfromterraform" # example value } variable "db_system_shape" { description = "shape" type = string default = "PostgreSQL.VM.Standard.E4.Flex.4.64GB" # example value #change the shape value as per your requirements } variable "db_system_instance_count" { description = "instance count" type = number default = 3 # example value } variable "db_system_instance_memory_size_in_gbs" { description = "RAM" type = number default = 64 # example value } variable "db_system_instance_ocpu_count" { description = "OCPU count" type = number default = 4 # example value } variable "db_system_storage_details_is_regionally_durable" { description = "regional" type = bool default = true } variable "db_system_credentials_password_details_password_type" { description = "type" type = string default = "PLAIN_TEXT" } variable "db_system_credentials_password_details_password" { description = "password" type = string default = "" } variable "db_system_credentials_username" { description = "username" type = string default = "admin" # example value } variable "db_system_storage_details_system_type" { description = "type" type = string default = "OCI_OPTIMIZED_STORAGE" } # OCI VCN parameters - psql instance deployed on this variable "vcn_cidr_block" { description = "vcn cidr" type = string default = "172.16.0.0/16" # example value } variable "vcn_display_name" { description = "vcn name" type = string default = "vcn-from-tf-psql" # example value } variable "public_subnet_cidr_block" { description = "subnet cidr range" type = string default = "172.16.1.0/24" # example value } variable "private_subnet_cidr_block" { description = "subnet cidr range" type = string default = "172.16.2.0/24" # example value } variable "public_subnet_display_name" { description = "public subnet name" type = string default = "public-subnet" # example value } variable "private_subnet_display_name" { description = "public subnet name" type = string default = "private-subnet" # example value } variable "internet_gateway_name" { description = "internet gateway name" type = string default = "internetgateway" # example value } variable "service_gateway_displayname" { description = "Service Gateway Display Name" type = string default = "servicegateway" # example value } variable "public_subnet_security_list_display_name" { description = "Public Subnet Security List Display Name" type = string default = "public_subnet_security_list" # example value } variable "private_subnet_security_list_display_name" { description = "Public Subnet Security List Display Name" type = string default = "public_subnet_security_list" # example value } variable "public_subnet_route_table_display_name" { description = "Public Subnet Route table Display Name" type = string default = "public_subnet_route_table" # example value } variable "private_subnet_route_table_display_name" { description = "Public Subnet Route table Display Name" type = string default = "private_subnet_route_table" # example value } # OCI Compute Instance parameters - We will use this instance to connect postgreSQL db instance variable "compute_shape" { type = string default = "VM.Standard.E4.Flex" # example value } variable "compute_cpus" { type = string default = "1" # example value } variable "compute_memory_in_gbs" { type = string default = "1" # example value } variable "compute_ssh_authorized_keys" { type = string default = "" } variable "api_private_key_for_ssh" { type = string default = "" } variable "source_operating_system_image_id" { description = "Oracle Linux 8 image ocid" type = string default = "ocid1.image.oc1.iad.aaaaaaaaszr5wpipg6qskiol3fhbitm56qdmumpbcpv6irzxuofi2nfmlhma" # example value # if you change the region , then change the default value from the region you have selected from this document -https://docs.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/images/image/998f1273-d4fd-4e16-8673-dd2517ddd724/ } variable "compute_instance_display_name" { description = "display name of the compute name" type = string default = "" }필요한 파일을 생성하고 필요한 값으로
variables.tf파일을 조정하면 폴더 구조에 다음 스크린샷에 표시된 설정이 반영됩니다.
작업 2: Terraform 스크립트 실행
터미널 또는 명령 프롬프트를 사용하여 다음 명령을 실행하여 Terraform을 초기화하고 OCI 테넌시 내에 리소스를 생성합니다. 이 명령은 Terraform을 초기화하고 OCI 테넌시에 지정된 리소스를 배치합니다.
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
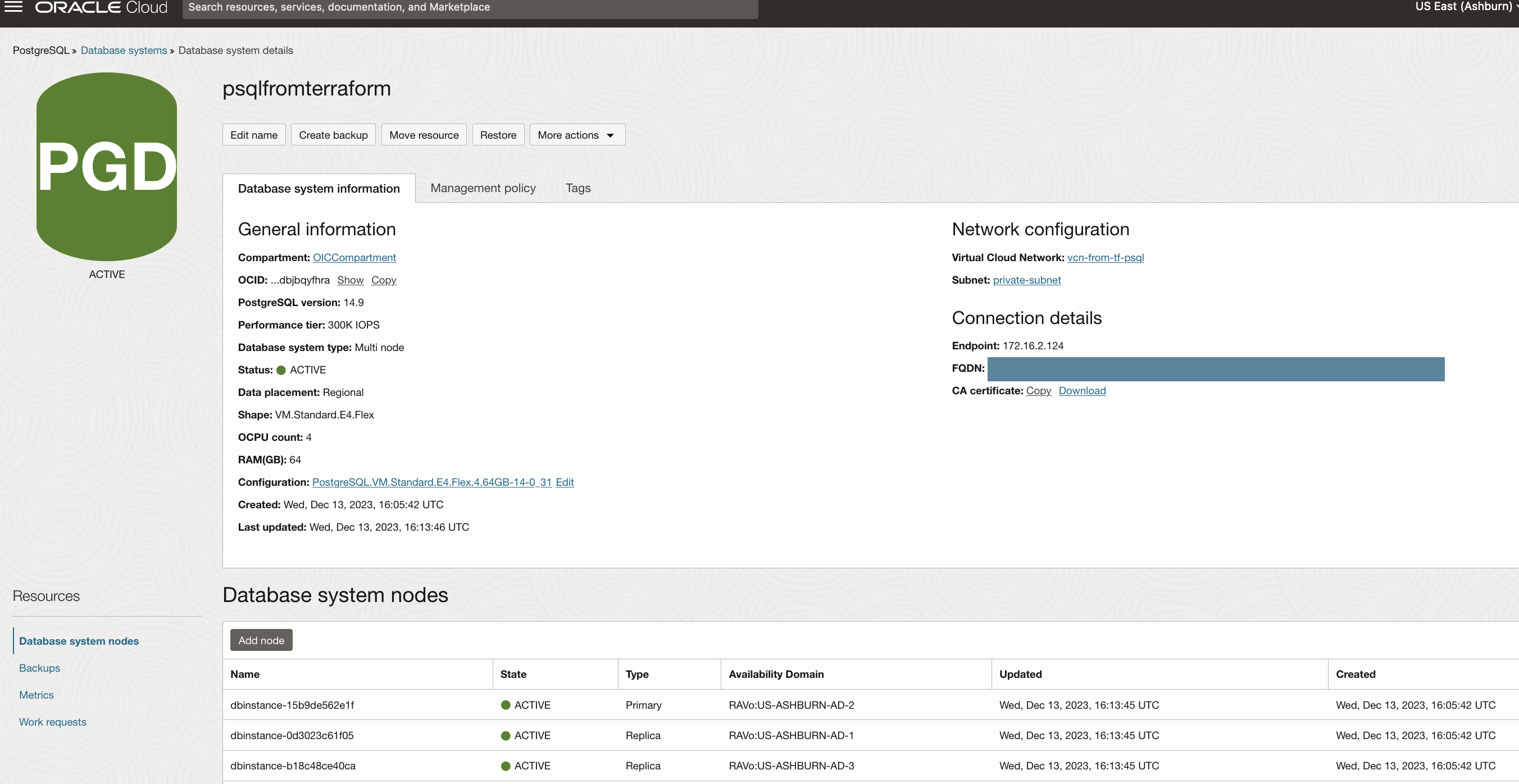
작업 3: OCI PostgreSQL 데이터베이스에 접속
완료 시 OCI 콘솔로 이동하여 OCI PostgreSQL 및 psql 클라이언트가 사전 로드된 컴퓨트 인스턴스를 찾습니다. 공용 IP를 사용하여 SSH를 통해 컴퓨트 인스턴스에 액세스한 다음 제공된 명령을 실행하여 OCI PostgreSQL 데이터베이스 시스템과의 접속을 설정합니다. SSH 포트 22 및 데이터베이스 포트 5432는 모두 vcn.tf 스크립트를 통해 자동으로 생성되므로 포트 관리에 필요한 작업이 없습니다. OCI PostgreSQL 데이터베이스 콘솔에서 가져올 수 있는 전용 끝점 IP와 variable.tf 파일에 지정한 사용자 이름 및 비밀번호를 업데이트합니다. 명령을 실행하면 연결할 암호를 묻는 메시지가 표시됩니다.
psql --version
psql -h endpoint_ip -U admin_username -d postgres
위의 다음 명령을 실행한 후 사용자는 관리되는 PostgreSQL 데이터베이스에 설정된 접속을 볼 수 있어야 합니다.

사용자가 OCI 관리 PostgreSQL 데이터베이스의 세 노드를 성공적으로 배치하고 컴퓨트 인스턴스를 사용하여 전용으로 접속했습니다.
관련 링크
확인
- 작성자 - Akarsha I K(클라우드 아키텍트)
추가 학습 자원
docs.oracle.com/learn에서 다른 실습을 살펴보거나 Oracle Learning YouTube 채널에서 더 많은 무료 학습 콘텐츠에 액세스하십시오. 또한 education.oracle.com/learning-explorer를 방문하여 Oracle Learning Explorer가 되십시오.
제품 설명서는 Oracle Help Center를 참조하십시오.
Deploy OCI Managed Database with PostgreSQL Service using Terraform
F91015-01
January 2024
Copyright © 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates.