1.7 Overview of Administration Tasks
Figure 1-3 shows the typical order of tasks that you should perform to create and manage Oracle Traffic Director instances.
Figure 1-3 Oracle Traffic Director Administration Workflow
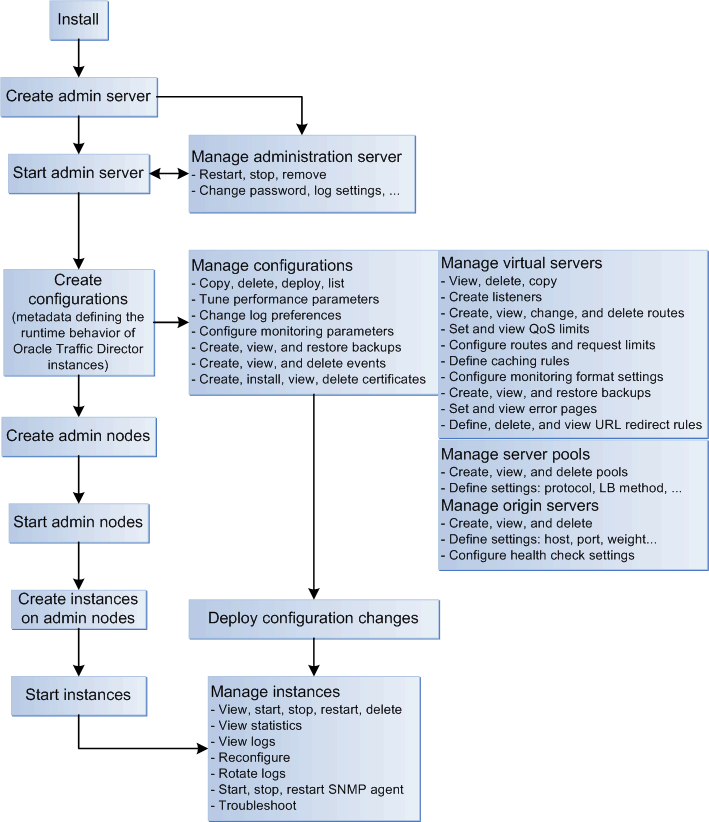
Description of ''Figure 1-3 Oracle Traffic Director Administration Workflow''
Note:
As the administrator of Oracle Traffic Director, you might perform several additional tasks such as managing security, tuning for performance, and troubleshooting problems. These tasks are not shown in the flowchart because they are not necessarily performed at definite points in a fixed sequence. All of these additional tasks are described in other chapters of this document.-
Install the product
You can install Oracle Traffic Director on Oracle Linux 5.6+ or Oracle Linux 6 on an x86_64 system, by using an interactive graphical wizard or in silent mode.
For more information, see the Oracle Traffic Director Installation Guide.
-
Create the administration server
After installing the product, you should create an administration server instance of Oracle Traffic Director. The administration server is a specially configured Oracle Traffic Director virtual server that you can use to administer Oracle Traffic Director instances.
For more information, see "Creating the Administration Server Instance" in the Oracle Traffic Director Installation Guide.
-
Manage the administration server
At times, you might want to stop the administration server and restart it, or change settings such as the administrator user name and password.
For more information, see Chapter 2, "Managing the Administration Server."
-
Access the administration console and command-line interface
You can use the administration console and command-line interface of Oracle Traffic Director to create, modify, and monitor Oracle Traffic Director instances.
For information about accessing the administration console and command-line interface, see Section 2.3, "Accessing the Administration Interfaces."
-
Create and manage administration nodes
Administration nodes are physical hosts on which you can create Oracle Traffic Director instances.
For information about managing administration nodes, see Chapter 3, "Managing Administration Nodes."
-
Create and manage configurations
After creating the administration nodes, create configurations that define your Oracle Traffic Director instances. A configuration is a collection of metadata that you can use to instantiate Oracle Traffic Director. Oracle Traffic Director reads the configuration when a server instance starts and while processing client requests.
For information about managing configurations, see Chapter 4, "Managing Configurations."
-
Create and manage instances
After creating a configuration, you can create Oracle Traffic Director server instances by deploying the configuration on one or more hosts. You can view the current state of each instance, start or stop it, reconfigure it to reflect configuration changes, and so on.
For information about managing instances, see Chapter 5, "Managing Instances."
-
Define and manage origin-server pools
For an Oracle Traffic Director instance to distribute client requests, you should define one or more origin-server pools or in the back end. For each origin-server pool, you can define the load-distribution method that Oracle Traffic Director should use to distribute requests. In addition, for each origin server in a pool, you can define how Oracle Traffic Director should control the request load.
For more information, see Chapter 6, "Managing Origin-Server Pools" and Chapter 7, "Managing Origin Servers."
-
Create and manage virtual servers and listeners
An Oracle Traffic Director instance running on a node contains one or more virtual servers. Each virtual server provides one or more listeners for receiving requests from clients. For each virtual server, you can configure parameters such as the origin-server pool to which the virtual server should route requests, the quality of service settings, request limits, caching rules, and log preferences.
For more information, see Chapter 8, "Managing Virtual Servers" and Chapter 10, "Managing Listeners."
-
Manage security
Oracle Traffic Director, by virtue of its external-facing position in a typical network, plays a critical role in protecting data and applications in the back end against attacks and unauthorized access from outside the network. In addition, the security and integrity of data traversing through Oracle Traffic Director to the rest of the network needs to be guaranteed.
For more information, see Chapter 11, "Managing Security."
-
Manage Logs
Oracle Traffic Director records data about server events such as configuration changes, instances being started and stopped, errors while processing requests, and so on in log files. You can use the logs to troubleshoot errors and to tune the system for improved performance.
For more information, see Chapter 12, "Managing Logs."
-
Monitor statistics
The state and performance of Oracle Traffic Director instances are influenced by several factors: configuration settings, volume of incoming requests, health of origin servers, nature of data passing through the instances, and so on. As the administrator, you can view metrics for all of these factors through the command-line interface and administration console, and extract the statistics in the form of XML files for detailed analysis. You can also adjust the granularity at which Oracle Traffic Director collects statistics.
For more information, see Chapter 13, "Monitoring Oracle Traffic Director Instances."
-
Set up Oracle Traffic Director instances for high availability
In the event that an Oracle Traffic Director instance or the node on which it runs fails, you need to ensure that the load-balancing service that the instance provides continues to be available uninterrupted. You can achieve this goal by configuring a backup Oracle Traffic Director instance that can take over processing of requests when the primary instance fails.
For more information, see Chapter 14, "Configuring Oracle Traffic Director for High Availability."
-
Tune for performance
Based on your analysis of performance statistics and to respond to changes in the request load profile, you might want to adjust the request processing parameters of Oracle Traffic Director to maintain or improve the performance. Oracle Traffic Director provides a range of performance-tuning controls and knobs that you can use to limit the size and volume of individual requests, control timeout settings, configure thread pool settings, SSL/TLS caching behavior, and so on.
For more information, see Chapter 15, "Tuning Oracle Traffic Director for Performance."
-
Diagnose and troubleshoot problems
Despite the best possible precautions, you might occasionally run into problems when installing, configuring, and monitoring Oracle Traffic Director instances. You can diagnose and solve some of these problems based on the information available in error messages and logs. For complex problems, you would need to gather certain data that Oracle support personnel can use to understand, reproduce, and diagnose the problem.
For more information, see Chapter 16, "Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Problems."