5 Preparing the Database for an Enterprise Deployment
This chapter describes procedures for preparing your database for an Oracle WebCenter Content enterprise deployment. The procedures include initial setup of the database, loading the metadata repository, and backing up the database.
This chapter includes the following sections:
5.1 Overview of Preparing the Database for an Enterprise Deployment
For the Oracle WebCenter Content enterprise topology, the database contains the Oracle Fusion Middleware repository, which is a collection of schemas used by various Oracle Fusion Middleware components, such as the Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle WebCenter Content components. This database is separate from the Oracle Identity Management database, which is used in the Oracle Identity Management enterprise deployment by components such as Oracle Internet Directory, DIP, and so on.
You must install the Oracle Fusion Middleware repository before you can configure the Oracle Fusion Middleware components. You install the Oracle Fusion Middleware metadata repository into an existing database using the Repository Creation Utility (RCU), which is available from the RCU distribution or from the location listed in Table 1-2. For the enterprise topology, an Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) database is highly recommended.
When you configure the Oracle SOA Suite components, the Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard will prompt you to enter the information for connecting to the database that contains the metadata repository.
5.2 Database Requirements
For the Oracle WebCenter Content reference topology, Oracle Database 11g is recommended. Table 5-1 provides a summary of the database schemas. Which database or databases you use depends on the topology that you are implementing.
Table 5-1 Mapping Between Databases and Schemas
| Database Name | Database Hosts | Service Name | Schemas in Database |
|---|---|---|---|
|
wccdb.example.com |
WCCDBHOST1 |
wccedg.example.com |
WCC_MDS |
The Oracle Metadata Services (MDS) Repository is a particular type of repository that contains metadata for some Oracle Fusion Middleware components. It can also include custom Java EE applications developed by your organization.
Before loading the metadata repository into your database, check that the database meets the requirements described in these sections:
5.2.1 Database Host Requirements
On the hosts WCCDBHOST1 and WCCDBHOST2 in the data tier, note the following requirements:
-
Oracle Clusterware
For 11g Release 1 (11.1) for Linux, see the Oracle Grid Infrastructure Installation Guide.
-
Oracle Real Application Clusters
For 11g Release 1 (11.1) for Linux, see the Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide for Linux and UNIX.
-
Automatic Storage Management (optional)
ASM gets installed for the node as a whole. It is recommended that you install it in a separate Oracle Home from the Database Oracle Home. This option comes in at runInstaller. In the Select Configuration page, select the Configure Automatic Storage Management option to create a separate ASM home.
5.2.2 Supported Database Versions
Oracle WebCenter Content requires the presence of a supported database and schemas. To check if your database is certified or to see all certified databases, refer to the "Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.x)" product area on the Oracle Fusion Middleware Supported System Configurations page:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/ias/downloads/fusion-certification-100350.html
To check the release of your database, you can query the PRODUCT_COMPONENT_VERSION view as follows:
SELECT VERSION FROM SYS.PRODUCT_COMPONENT_VERSION WHERE PRODUCT LIKE 'Oracle%';
Notes:
-
Oracle WebCenter Content requires that the database used to store its metadata (11g) supports the AL32UTF8 character set. Check the database documentation for information on choosing a character set for the database.
-
For Oracle WebCenter Content enterprise deployments, Oracle recommends using GridLink data sources to connect to Oracle RAC databases. To use the Oracle Single Client Access Name (SCAN) feature with GridLink, the Oracle RAC database version must be Oracle Database 11gR2 (11.2 or later, Enterprise Edition).
-
Oracle Database 11g is required for using Oracle Enterprise Capture because Capture uses Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS), which works only with Oracle Database for its schema.
5.2.3 Initialization Parameters
Ensure that the following initialization parameter is set to the required minimum value. It is checked by Repository Creation Utility.
Table 5-2 Required Initialization Parameters
| Configuration | Parameter | Required Value | Parameter Class |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Oracle SOA Suite |
|
400 or greater |
Static |
|
Oracle WebCenter Content |
|
100 or greater |
Static |
|
Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle WebCenter Content |
|
500 or greater |
Static |
To check the value of the initialization parameter using SQL*Plus, you can use the SHOW PARAMETER command.
As the SYS user, issue the SHOW PARAMETER command as follows:
SHOW PARAMETER processes
Set the initialization parameter using the following command:
ALTER SYSTEM SET processes=500 open_cursors=500 SCOPE=SPFILE;
Restart the database.
Note:
The method that you use to change a parameter's value depends on whether the parameter is static or dynamic, and on whether your database uses a parameter file or a server parameter file. For details on parameter files, server parameter files, and how to change a parameter value, see the Oracle Database Administrator's Guide.5.3 Creating Database Services
When multiple Oracle Fusion Middleware products are sharing the same database, each product should be configured to connect to a separate, dedicated database service. For more information about connecting to an Oracle Database using services, see "Overview of Connecting to Oracle Database Using Services and VIP Addresses" in the Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide. For complete instructions on creating and managing database services, see "Introduction to Automatic Workload Management" in the Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide.
Runtime connection load-balancing requires configuring Oracle RAC Load Balancing Advisory with service-level goals for each service for which load balancing is enabled. You can configure the Oracle RAC Load Balancing Advisory for SERVICE_TIME or THROUGHPUT. Set the connection load-balancing goal to SHORT. For Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1), use the DBMS_SERVICE package for this modification. For Oracle Database 11g Release 2 (11.2), use the Server Control Utility (SRVCTL) instead.
The Oracle WebCenter Content installation is configured to use the service wccedg.example.com.
Note:
For simplicity, the data source configuration screens in this guide use the same service name (wccedg.example.com).This section includes the following topics:
-
Section 5.3.1, "Creating Database Services for 11g Release 1 (11.1) Databases"
-
Section 5.3.2, "Creating Database Services for 11g Release 2 (11.2) Databases"
5.3.1 Creating Database Services for 11g Release 1 (11.1) Databases
You can create and modify 11g Release 1 (11.1) database services using the DBMS_SERVICE package.
To create and modify an 11.1 database service:
-
Log in to SQL*Plus, and create the service:
sqlplus "sys/password as sysdba" SQL> EXECUTE DBMS_SERVICE.CREATE_SERVICE (SERVICE_NAME => 'wccedg.example.com', NETWORK_NAME => 'wccedg.example.com' );Notes:
-
For the service name of an Oracle RAC database, use lowercase letters, followed by the domain name. For example:
wccedg.example.com -
Enter the
EXECUTE DBMS_SERVICEcommand shown on a single line.For more information about the
DBMS_SERVICEpackage, see the Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
-
-
Add the service to the database and assign it to the instances using the
srvctlcommand of SRVCTL:srvctl start service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com
-
Start the service:
srvctl start service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com
Note:
For complete instructions on creating and managing database services with SRVCTL, see "Administering Services with SRVCTL" in the Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide. -
Modify the service for the appropriate service goals, with either of these
EXECUTEcommands:SQL>EXECUTE DBMS_SERVICE.MODIFY_SERVICE (service_name => 'wccedg.example.com',goal => DBMS_SERVICE.GOAL_THROUGHPUT, clb_goal =>DBMS_SERVICE.CLB_GOAL_SHORT);
SQL>EXECUTE DBMS_SERVICE.MODIFY_SERVICE (service_name => 'wccedg.example.com', goal => DBMS_SERVICE.GOAL_SERVICE_TIME, clb_goal =>DBMS_SERVICE.CLB_GOAL_SHORT);
5.3.2 Creating Database Services for 11g Release 2 (11.2) Databases
You can create and modify 11g Release 2 (11.2) database services using the srvctl command.
To create and modify an 11.2 database service:
-
Add the service to the database and assign it to the instances using the
srvctlcommand:srvctl add service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com -r wccdb1,wccdb2 -q FALSE -m NONE -e SELECT -w 0 -z 0
Descriptions of the command-line arguments follow.
Option Argument -dUnique name of the database -sService name -rList of preferred instances, separated by commas -q AQ HA notifications ( TRUEorFALSE)-eFailover type ( NONE,SESSION, orSELECT)-mFailover method ( NONEorBASIC)-wFailover delay (integer) -zFailover retries (integer) -
Start the service with the
srvctl start servicecommand:srvctl start service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com
-
Modify the service for the appropriate service goal, with either of these
srvctl modify servicecommands:srvctl modify service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com -B SERVICE_TIME -j SHORT
srvctl modify service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com -B THROUGHPUT -j SHORT
For more information about the different service definitions, see "Load Balancing Advisory" in the Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide.
-
Validate that the service started, with the
srvctl status servicecommand:srvctl status service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com Service wccedg.example.com is running on instance(s) wccdb1,wccdb2
-
Validate that the service was created correctly, with the
srvctl config servicecommand:srvctl config service -d wccdb -s wccedg.example.com Service name: wccedg.example.com Service is enabled Server pool: wccdb_wccedg.example.com Cardinality: 2 Disconnect: false Service role: PRIMARY Management policy: AUTOMATIC DTP transaction: false AQ HA notifications: false Failover type: SELECT Failover method: NONE TAF failover retries: 0 TAF failover delay: 0 Connection Load Balancing Goal: LONG Runtime Load Balancing Goal: NONE TAF policy specification: NONE Edition: Preferred instances: wccdb1,wccdb2 Available instances:
Note:
For more information about the SRVCTL command, see "Administering Services with SRVCTL" in the Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide.5.4 Creating Database Schemas
The Repository Creation Utility (RCU) is available from the RCU distribution. The RCU used to seed the database must match the patch set level of the Oracle WebCenter Content installation. This means that if you install Oracle WebCenter Content 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.9) in this enterprise deployment, you must use RCU 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.9).
To load the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository into a database:
-
Open the Repository Creation Utility (RCU) distribution, and then start RCU from the
bin/directory in the RCU home directory:cd RCU_HOME/bin ./rcu -
On the Welcome screen (if displayed), click Next.
-
On the Create Repository screen, select Create to load component schemas into a database. Click Next.
-
On the Database Connection Details screen (Figure 5-1), enter the connect information for your database:
-
Database Type: Choose Oracle Database.
-
Host Name: Specify the name of the node on which the database resides. For the Oracle RAC database, specify the VIP name, scan address, or one of the node names as the host name; for example,
dbscan.example.com. -
Port: Specify the listen port number for the database: 1521.
-
Service Name: Specify the service name of the database (
wccedg.example.com). -
Username: Specify the name of the user with
DBAorSYSDBAprivileges:SYS. -
Password: Enter the password for the
SYSuser. -
Role: Choose the database user's role from the list: SYSDBA (required by the
SYSuser).
Click Next.
Figure 5-1 Database Connection Details Screen
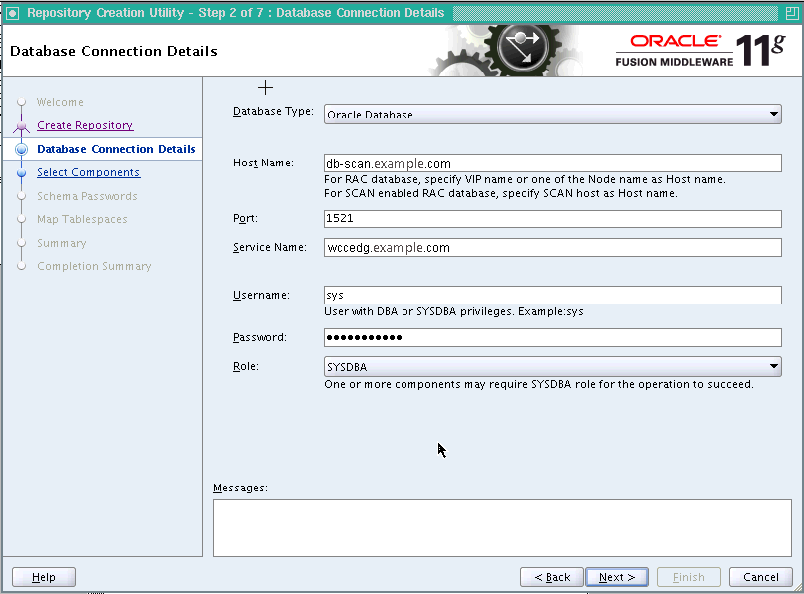
Description of "Figure 5-1 Database Connection Details Screen"
-
-
If your database is not using the UTF-8 character set, you will see a warning message indicating that there may be data loss if you are going to use the database for multilingual support. If you are not planning to use multilingual support, then you can click Ignore. Otherwise, click Stop.
-
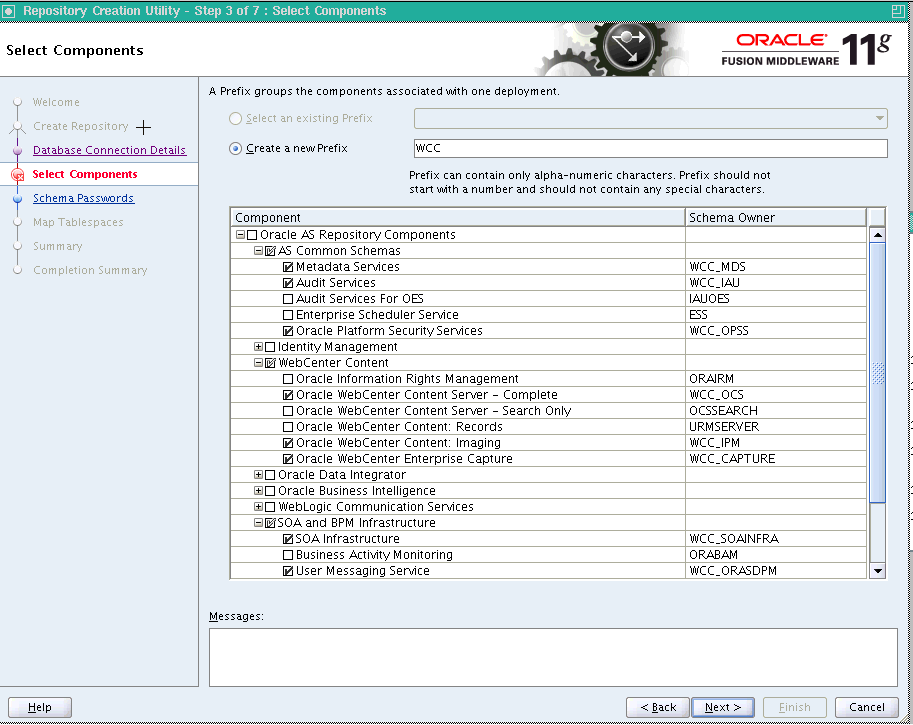
On the Select Components screen (Figure 5-2), perform the following steps:
-
Select Create a new Prefix, and enter a prefix to use for the database schemas; for example
WCC. You can specify up to six characters as a prefix. Prefixes are used to create logical groupings of multiple repositories in a database. For more information, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide.Tip:
Note the name of the schema because the upcoming steps require this information. -
Select the appropriate components from the following table for the topology you are using.
Table 5-3 shows which RCU components to select for the Oracle WebCenter Content feature sets you are using.
Table 5-3 RCU Components for an Oracle WebCenter Content Topology
Component Group RCU Components to Select Schema Names AS Common Services
Metadata Services
Audit Services
Oracle Platform Security Services
WCC_MDS
WCC_IAU
WCC_OPSS
WebCenter Content
Oracle WebCenter Content Server - Complete
Oracle WebCenter Content: Imaging
Oracle WebCenter Enterprise Capture
WCC_OCS
WCC_IPM
WCC_CAPTURE
SOA and BPM Infrastructure
SOA Infrastructure
User Messaging Service
WCC_SOAINFRA
WCC_ORASDPM
The MDS schema is necessary for the WebCenter Content user interface. This schema can be in the same database as the other schemas for the enterprise deployment reference topology. However, if WS_Policy is used in an Oracle WebCenter Content setup, which would require an MDS schema to implement the WS_Policy, then the WebCenter Content user interface requires its own MDS schema. You can create a new schema for MDS in the same database, using a different prefix.
Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) works only with Oracle Database 11g for its schema. The OPSS schema is necessary for a cluster setup (unless you are using Oracle Internet Directory and are going to reassociate the security store using it).
Either an OPSS schema or Oracle Internet Directory is necessary for a Capture cluster because the
system-jazn-data.xmlfile is not sufficient for a cluster setup. If the security store is not in either the OPSS schema in the database or Oracle Internet Directory, the nodes in a two-node cluster get out of sync because thesystem-jazn-data.xmlfile on the second node in the cluster gets overwritten. Node Manager will sync the data from the first node and overwrite the file on the second node. With the OPSS schema or Oracle Internet Directory, the application data is preserved in a shared location to which both nodes have access.If you use OPSS, a data source for it must be created manually after the domain is created.
Click Next.
-
-
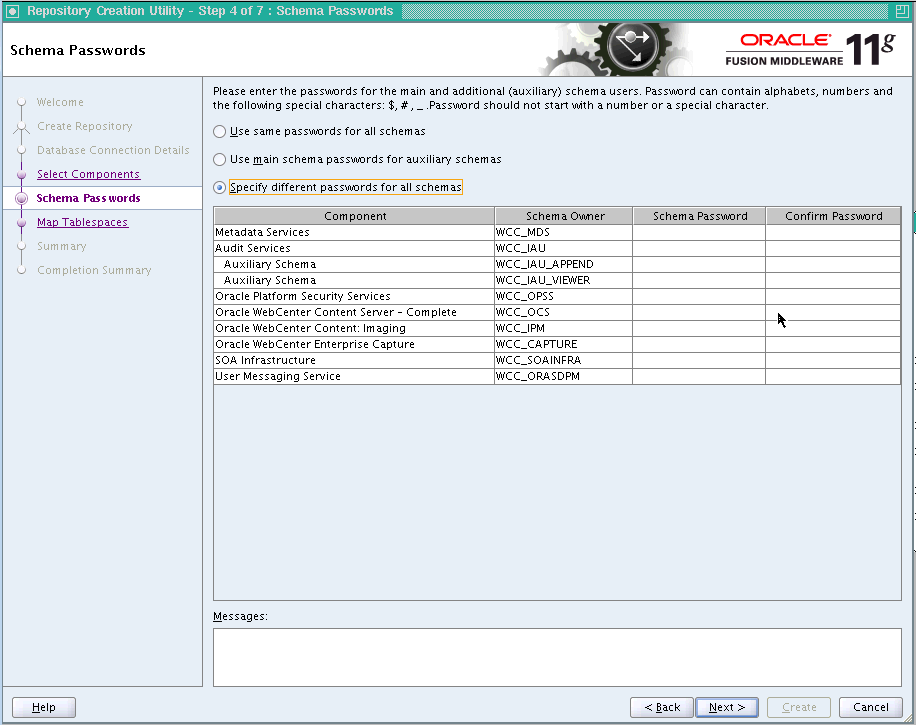
On the Schema Passwords screen (Figure 5-3), select Specify different passwords for all schemas, and click Next. On the subsequent screen refresh, enter a schema passwords for each component.
Tip:
Note the name of the schema because the upcoming steps require this information. -
On the Map Tablespaces screen, choose the tablespaces for the selected components, and click Next.
A confirmation dialog opens stating that any tablespace that does not already exist in the selected schema will be created. Click OK to acknowledge this message.
-
On the Summary screen, click Create.
-
On the Completion Summary screen, click Close.
-
Verify that the required schemas were created successfully by connecting to the database with the new user added:
ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplusLog in as the
WCC_OCSuser, and enter the password. You can perform a simple verification by querying the schema version registry:-bash-3.00$ $ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus WCC_OCS/password as SYSDBA SQL> SELECT version, status FROM schema_version_registry where owner = 'WCC_OCS'; VERSION STATUS ----------------------------------------- 11.1.1.9.0 VALID
Note:
Oracle recommends using the database used for Oracle Identity Management (see Chapter 18, "Integrating with Oracle Identity Management") to store the Oracle WSM policies. It is therefore expected that you will use the Oracle Identity Management database information for the OWSM MDS schemas, which will be different from the database information used for the rest of the Oracle SOA Suite schemas. To create the required schemas in the database, repeat the preceding steps using the Oracle Identity Management database information, but select only AS Common Schemas: Metadata Services on the Select Components screen (step 6).5.5 Backing Up the Database
After you have loaded the metadata repository into your database, you should make a backup before installing the software for your enterprise deployment.
Backing up the database is for the explicit purpose of quick recovery from any issue that may occur in the further steps. You can choose to use your backup strategy for the database for this purpose or simply make a backup using operating system tools or RMAN for this purpose. Oracle recommends that you use Oracle Recovery Manager for the database, particularly if the database was created using Oracle ASM. If possible, you can also perform a cold backup using operating system tools such as tar.