4 Preparing the File System for an Enterprise Deployment
This chapter describes how to prepare your file system for an Oracle WebCenter Portal enterprise deployment. It provides information about recommended directory structure and locations, and includes a procedure for configuring shared storage.
This chapter includes the following topics:
-
Overview of Preparing the File System for Enterprise Deployment
-
Terminology for Directories and Directory Environment Variables
4.1 Overview of Preparing the File System for Enterprise Deployment
It is important to set up your file system in a way that makes the enterprise deployment easier to understand, configure, and manage. Oracle recommends setting up your files system according to information in this chapter. The terminology defined in this chapter is used in diagrams and procedures throughout the guide.
Use this chapter as a reference to help understand the directory variables used in the installation and configuration procedures. Other directory layouts are possible and supported, but the model adopted in this guide is chosen for maximum availability, providing both the best isolation of components and symmetry in the configuration and facilitating backup and disaster recovery. The rest of the document uses this directory structure and directory terminology.
4.2 Terminology for Directories and Directory Environment Variables
This section describes the directory environment variables used throughout this guide for configuring the Oracle WebCenter Portal enterprise deployment. The following directory variables are used to describe the directories installed and configured in the guide:
-
ORACLE_BASE: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the base directory under which Oracle products are installed.
-
MW_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the location where Oracle Fusion Middleware (FMW) resides.
-
WL_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path contains installed files necessary to host a WebLogic Server.
-
ORACLE_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the location where either Oracle SOA Suite or Oracle WebCenter Portal is installed.
-
ORACLE_COMMON_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the Oracle home that contains the binary and library files required for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and Java Required Files (JRF).
-
DOMAIN Directory: This directory path refers to the location where the Oracle WebLogic Server domain information (configuration artifacts) is stored. Different Oracle WebLogic servers can use different domain directories even when in the same node, as described in the following text.
-
ORACLE_INSTANCE: An Oracle instance contains one or more system components, such as Oracle Web Cache, Oracle HTTP Server, or Oracle Internet Directory. An Oracle instance directory contains updateable files, such as configuration files, log files, and temporary files.
-
JAVA_HOME: This is the location where JRockit is installed.
Examples documented in this guide use JRockit. Any certified version of Java can be used and is fully supported unless otherwise noted.
-
ASERVER_HOME: This is the primary location of the domain configuration. A typical example is:
/u01/oracle/config/domains/domain_name -
MSERVER_HOME: This is a copy of the domain configuration used to start and stop Managed Servers. A typical example is:
/u02/private/oracle/config/domains/domain_name -
WEBGATE_ORACLE_HOME: This is the location of the WebGate installation.
Tip:
You can simplify directory navigation by using environment variables as shortcuts to the locations in this section. For example, you could use an environment variable called $ORACLE_BASE in Linux to refer to /u01/app/oracle (that is, the recommended ORACLE_BASE location). In Windows, you would use %ORACLE_BASE% and use Windows-specific commands.4.3 Recommended Locations for the Different Directories
The following sections describe some basic recommendations for using shared storage for an enterprise deployment topology:
-
Shared Storage Recommendations for Binary (Oracle Home) Directories
-
Shared Storage Recommendations for Domain Configuration Files
-
Shared Storage Recommendations for JMS File Stores and Transaction Logs
4.3.1 Shared Storage Recommendations for Binary (Oracle Home) Directories
The following sections describe guidelines for using shared storage for your Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle home directories:
4.3.1.1 About the Binary (Oracle Home) Directories
When you install any Oracle Fusion Middleware product, you install the product binaries into an Oracle home. The binary files installed in the Oracle home are read-only and remain unchanged unless the Oracle home is patched or upgraded to a newer version.
In a typical production environment, the Oracle home files are saved in a separate location from the domain configuration files, which you create using the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard.
The Middleware home for an Oracle Fusion Middleware installation contains the binaries for Oracle WebLogic Server, the Oracle Fusion Middleware infrastructure files, and any Oracle Fusion Middleware product-specific directories.
For more information about the structure and contents of an Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle home, see Concepts.
4.3.1.2 About Sharing a Single Oracle Home for Multiple Domains
Oracle Fusion Middleware enables you to configure multiple Oracle WebLogic Server domains from a single Oracle home. This allows you to install the Oracle home in a single location on a shared volume and reuse the Oracle home for multiple hosts installations.
Note:
The domain directories of the Managed Servers can reside in local or shared storage, except that the Oracle WebCenter Content and Oracle WebCenter Content: Inbound Refinery Managed Servers cannot reside in shared storage. These Managed Servers use node-specific files, such asintradoc.cfg.When an Oracle home is shared by multiple servers on different hosts, there are some best practices to keep in mind. In particular, be sure that the Oracle Inventory (oraInventory) on each host is updated for consistency and for the application of patches.
To update the oraInventory for a host and attach an Oracle home on shared storage, use the following command:
ORACLE_HOME/oui/bin/attachHome.sh
For more information about oraInventory, see the "Oracle Universal Installer Inventory" section in the Oracle Universal Installer and OPatch User's Guide for Windows and UNIX.
4.3.1.3 About Using Redundant Binary (Oracle Home) Directories
For maximum availability, Oracle recommends using redundant binary installations on shared storage.
In this model, you install two identical Oracle homes for your Oracle Fusion Middleware software on two different shared volumes. You then mount one of the Oracle homes to one set of servers, and the other Oracle home to the remaining servers. Each Oracle home has the same mount point, so the Oracle home always has the same path, regardless of which Oracle home the server is using.
Should one Oracle home become corrupted or unavailable, only half your servers are affected. For additional protection, Oracle recommends that you disk mirror these volumes.
If separate volumes are not available on shared storage, Oracle recommends simulating separate volumes using different directories within the same volume and mounting these to the same mount location on the host side. Although this does not guarantee the protection that multiple volumes provide, it does allow protection from user deletions and individual file corruption.
4.3.2 Shared Storage Recommendations for Domain Configuration Files
The following sections describe guidelines for using shared storage for the Oracle WebLogic Server domain configuration files you create when you configure your Oracle Fusion Middleware products in an enterprise deployment:
-
About Oracle WebLogic Server Administration and Managed Server Domain Configuration Files
-
Shared Storage Requirements for Administration and Managed Server Domain Configuration Files
4.3.2.1 About Oracle WebLogic Server Administration and Managed Server Domain Configuration Files
When you configure an Oracle Fusion Middleware product, you create or extend an Oracle WebLogic Server domain. Each Oracle WebLogic Server domain consists of a single Administration Server and one or more Managed Servers.
For more information about Oracle WebLogic Server domains, see Understanding Domain Configuration for Oracle WebLogic Server.
In an enterprise deployment, it is important to understand that the Managed Servers in a domain can be configured for active-active high availability. However, the Administration server cannot. The Administration Server is a singleton service. That is, it can be active on only one host at any given time.
4.3.2.2 Shared Storage Requirements for Administration and Managed Server Domain Configuration Files
Oracle recommends creating two copies of the domain configuration files:
-
One copy is for the Administration Server configuration files.
You install this directory on shared storage and mount it exclusively to the host that is running the Administration Server.
In the event of the failure of that host, you can mount the directory on a different host and the Administration Server started on that host.
-
The other copy is for the Managed Server configuration files.
The Managed Servers' domain directories can reside in local or shared storage.
Sharing domain directories for Managed Servers facilitates the scale-out procedures. However, sharing the Managed Server configuration files can also have a potential performance impact.
As a result, the deployment you decide upon should conform to the requirements (if any) of the storage system. Some storage systems offer configuration options to facilitate multiple machines mounting the same shared volume.
The configuration steps provided for this enterprise deployment topology assume that a local domain directory for each node is used for each Managed Server.
4.3.3 Shared Storage Recommendations for JMS File Stores and Transaction Logs
JMS file stores and JTA transaction logs must be placed on a shared storage to ensure that they are available from multiple hosts for recovery in the case of a server failure or migration.
For more information about saving JMS and JTA information in a file store, see the "Using the WebLogic Persistent Store" section in Configuring Server Environments for Oracle WebLogic Server.
4.3.4 Recommended Directory Locations
This section describes the directories recommended. Wherever a shared storage location is directly specified, it is implied that shared storage is required for that directory. When using local disk or shared storage is optional the mount specification is qualified with "if using a shared disk." The shared storage locations are examples and can be changed as long as the provided mount points are used. However, Oracle recommends this structure in the shared storage device for consistency and simplicity.
ORACLE_BASE:
Recommended directory: /u01/app/oracle
Domain Directory for Administration Server Domain Directory:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name (The last domain_name directory is added by Configuration Wizard.)
-
Mount point on machine:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver -
Shared storage location:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver -
Mounted from: Only the node where the Administration Server is running needs to mount this directory. When the Administration Server is relocated (failed over) to a different node, the node then mounts the same shared storage location on the same mount point. The remaining nodes in the topology do not need to mount this location
Domain Directory for Managed Server Domain Directory:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name
-
If you are using a shared disk, the mount point on the machine is ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver mounted to ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/Noden/mserver/ (each node uses a different domain directory for Managed Servers).
Note:
This procedure is really shared storage dependent. The above example is specific to NAS, but other storage types may provide this redundancy with different types of mappings.Location for JMS file-based stores and Tlogs (SOA only):
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/jms
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs
-
Mount point: ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/
-
Shared storage location: ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/
-
Mounted from: All nodes running Oracle SOA Suite must mount this shared storage location so that transaction logs and JMS stores are available when server migration to another node take place.
Location for Application Directory for the Administration Server
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/applications
-
Mount point: ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/
-
Shared storage location: ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver
-
Mounted from: Only the node where the Administration Server is running must mount this directory. When the Administration Server is relocated (failed over) to a different node, the node then mounts the same shared storage location on the same mount point. The remaining nodes in the topology do not need to mount this location
Location for Applications Directory for Managed Server
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/applications
Note:
This directory is local in the context of a WebCenter Portal enterprise deployment.MW_HOME (application tier)
Recommended directory: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
-
Mount point: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
-
Shared storage location: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw (VOL1 and VOL2)
Note:
When there is just one volume available in the shared storage, you can provide redundancy using different directories to protect from accidental file deletions and for patching purposes. Two MW_HOMEs would be available; at least one at ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw1, and another at ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw2. These MW_HOMEs are mounted on the same mount point in all nodes. -
Mounted from: Nodes alternatively mount VOL1 or VOL2 so that at least half of the nodes use one installation, and half use the other.
In a WebCenter Portal enterprise deployment topology, SOAHOST1 and WCPHOST1 mounts
VOL1and SOAHOST2 and WCPHOST2 mountsVOL2. When only one volume is available, nodes mount the two suggested directories in shared storage alternately. For example, SOAHOST1 would use ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw1 as a shared storage location, and SOAHOST2 would use ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw2 as a shared storage location).
ORACLE_HOME (web tier):
Recommended directory: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/web
-
Mount point: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
-
Shared storage location: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw (
VOL1andVOL2)Note:
Web tier installation is typically performed on local storage to the WEBHOST nodes. When using shared storage, consider the appropriate security restrictions for access to the storage device across tiers.This enterprise deployment guide assumes that the Oracle web tier will be installed onto local disk. You may install the Oracle Web Tier binaries (and the ORACLE_INSTANCE) onto shared disk. If so, the shared disk MUST be separate from the shared disk used for the application tier.
-
Mounted from: For Shared Storage installations, nodes alternatively mount
VOL1orVOL2so that at least half of the nodes use one installation, and half use the other.In a WebCenter Portal enterprise deployment topology, WEBHOST1 mounts
VOL1and WEBHOST2 mountsVOL2. When only one volume is available, nodes mount the two suggested directories in shared storage alternately. For example, WEBHOST1 would useORACLE_BASE/product/fmw1as a shared storage location, and WEBHOST2 would useORACLE_BASE/product/fmw2as a shared storage location).
WL_HOME:
Recommended directory: MW_HOME/wlserver_10.3
ORACLE_HOME:
Recommended directories
-
MW_HOME/wc(Oracle home for WebCenter Portal) -
MW_HOME/soa(Oracle home for SOA Suite) -
MW_HOME/wcc(Oracle home for Oracle WebCenter Content)
ORACLE_COMMON_HOME:
Recommended directory: MW_HOME/oracle_common
ORACLE_INSTANCE (OHS instance):
Recommended directory: ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name
-
If you are using a shared disk, the mount point on the machine follows:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name
Mounted to:
ORACLE_BASE/admin/instance_name (VOL1)
Note:
(VOL1)is optional; you could also use(VOL2).
4.3.5 Directory Structure and Configurations
This section provides diagrams and to help illustrate the recommended directory structure and shared storage.
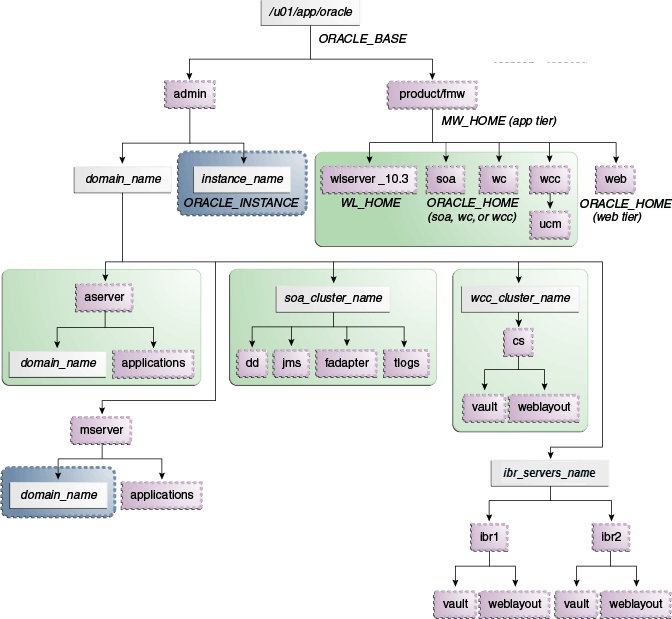
Figure 4-1 shows this directory structure in a diagram.
The directory structure in Figure 4-1 does not show other required internal directories, such as oracle_common and jrockit.
Table 4-1 explains what the various color-coded elements in the diagram mean.
Table 4-1 Directory Structure Elements
| Element | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
|
The Administration Server domain directories, applications, deployment plans, file adapter control directory, JMS and TX logs, and the entire MW_HOME are on a shared disk. |
|
|
The Managed Server domain directories can be on a local disk or a shared disk. Further, if you want to share the Managed Server domain directories on multiple nodes, then you must mount the same shared disk location across the nodes. The |
|
|
Fixed name. |
|
|
Installation-dependent name. |
Figure 4-2 shows an example configuration for shared storage with multiple volumes for WebCenter Portal. The example shows SOAHOST1 and SOAHOST2. In addition, Managed Server directories on WCPHOST1 and WCPHOST2 appear on VOL1 and VOL2 as shown.
Figure 4-2 Example Configuration for Shared Storage
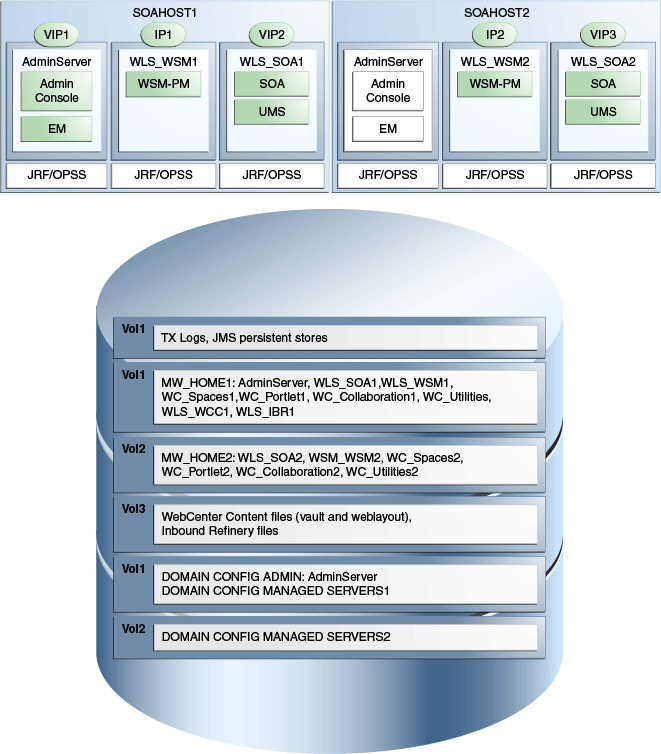
Description of "Figure 4-2 Example Configuration for Shared Storage"
Table 4-2 summarizes the directory structure for the domain. In the table:
-
WLS_WCP refers to all the WebCenter Portal Managed Servers: WC_Spaces, WC_Portlet, WC_Utilities, WC_Collaboration
-
WLS_WCC refers to a WebCenter Content Managed Server.
-
WLS_IBR refers to an Inbound Refinery Managed Server.
Table 4-2 Content of Shared Storage
| Server | Type of Data | Volume in Shared Storage | Directory | Files |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WLS_SOA1 |
Tx Logs |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs |
The transaction directory is common (decided by WebLogic Server), but the files are separate. |
|
WLS_SOA2 |
Tx Logs |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs |
The transaction directory is common (decided by WebLogic Server), but the files are separate. |
|
WLS_SOA1 |
JMS Stores |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/jms |
The transaction directory is common (decided by WebLogic Server), but the files are separate; for example: SOAJMSStore1, UMSJMSStore1, and so on. |
|
WLS_SOA2 |
JMS Stores |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/jms |
The transaction directory is common (decided by WebLogic Server), but the files are separate; for example: SOAJMSStore2, UMSJMSStore2, etc. |
|
WLS_SOA1 |
WLS Install |
VOL1 |
MW_HOME |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_SOA2 |
WLS Install |
VOL2 |
MW_HOME |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCP1 |
WLS Install |
VOL1 |
MW_HOME |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCP2 |
WLS Install |
VOL2 |
MW_HOME |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_SOA1 |
SOA Install |
VOL1 |
MW_HOME/soa |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_SOA2 |
SOA Install |
VOL2 |
MW_HOME/soa |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCP1 |
WebCenter Portal Install |
VOL1 |
MW_HOME/wc |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCP2 |
WebCenter Portal Install |
VOL2 |
MW_HOME/wc |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCC1 |
WebCenter Content Install |
VOL1 |
MW_HOME/wcc |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCC2 |
WebCenter Content Install |
VOL2 |
MW_HOME/wcc |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_SOA1 |
Domain Config |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/aserver/domain_name |
Used by only one Server where the Administration server is running. |
|
WLS_SOA1 |
Domain Config |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_SOA2 |
Domain Config |
VOL2 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCP1 |
Domain Config |
VOL1 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCP2 |
Domain Config |
VOL2 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/mserver/domain_name |
Individual in each volume, but both servers see same directory structure. |
|
WLS_WCC1 |
Web and Vault Files |
VOL3 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/wcc_cluster_name/cs/vault |
Directory for |
|
WLS_WCC1 |
Web and Vault Files |
VOL3 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/wcc_cluster_name/cs/weblayout |
Directory for |
|
WLS_WCC2 |
Web and Vault Files |
VOL3 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/wcc_cluster_name/cs/vault |
Directory for |
|
WLS_WCC2 |
Web and Vault Files |
VOL3 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/wcc_cluster_name/cs/weblayout |
Directory for |
|
WLS_IBR1 |
Inbound Refinery Files |
VOL3 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/ibr_servers_name/ibr1 |
Directory for Inbound Refinery files on a separate volume with locking disabled. |
|
WLS_IBR2 |
Inbound Refinery Files |
VOL3 |
ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/ibr_servers_name/ibr2 |
Directory for Inbound Refinery files on a separate volume with locking disabled. |
Note:
VOL3 is mounted as an NFS nolock volume. For details, see Section 4.4, "Configuring Shared Storage".4.4 Configuring Shared Storage
Use the following commands to create and mount shared storage locations so that SOAHOST1, SOAHOST2, WCPHOST1, and WCPHOST2 can see the same location for binary installation in two separate volumes.
Note:
The user ID used to create a shared storage file system owns and has read, write, and execute privileges for those files. Other users in the operating system group can read and execute the files, but they do not have write privileges. For more information about installation and configuration privileges, see the "Understanding Installation and Configuration Privileges and Users" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide.In the commands, nasfiler is the shared storage filer.
From SOAHOST1 and WCPHOST1:
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol1/ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw -t nfs
From SOAHOST2 and WCPHOST2:
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol2/ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw -t nfs
Note:
If only one volume is available, you can provide redundancy for the binaries by using two different directories in the shared storage and mounting them to the same directory in the SOA Servers:
From SOAHOST1:
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol1/ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw1 ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw -t nfs
From SOAHOST2:
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol1/ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw2 ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw -t nfs
The following commands show how to share the SOA transaction logs location across different nodes:
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol1/ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs -t nfs mount nasfiler:/vol/vol1/ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/soa_cluster_name/tlogs -t nfs
From WCPHOST1 and WCPHOST2:
The following commands show how to share WebCenter Content and Inbound Refinery files across different nodes:
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol3/ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/wcc_cluster_name ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/wcc_cluster_name -t nfs -o rw,bg,hard,vers=3,nolock,noac mount nasfiler:/vol/vol3/ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/ibr_servers_name/ ORACLE_BASE/admin/domain_name/ibr_servers_name -t nfs -o rw,bg,hard,vers=3,nolock,noac
And likewise for WCPHOST2.
Notes:
-
The
nolockoption is recommended here because WebCenter Content manages its own locking, and the default locking functions may interfere with the WebCenter Content lock management. -
The
noacoption is also recommended for file systems where there is frequent access to the same files from different machines.
Validating the Shared Storage Configuration
Ensure that you can read and write files to the newly mounted directories by creating a test file in the shared storage location you just configured.
For example:
$ cd newly mounted directory
$ touch testfile
Verify that the owner and permissions are correct:
$ ls -l testfile
Then remove the file:
$ rm testfile
Note:
The shared storage can be a NAS or SAN device. The following illustrates an example of creating storage for a NAS device from SOAHOST1. The options may differ depending on the specific storage device.
mount nasfiler:/vol/vol1/fmw11shared ORACLE_BASE/wls -t nfs -o rw,bg,hard,nointr,tcp,vers=3,timeo=300,rsize=32768, wsize=32768
Contact your storage vendor and machine administrator for the correct options for your environment.