7 Creating and Using Packages
This chapter gives an introduction to Packages and Steps. It also passes through the creating process of a Package and provides additional information about handling steps within a Package.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Introduction to Packages
The Package is a large unit of execution in Oracle Data Integrator. A Package is made up of a sequence of steps organized into an execution diagram.
Each step can either succeed or fail its execution. Depending on the execution result (success or failure), a step can branch to another step.
Introduction to Steps
Table 7-1 lists the different types of steps. References are made to sections that provide additional details
| Type | Description | See Section |
|---|---|---|
|
Flow (Mapping) |
Executes a Mapping. |
|
|
Procedure |
Executes a Procedure. |
|
|
Variable |
Declares, sets, refreshes or evaluates the value of a variable. |
|
|
Oracle Data Integrator Tools |
These tools, available in the Toolbox, provide access to all Oracle Data Integrator API commands, or perform operating system calls. |
|
|
Models, Sub-models, and Datastores |
Performs journalizing, static check or reverse-engineering operations on these objects |
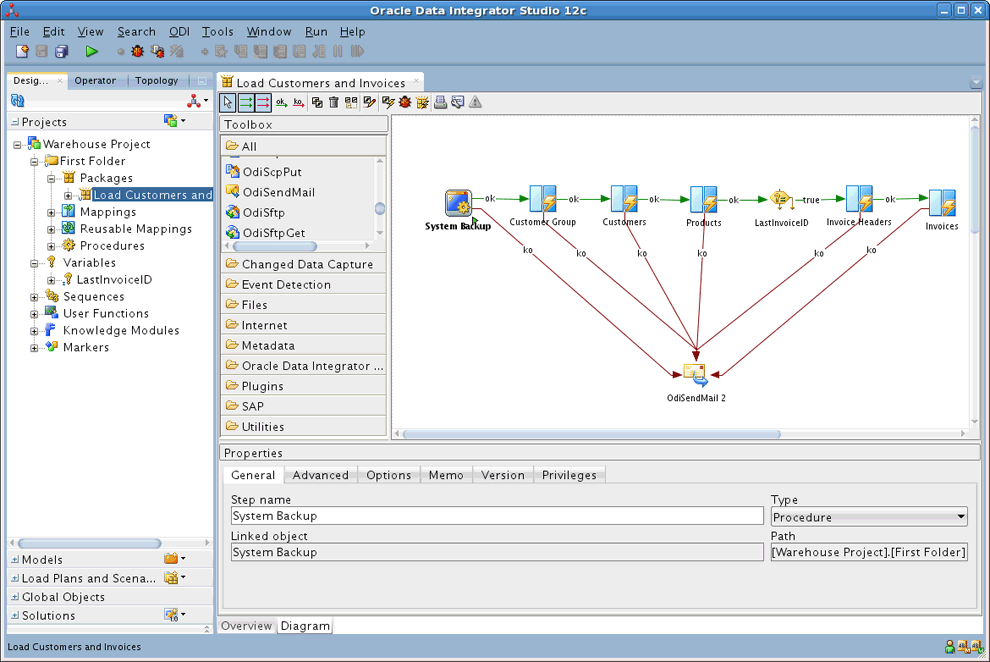
For example, the "Load Customers and Invoice" Package example shown in Figure 7-1 performs the following actions:
-
Execute procedure "System Backup" that runs some backup operations.
-
Execute mapping "Customer Group" that loads the customer group datastore.
-
Execute mapping "Customer" that loads the customer datastore.
-
Execute mapping "Product" that loads the product datastore.
-
Refresh variable "Last Invoice ID" step to set the value of this variable for use later in the Package.
-
Execute mapping "Invoice Headers" that load the invoice header datastore.
-
Execute mapping "Invoices" that load the invoices datastore.
-
If any of the steps above fails, then the Package runs the "OdiSendMail 2" step that sends an email to the administrator using an Oracle Data Integrator tool.
Introduction to Creating Packages
Packages are created in the Package Diagram Editor. See "Introduction to the Package editor" for more information.
Creating a Package consists of the following main steps:
-
Creating a New Package. See "Creating a new Package" for more information.
-
Working with Steps in the Package (add, duplicate, delete, and so on). See "Working with Steps" for more information.
-
Defining Step Sequences. See "Defining the Sequence of Steps" for more information.
-
Running the Package. See "Running a Package" for more information.
Introduction to the Package editor
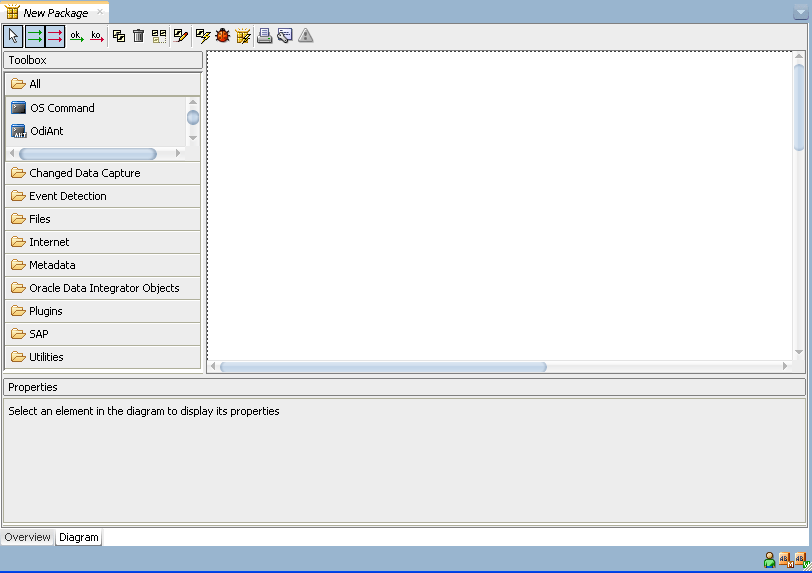
The Package editor provides a single environment for designing Packages. Figure 7-2 gives an overview of the Package editor.
Table 7-2 Package editor Sections
| Section | Location in Figure | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Package Diagram |
Middle |
You drag components such as mappings, procedures, datastores, models, sub-models or variables from the Designer Navigator into the Package Diagram for creating steps for these components. You can also define sequence of steps and organize steps in this diagram. |
|
Package Toolbox |
Left side of the Package diagram |
The Toolbox shows the list of Oracle Data Integrator tools available and that can be added to a Package. These tools are grouped by type. |
|
Package Toolbar |
Top of the Package diagram |
The Package Toolbar provides tools for organizing and sequencing the steps in the Package. |
|
Properties Panel |
Under the Package diagram |
This panel displays the properties for the object that is selected in the Package Diagram. |
Creating a new Package
To create a new Package:
-
In the Project tree in Designer Navigator, click the Packages node in the folder where you want to create the Package.
-
Right-click and select New Package.
-
In the New Package dialog, type in the Name, and optionally a Description, of the Package. Click OK.
-
Use the Overview tab to set properties for the package.
-
Use the Diagram tab to design your package, adding steps as described in "Working with Steps".
-
From the File menu, click Save.
Working with Steps
Packages are an organized sequence of steps. Designing a Package consists mainly in working with the steps of this Package.
Adding a Step
Adding a step depends on the nature of the steps being inserted. See Table 7-1, "Step Types" for more information on the different types of steps. The procedures for adding the different type of steps are given below.
Adding a Mapping step
To insert a Mapping step:
-
Open the Package editor and go to the Diagram tab.
-
In the Designer Navigator, expand the project node and then expand the Mappings node, to show your mappings for this project.
-
Drag and drop a mapping into the diagram. A Flow (Mapping) step icon appears in the diagram.
-
Click the step icon in the diagram. The properties panel shows the mapping's properties.
-
In the properties panel, modify properties of the mapping as needed.
-
From the File menu, click Save.
Adding a Procedure step
To insert a Procedure step:
-
Open the Package editor and go to the Diagram tab.
-
In the Designer Navigator, expand the project node and then expand the Procedures node, to show your procedures for this project.
-
Drag and drop a procedure into the diagram. A Procedure step icon appears in the diagram.
-
Click the step icon in the diagram. The properties panel shows the procedure's properties.
-
In the properties panel, modify properties of the procedure as needed.
-
From the File menu, click Save.
Variable Steps
There are different variable step types within Oracle Data Integrator:
-
Declare Variable: When a variable is used in a Package (or in elements of the topology which are used in the Package), Oracle strongly recommends that you insert a Declare Variable step in the Package. This step explicitly declares the variable in the Package.
-
Refresh Variable: This variable step refreshes the variable by running the query specified in the variable definition.
-
Set Variable: There are two functions for this step:
-
Assign sets the current value of a variable.
-
Increment increases or decreases a numeric value by the specified amount.
-
-
Evaluate Variable: This variable step type compares the value of the variable with a given value according to an operator. If the condition is met, then the evaluation step is true, otherwise it is false. This step allows for branching in Packages.
To add a Variable step (of any type):
-
Open the Package editor and go to the Diagram tab.
-
In the Designer Navigator, expand the project node and then expand the Variables node, to show your variables for this project. Alternatively, expand the Global Objects node and expand the Variables node, to show global variables.
-
Drag and drop a variable into the diagram. A Variable step icon appears in the diagram.
-
Click the step icon in the diagram. The properties panel shows the variable's properties.
-
In the properties panel, modify properties of the variable as needed. On the General tab, select the variable type from the Type list.
-
For Set Variables, select
Assign, orIncrementif the variable is of Numeric type. For Assign, type into the Value field the value to be assigned to the variable (this value may be another variable). For Increment, type into the Increment field a numeric constant by which to increment the variable. -
For Evaluate Variables, select the Operator used to compare the variable value. Type in the Value field the value to compare with your variable. This value may be another variable.
Notes:
-
You can specify a list of values in the Value field. When using the
INoperator, use the semicolon character (;) to separate the values of a list. -
An evaluate variable step can be branched based on the evaluation result. See "Defining the Sequence of Steps" for more information on branching steps.
-
-
-
From the File menu, click Save.
Adding Oracle Data Integrator Tool Steps
Oracle Data Integrator provides tools that can be used within Packages for performing simple operations. The tools are either built-in tools or Open Tools that enable you to enrich the data integrator toolbox.
To insert an Oracle Data Integrator Tool step:
-
Open the Package editor and go to the Diagram tab.
-
From the Package Toolbox, select the tool that you want to use. Note that Open tools appear in the Plugins group.
-
Click in the Package diagram. A step corresponding to your tool appears.
Tip:
As long as a tool is selected, left-clicking in the diagram will continue to place steps. To stop placing steps, click the Free Choice button in the Package Toolbar. The mouse pointer changes to an arrow, indicating you are no longer placing tools. -
Click the step icon in the diagram. The properties panel shows the tool's properties.
-
Set the values for the parameters of the tool. The parameters descriptions appear when you select one, and are detailed in Oracle Data Integrator Tool Reference
-
You can edit the code of this tool call in the Command tab.
-
From the File menu, click Save.
The following tools are frequently used in Oracle Data Integrator Package:
-
OdiStartScen: starts an Oracle Data Integrator scenario synchronously or asynchronously. To create an OdiStartScen step, you can directly drag and drop the scenario from the Designer Navigator into the diagram.
-
OdiInvokeWebService: invokes a web service and saves the response in an XML file. OdiInvokeWebService uses the HTTP Analyzer tool to set up and test the tool parameters. For more information, see "Using HTTP Analyzer".
-
OS Command: calls an Operating System command. Using an operating system command may make your Package platform-dependent.
The Oracle Data Integrator tools are listed in Oracle Data Integrator Tool Reference
Note:
When setting the parameters of a tool using the steps properties panel, graphical helpers allow value selection in a user-friendly manner. For example, if a parameter requires a project identifier, the graphical mapping will redesign it and display a list of project names for selection. By switching to the Command tab, you can review the raw command and see the identifier.Adding a Model, Sub-Model or Datastore
You can perform journalizing, static check or reverse-engineering operations on models, sub-models, and datastores.
To insert a check, reverse engineer, or journalizing step in a Package:
Notes:
-
To perform a static check, you must define the CKM in the model.
-
To perform journalizing operations, you must define the JKM in the model.
-
Reverse engineering options set in the model definition are used for performing reverse-engineering processes in a package.
-
Open the Package editor and go to the Diagram tab.
-
In Designer Navigator, select the model, sub-model or datastore to check from the Models tree.
-
Drag and drop this model, sub-model or datastore into the diagram.
-
In the General tab of the properties panel, select the Type:
Check,Reverse Engineer, orJournalizing.-
For Check steps, select Delete Errors from the Checked Tables if you want this static check to remove erroneous rows from the tables checked in this process.
-
For Journalizing steps, set the journalizing options. See Chapter 4, "Using Journalizing," for more information on these options.
-
-
From the File menu, click Save.
Deleting a Step
Caution:
It is not possible to undo a delete operation in the Package diagram.To delete a step:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the step to delete in the diagram.
-
Right-click and then select Delete Step. Or, hit the Delete key on your keyboard.
-
Click Yes to continue.
The step disappears from the diagram.
Duplicating a Step
To duplicate a step:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the step to duplicate in the diagram.
-
Right-click and then select Duplicate Step.
A copy of the step appears in the diagram.
Running a Step
To run a step:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the step to run in the diagram.
-
Right-click and then select Execute Step.
-
In the Run dialog, select the execution parameters:
-
Select the Context into which the step must be executed.
-
Select the Logical Agent that will run the step.
-
Select a Log Level.
-
Optionally, select Simulation. This option performs a simulation of the run operation and generates a run report, without actually affecting data.
-
-
Click OK.
-
The Session Started Window appears.
-
Click OK.
You can review the step execution in the Operator Navigator.
Editing a Step's Linked Object
The step's linked object is the mapping, procedure, variable, or other object from which the step is created. You can edit this object from the Package diagram.
To edit a step's linked object:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the step to edit in the diagram.
-
Right-click and then select Edit Linked Object.
The Editor for the linked object opens.
Arranging the Steps Layout
The steps can be rearranged automatically or manually in the diagram in order to make it more readable.
You can use the Reorganize button from the toolbar to automatically reorganize all of the steps in your package.
To manually arrange the steps in the diagram:
-
From the Package toolbar menu, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the steps you wish to arrange using either of the following methods:
-
Keep the CTRL key pressed and select each step.
-
Drag a box around multiple items in the diagram with the left mouse button pressed.
-
-
To arrange the selected steps, you may either:
-
Drag them to arrange their position into the diagram
-
Right-click, then select a Vertical Alignment or Horizontal Alignment option from the context menu.
-
Defining the Sequence of Steps
Once the steps are created, you must order them into a data processing chain. This chain has the following rules:
-
It starts with a unique step defined as the First Step.
-
Each step has two termination states: Success or Failure.
-
A step in failure or success can be followed by another step, or by the end of the Package.
-
In case of failure, it is possible to define a number of retries.
A Package has one entry point, the First Step, but several possible termination steps.
The table below details the conditions that lead a step to a Failure state. In other situations, the steps ends in a Success state.
Note:
By default, open transactions are not rolled back in a failure state. You can change this behavior using the Physical Agent property "Rollback all open transactions on step failure". Refer to the ODI Studio Online Help for details.| Step Type | Failure conditions |
|---|---|
| Flow |
|
| Procedure | Error in a procedure command. |
| Refresh Variable | Error while running the refresh query. |
| Set Variable | Error when setting the variable (invalid value). |
| Evaluate Variable | The condition defined in the step is not matched. |
| Declare Variable | This step has no failure condition and always succeeds. |
| Oracle Data Integrator Tool | Oracle Data Integrator Tool return code is different from zero. If this tool is an OS Command, a failure case is a command return code different from zero. |
| Journalize Datastore, Model or Sub-Model | Error in a journalizing command. |
| Check Datastore, Model or Sub-Model | Error in the check process. |
| Reverse Model | Error in the reverse-engineering process. |
To define the first step of the Package:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the step to set as the first one in the diagram.
-
Right-click and then select First Step.
The first step symbol appears on the step's icon.
To define the next step upon success:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Next Step on Success tool.
-
Drag a line from one step to another, using the mouse.
-
Repeat this operation to link all your steps in a success path sequence. This sequence should start from the step defined as the First Step.
Green arrows representing the success path are shown between the steps, with an ok labels on these arrows. In the case of an evaluate variable step, the label is true.
To define the next step upon failure:
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Next Step on Failure tool.
-
Drag a line from one step to another, using the mouse.
-
Repeat this operation to link steps according to your workflow logic.
Red arrows representing the failure path are shown between the steps, with a ko labels on these arrows. In the case of an evaluate variable step, the arrow is green and the label is false.
To define the end of the Package upon failure:
By default, a step that is linked to no other step after a success or failure condition will terminate the Package when this success or failure condition is met. You can set this behavior by editing the step's behavior.
-
In the Package toolbar tab, select the Free Choice tool.
-
Select the step to edit.
-
In the properties panel, select the Advanced tab.
-
Select End in Processing after failure or Processing after success. The links after the step disappear from the diagram.
-
You can optionally set a Number of attempts and a Time between attempts for the step to retry a number of times with an interval between the retries.
Running a Package
To run a Package:
-
Use any of the following methods:
-
In the Projects node of the Designer Navigator, expand a project and select the Package you want to execute. Right-click and select Run, or click the Run button in the ODI Studio toolbar, or select Run from the Run menu of the ODI menu bar.
-
In the package editor, select the package by clicking the tab with the package name at the top of the editor. Click the Run button in the ODI Studio toolbar, or select Run from the Run menu of the ODI menu bar.
-
-
In the Run dialog, select the execution parameters:
-
Select the Context into which the package must be executed.
-
Select the Logical Agent that will run the package.
-
Select a Log Level.
-
Optionally, select Simulation. This option performs a simulation of the run operation and generates a run report, without actually affecting data.
-
-
Click OK.
-
The Session Started Window appears.
-
Click OK.
You can review the Package execution in the Operator Navigator.